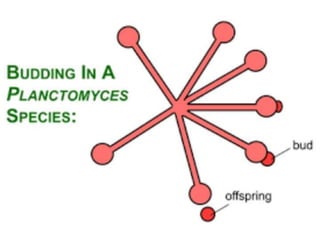
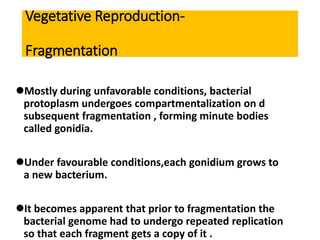
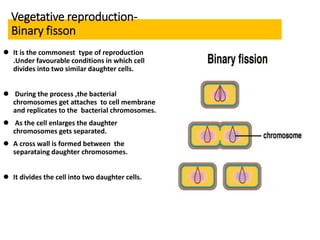
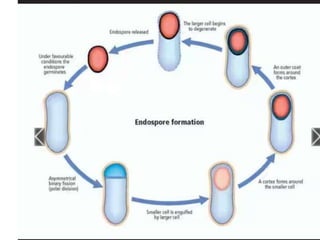
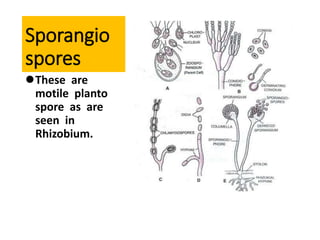
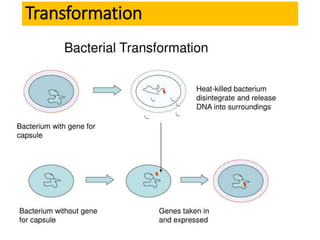
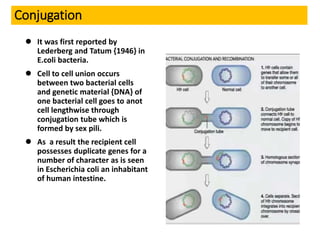
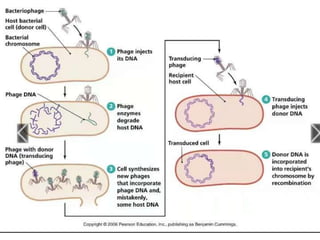
Bacteria reproduce through three main types: vegetative reproduction, asexual reproduction, and sexual reproduction. Vegetative reproduction includes budding, fragmentation, and binary fission. Asexual reproduction involves endospore formation, conidia, and sporangiosores. Sexual reproduction occurs through transformation, conjugation, and transduction, which allow for genetic recombination between bacterial cells.