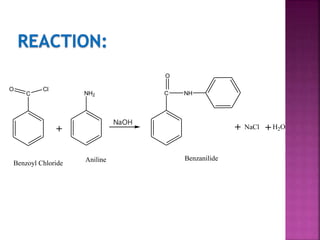
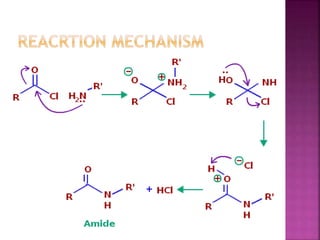
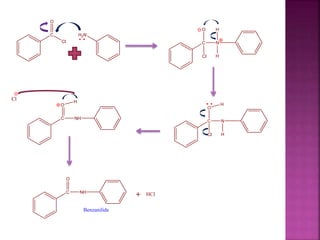
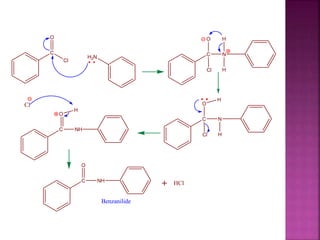
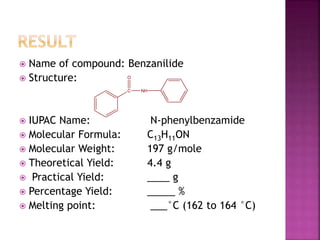
This document describes the synthesis of benzanilide from aniline via a Schotten-Baumann reaction. Aniline reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of sodium hydroxide to form benzanilide and hydrochloric acid. The reaction involves benzoylation, where the benzoyl group is inserted in place of the active hydrogen on the amine group of aniline. Details of the reaction mechanism, chemicals used, equipment needed and procedure for synthesizing benzanilide are provided. The theoretical and percent yields are also calculated.