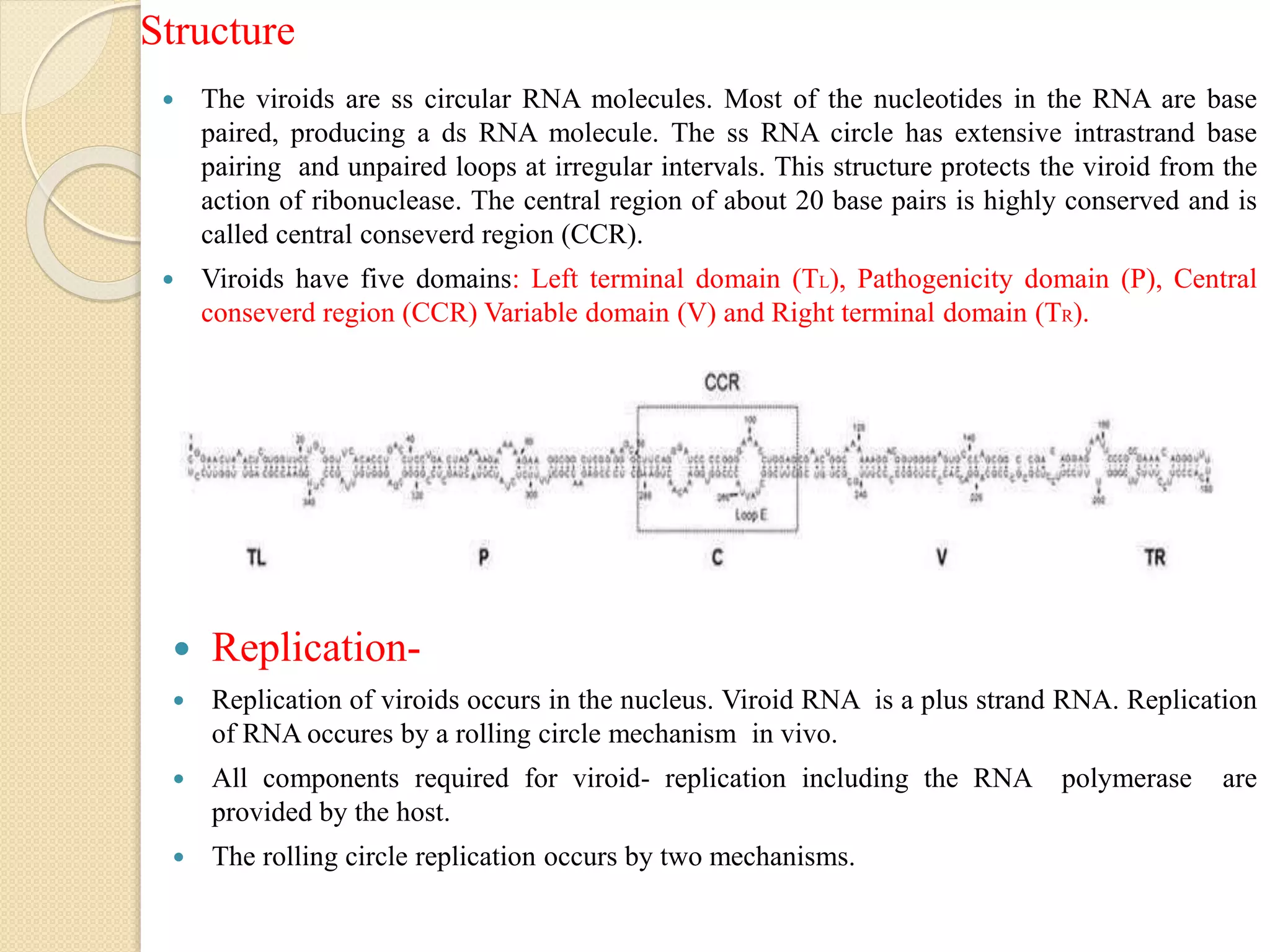
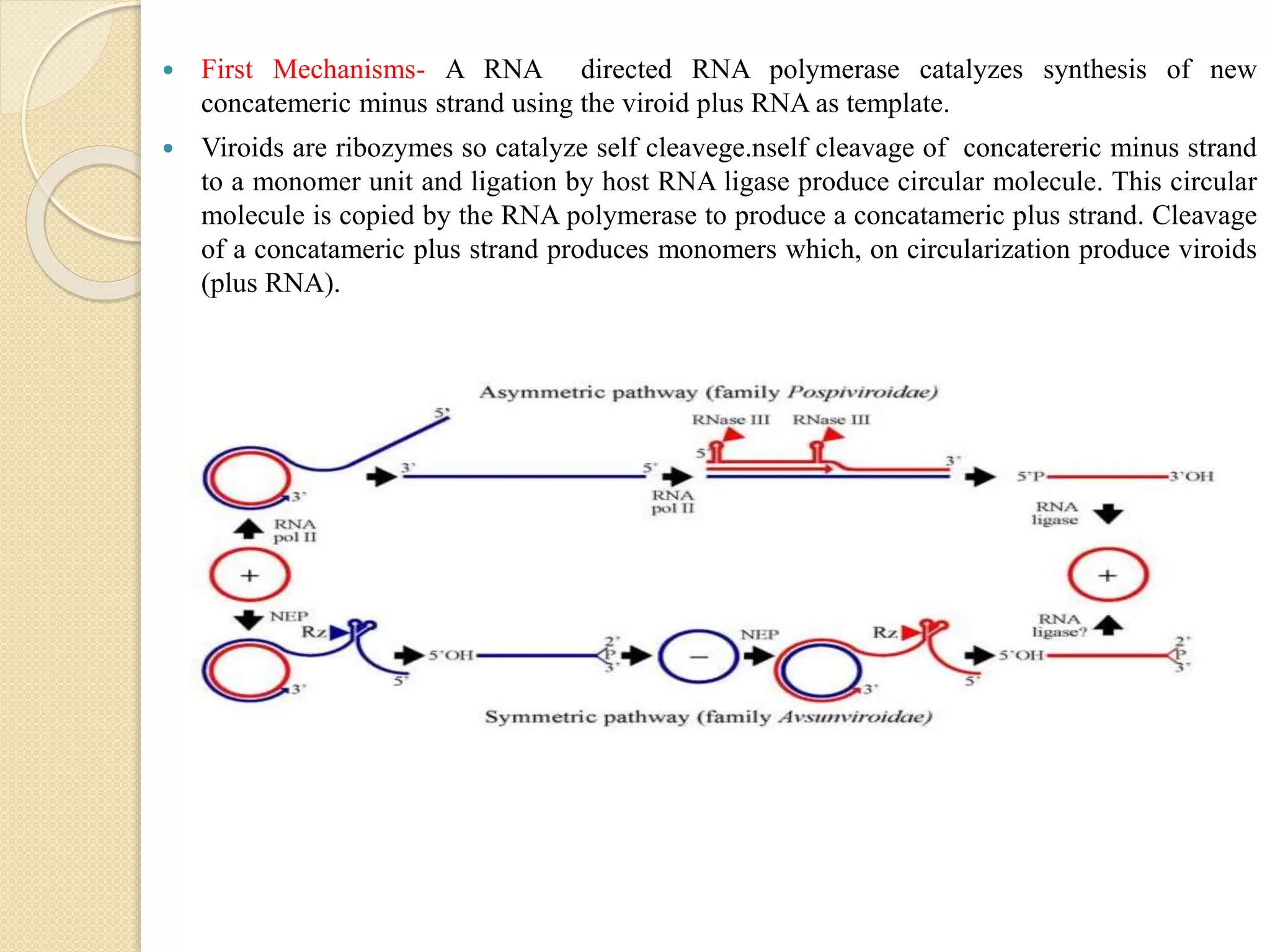
This document summarizes key information about viroids. It defines viroids as the smallest known infectious agents, consisting of small circular RNA molecules without capsids. The first viroid discovered was the potato spindle tuber viroid. Viroids are obligate parasites that replicate through a rolling circle mechanism in the nucleus of host cells. They have extensive intrastrand base pairing that allows them to avoid degradation. While viroids do not code for proteins, the hepatitis D viroid produces two RNA molecules, one that codes for the delta antigen protein. Viroids can cause economic losses through various plant diseases.