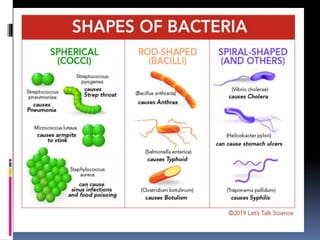
This document discusses the general characteristics of cellular and acellular microorganisms. It focuses on bacteria, describing them as single-celled prokaryotes without organelles or nuclei. Bacteria reproduce through binary fission and can exchange genes through horizontal transfer. The document outlines bacterial cell structure, shapes, whether they are aerobic or anaerobic, and some important terms related to bacteria.