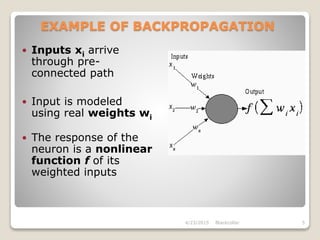
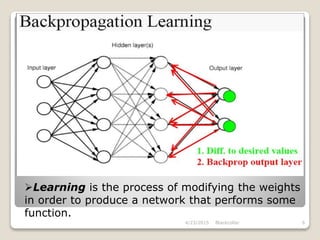
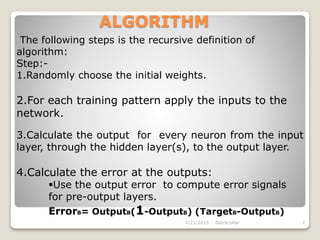
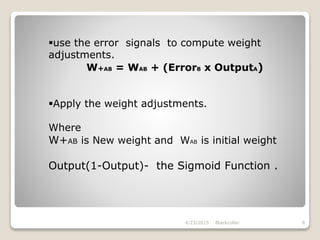
The document describes the backpropagation algorithm, which is commonly used to train artificial neural networks. It calculates the gradient of a loss function with respect to the network's weights in order to minimize the loss during training. The backpropagation process involves propagating inputs forward and calculating errors backward to update weights. It has advantages like being fast, simple, and not requiring parameter tuning. However, it can be sensitive to noisy data and outliers. Applications of backpropagation include speech recognition, character recognition, and face recognition.