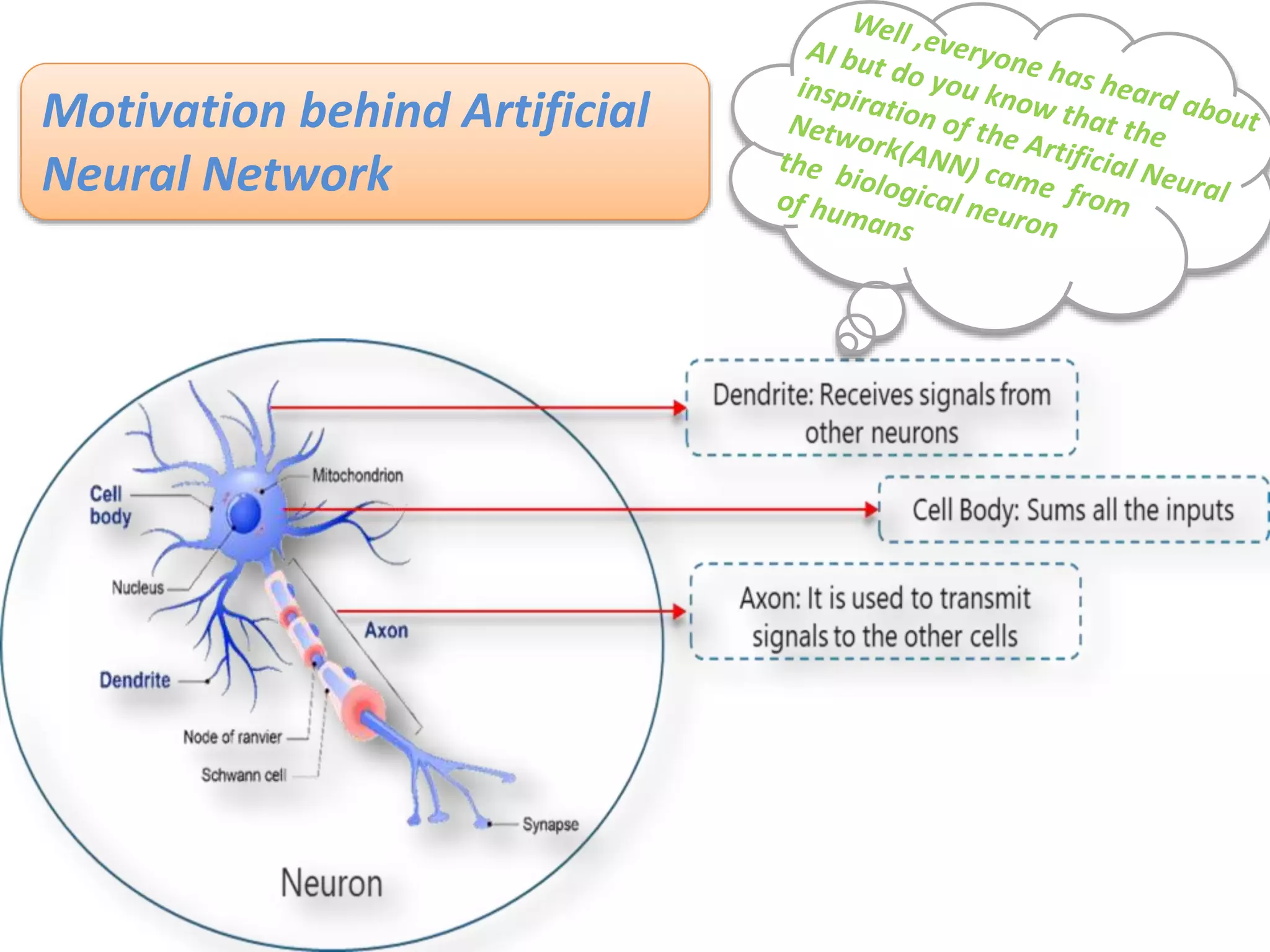
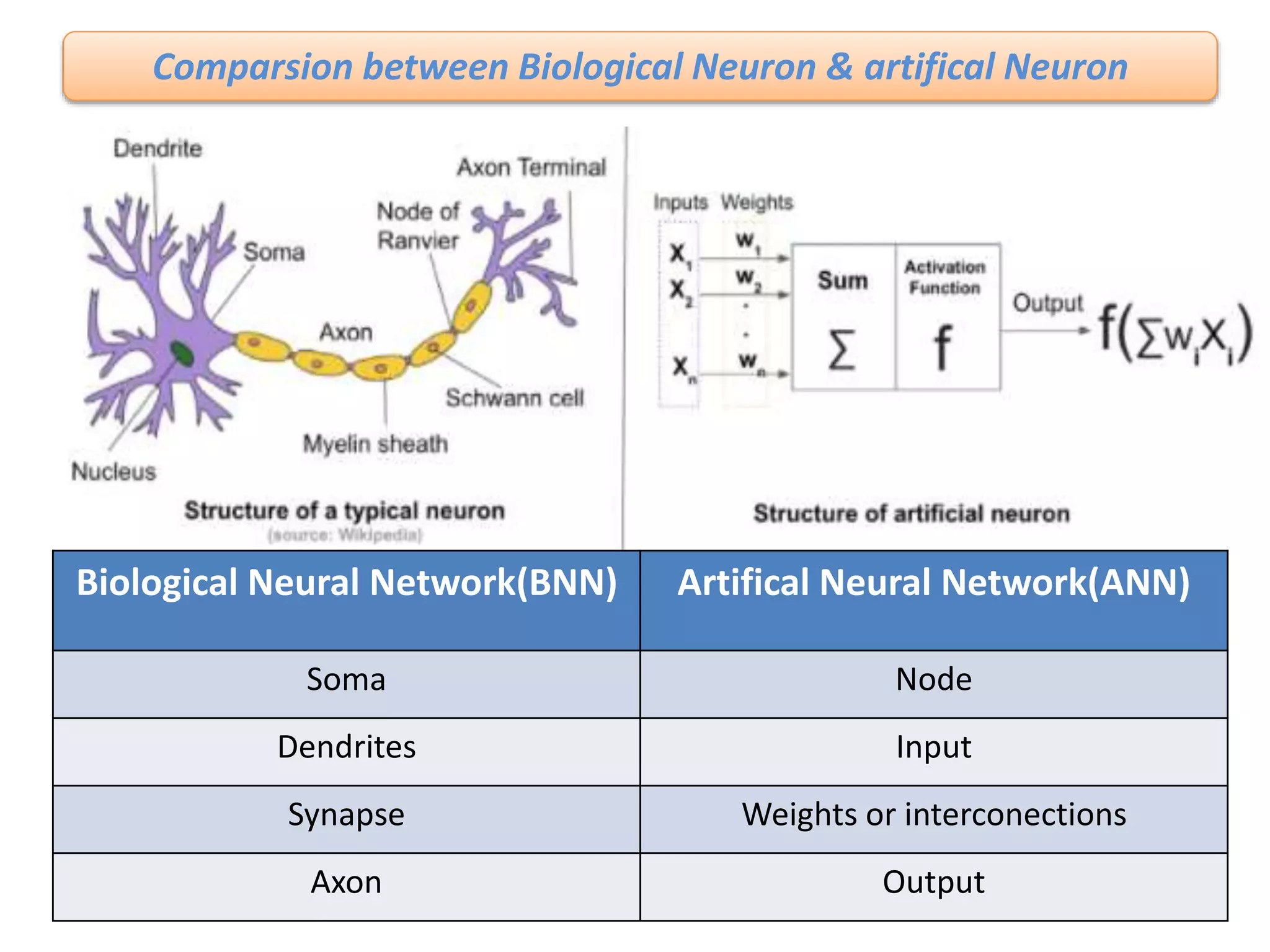
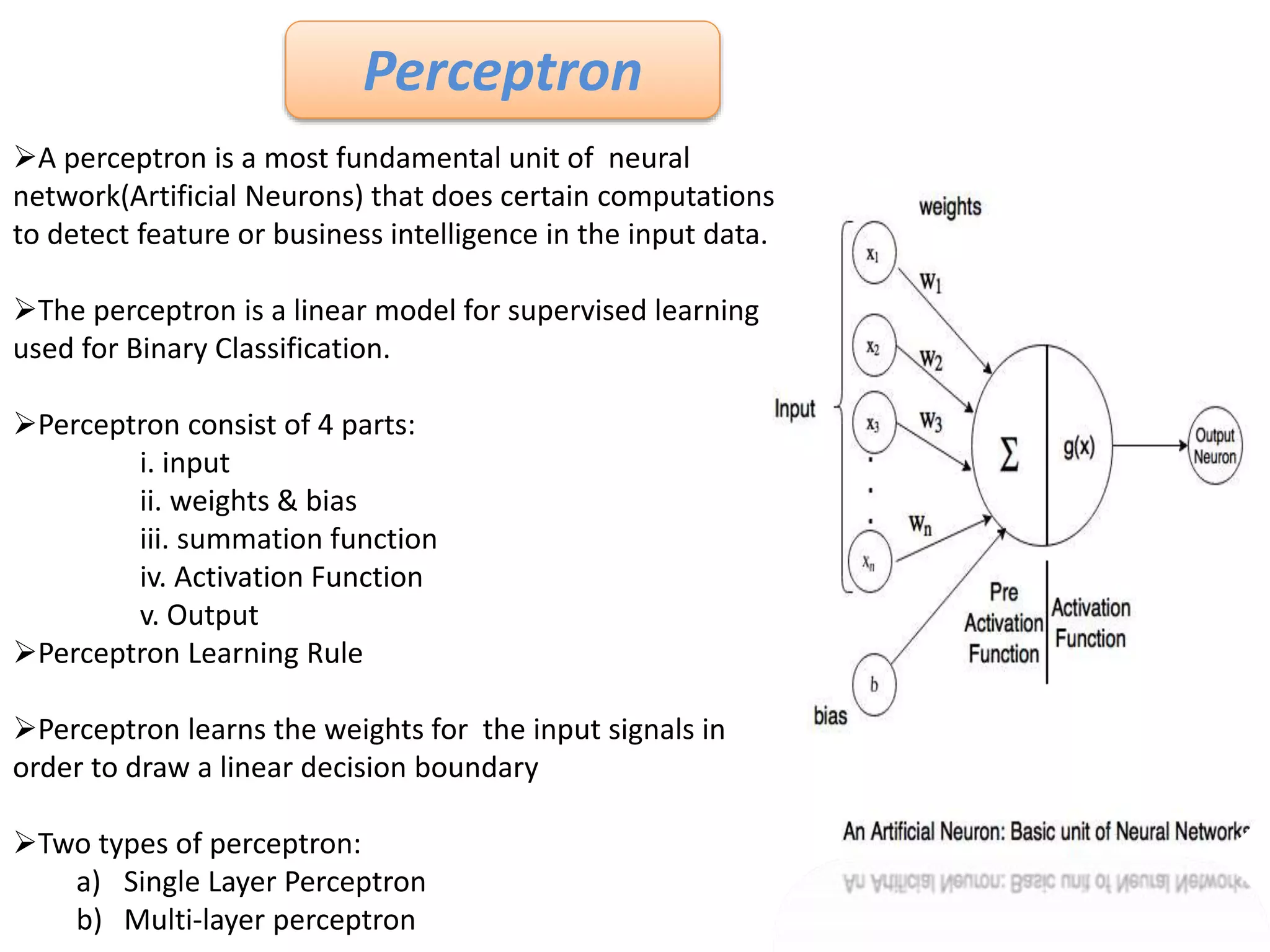
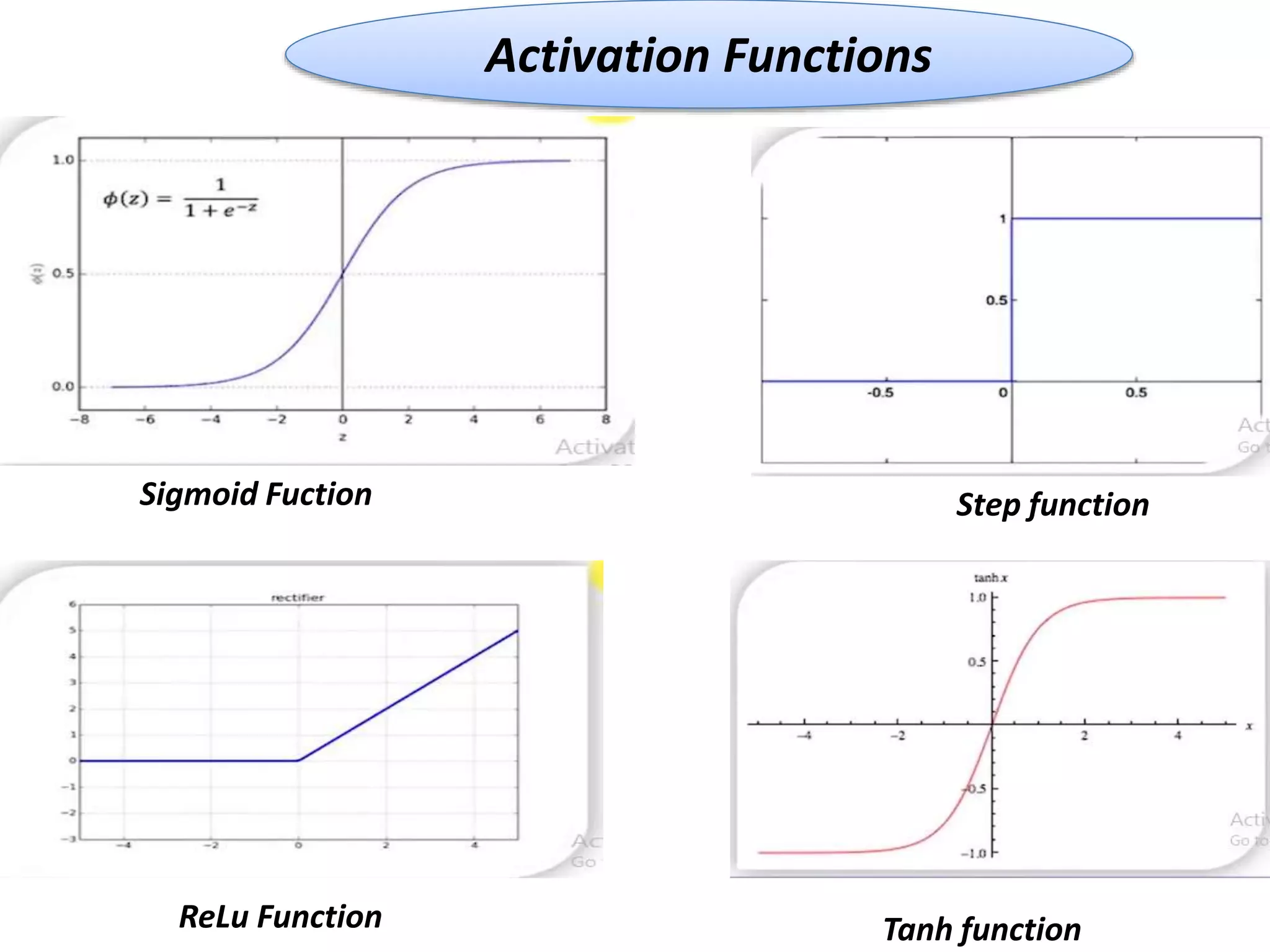
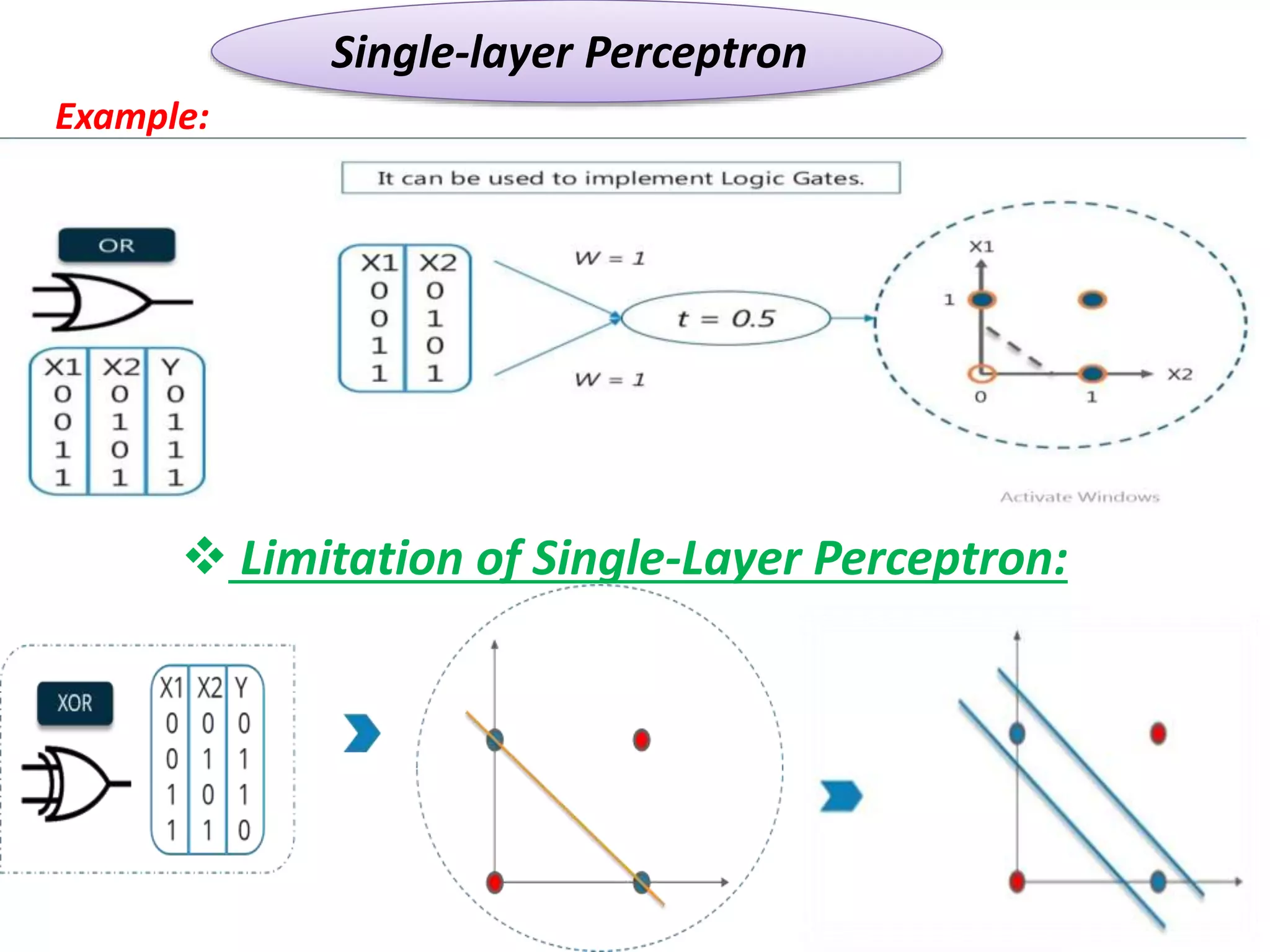
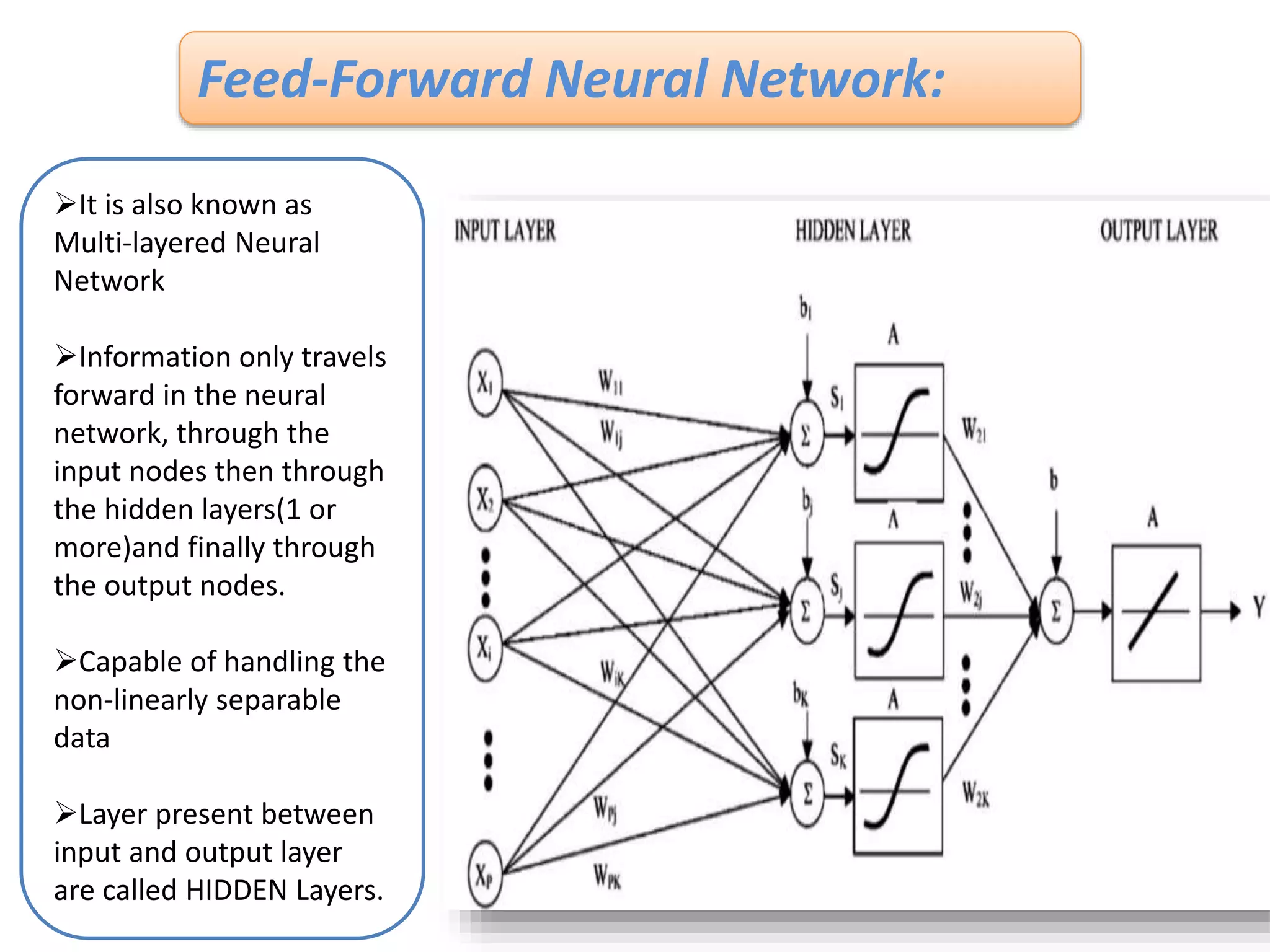
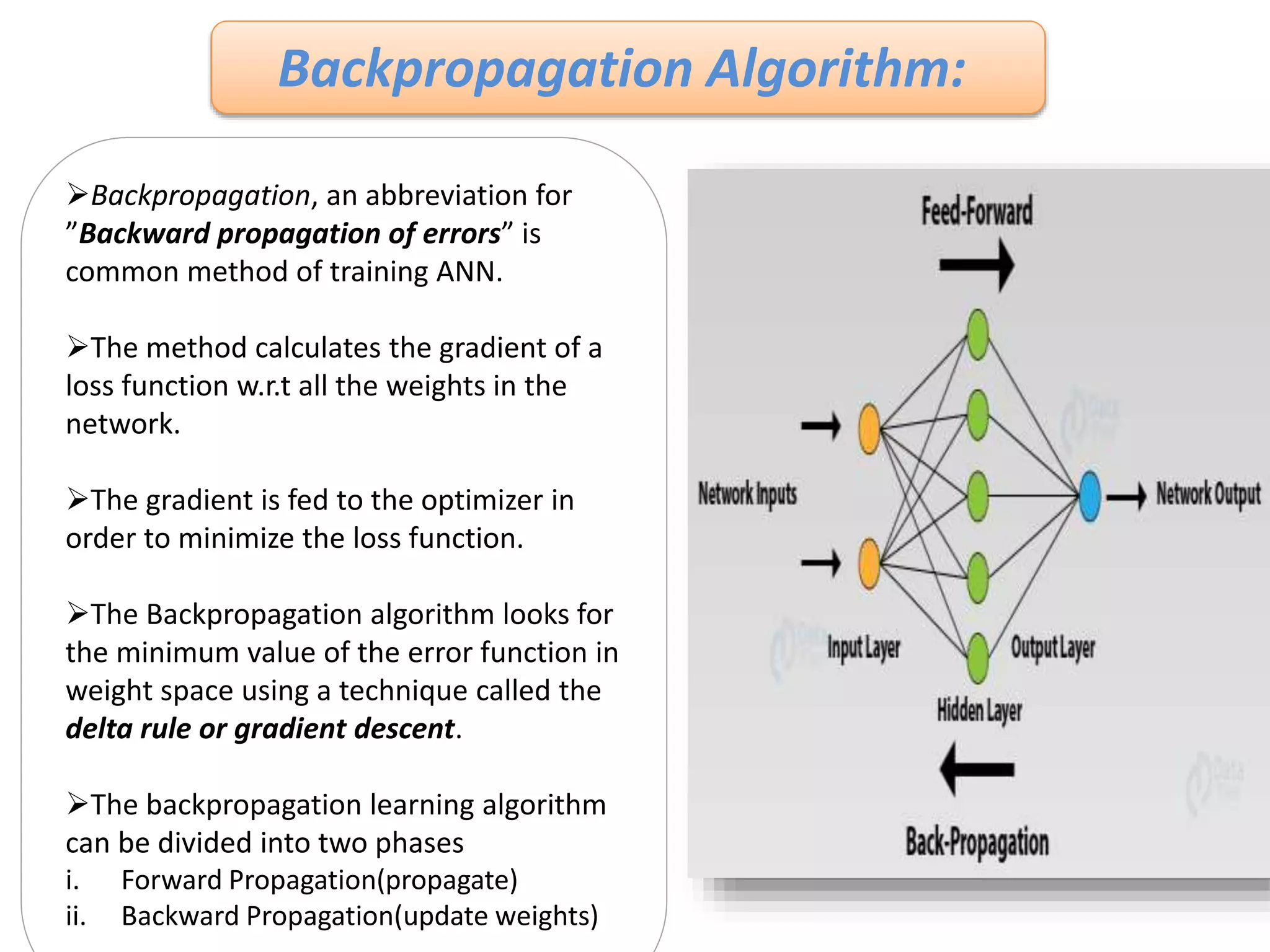
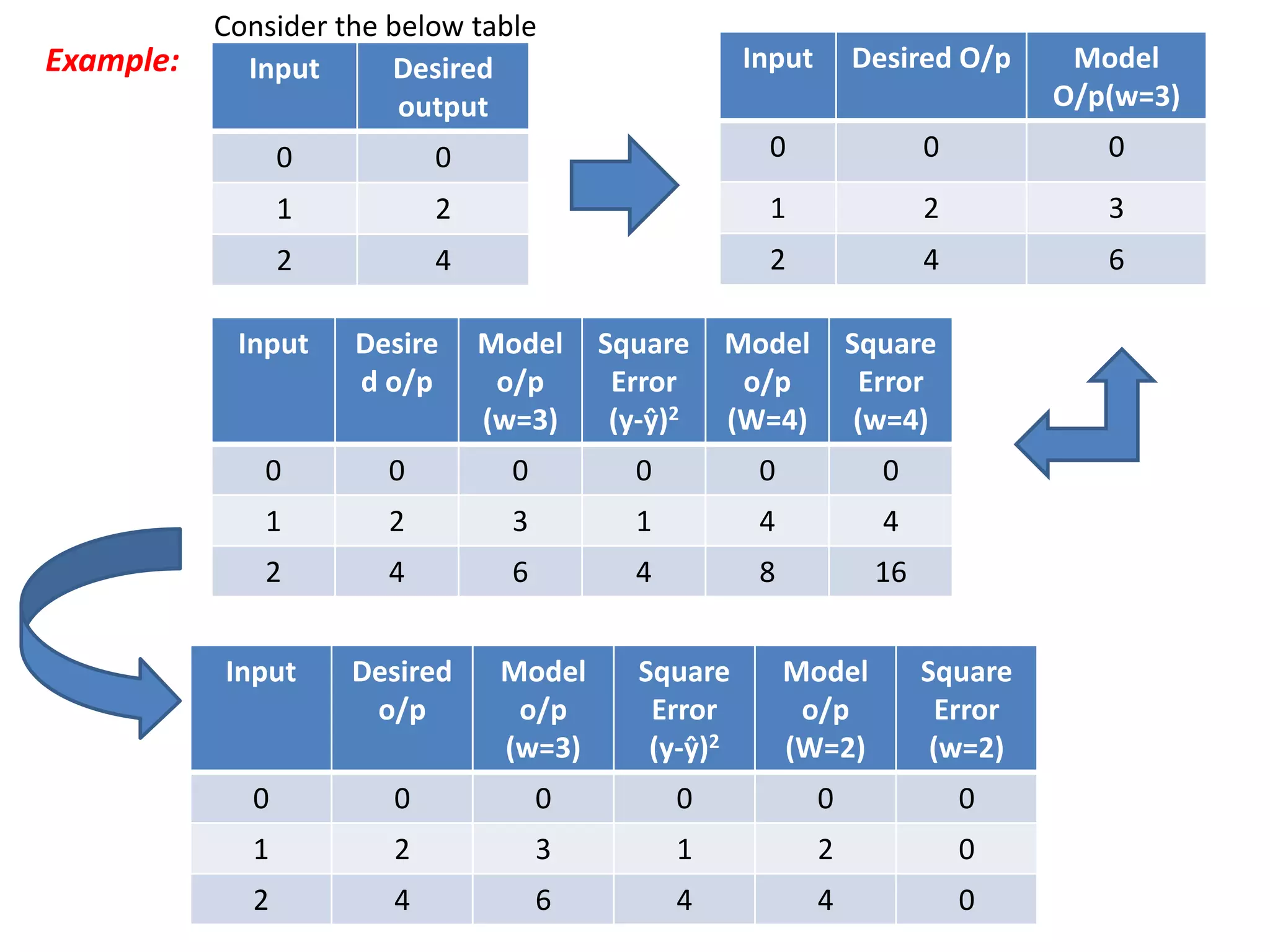
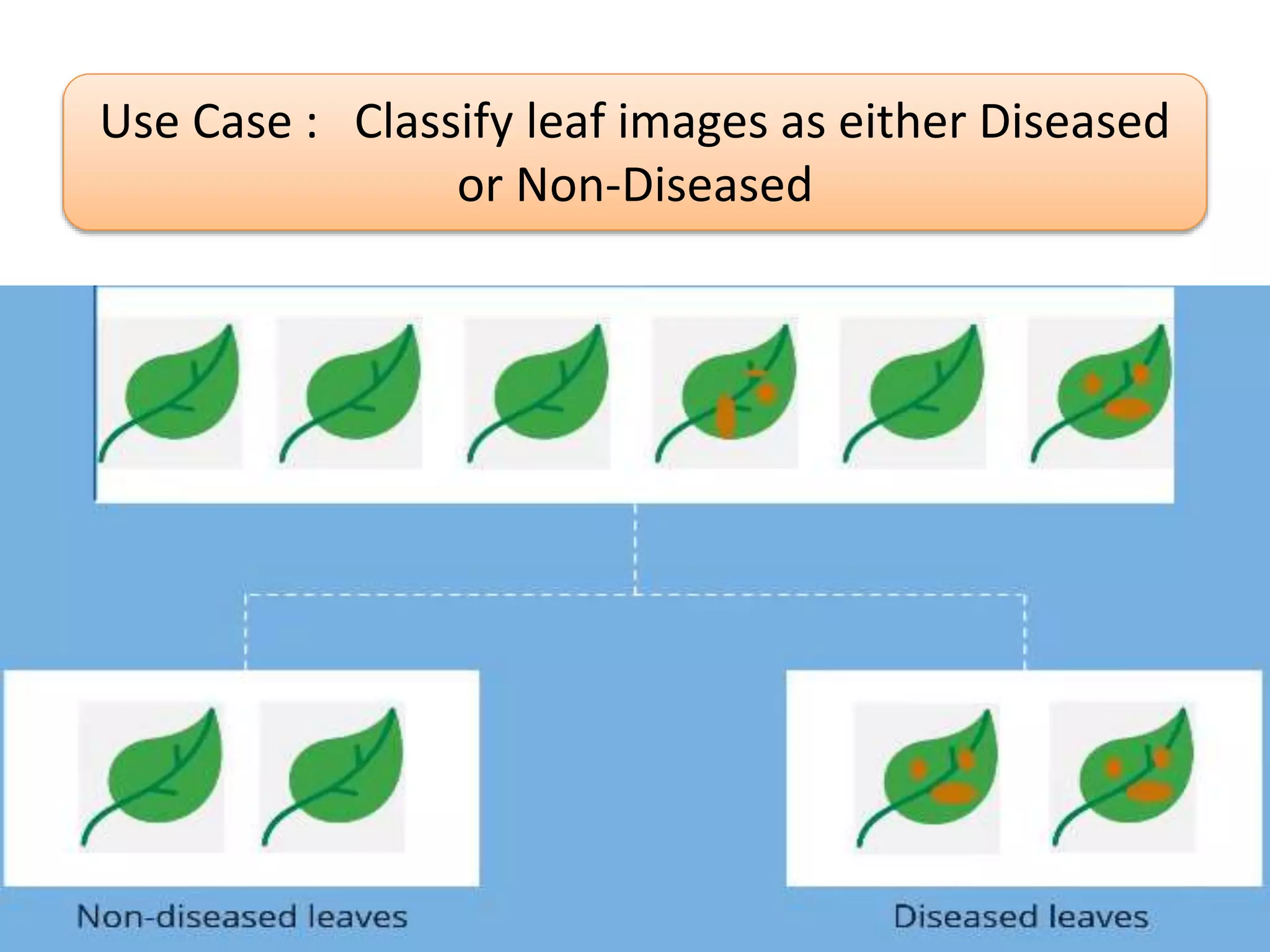
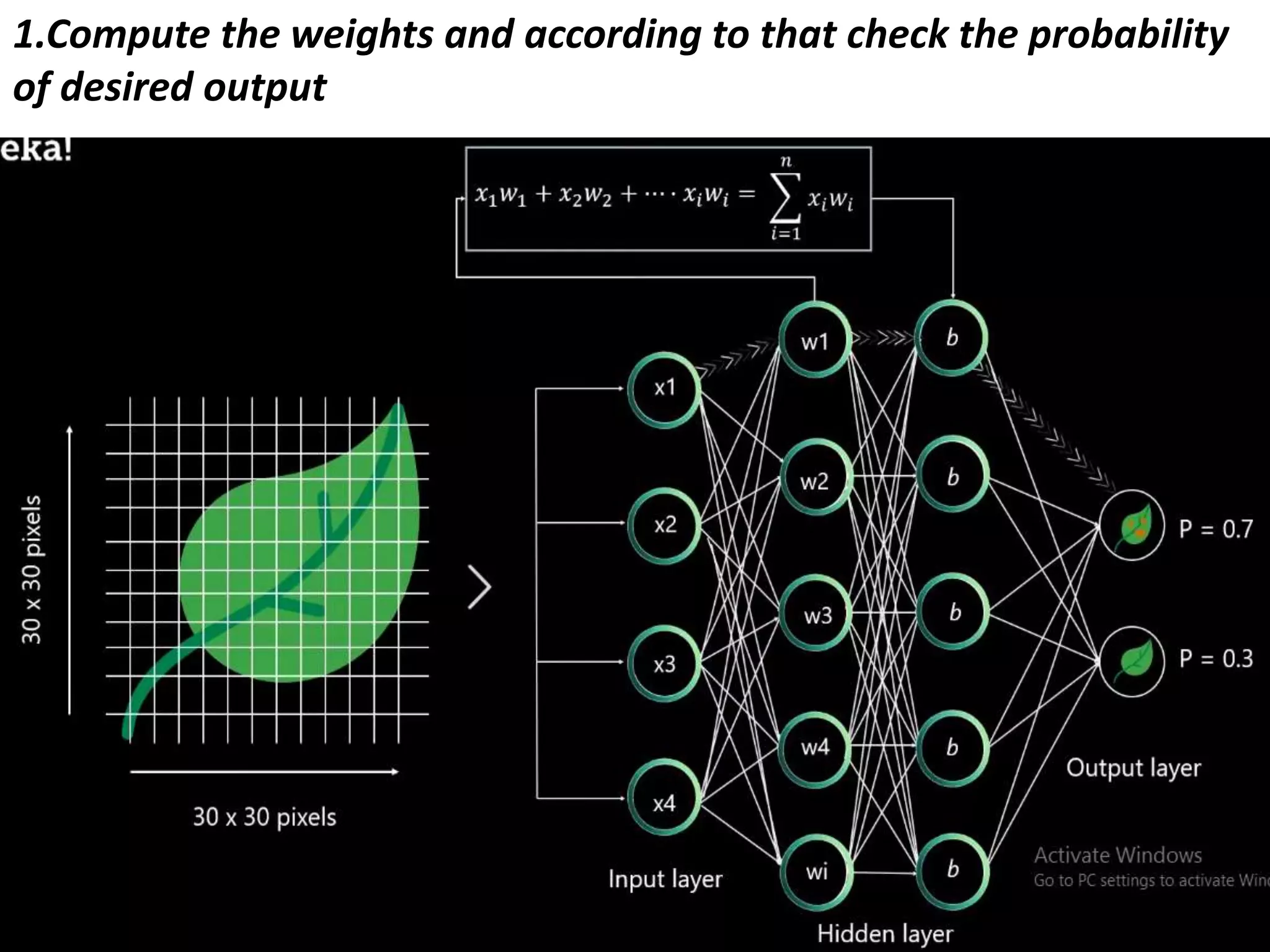
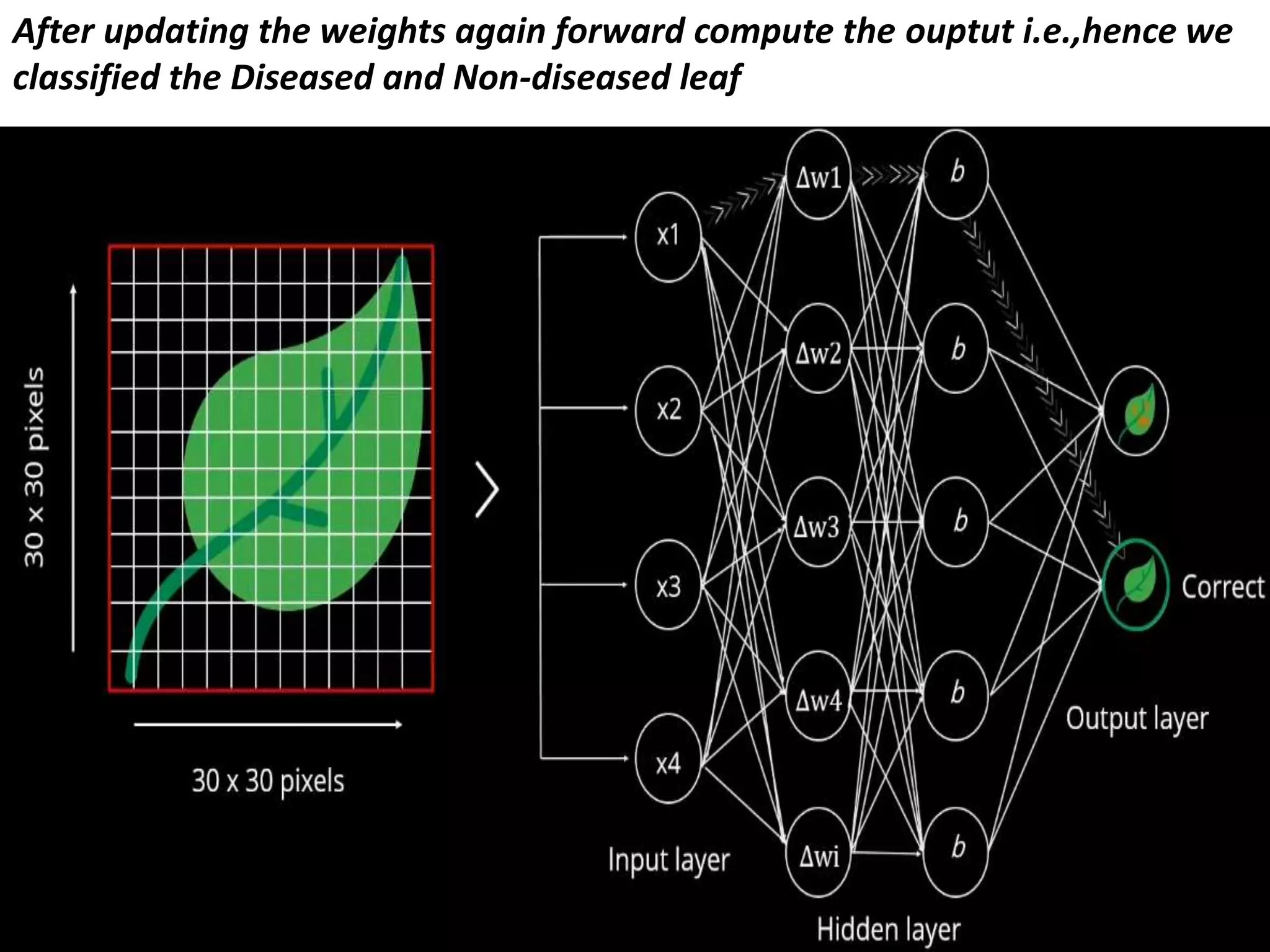
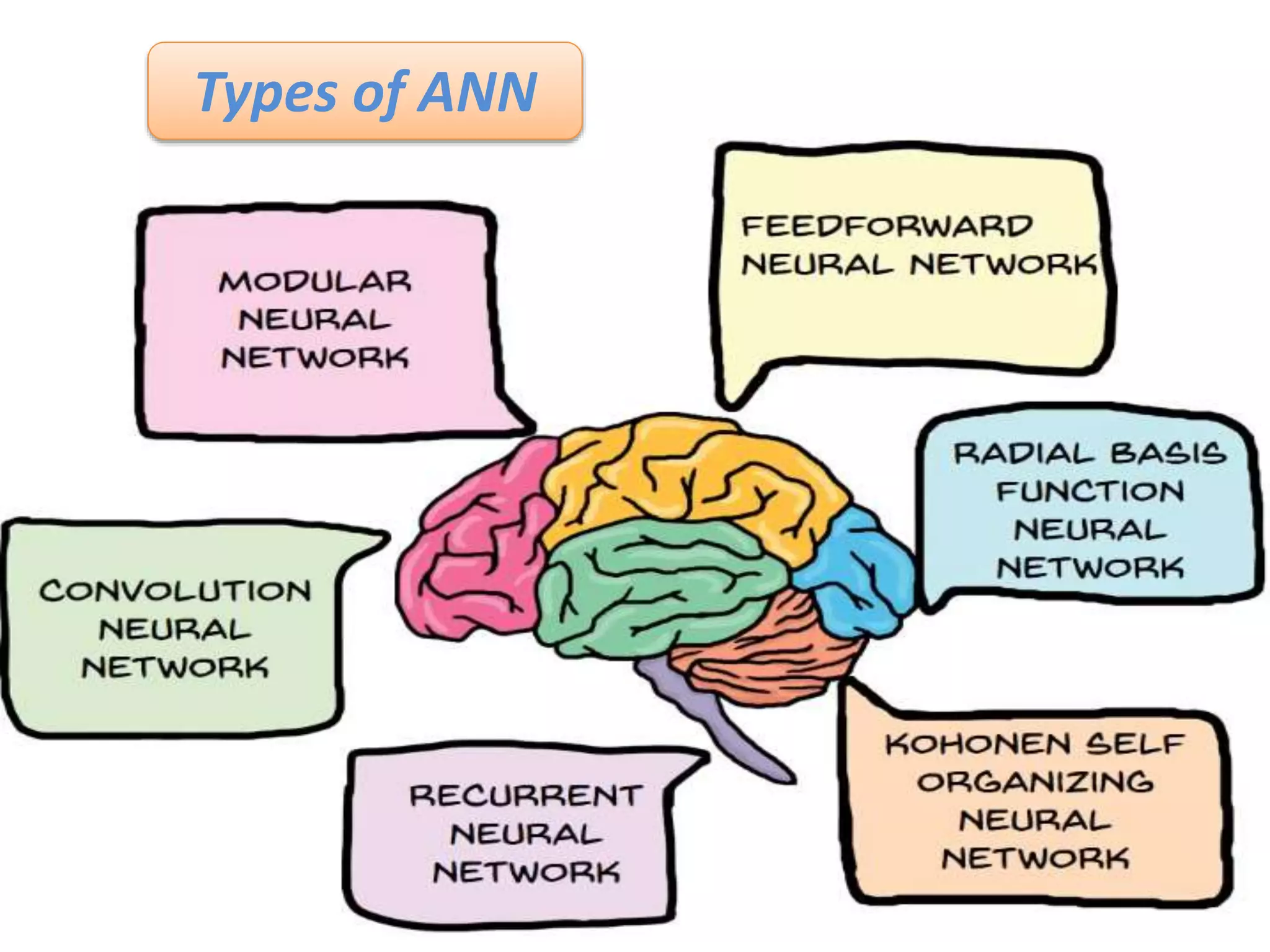
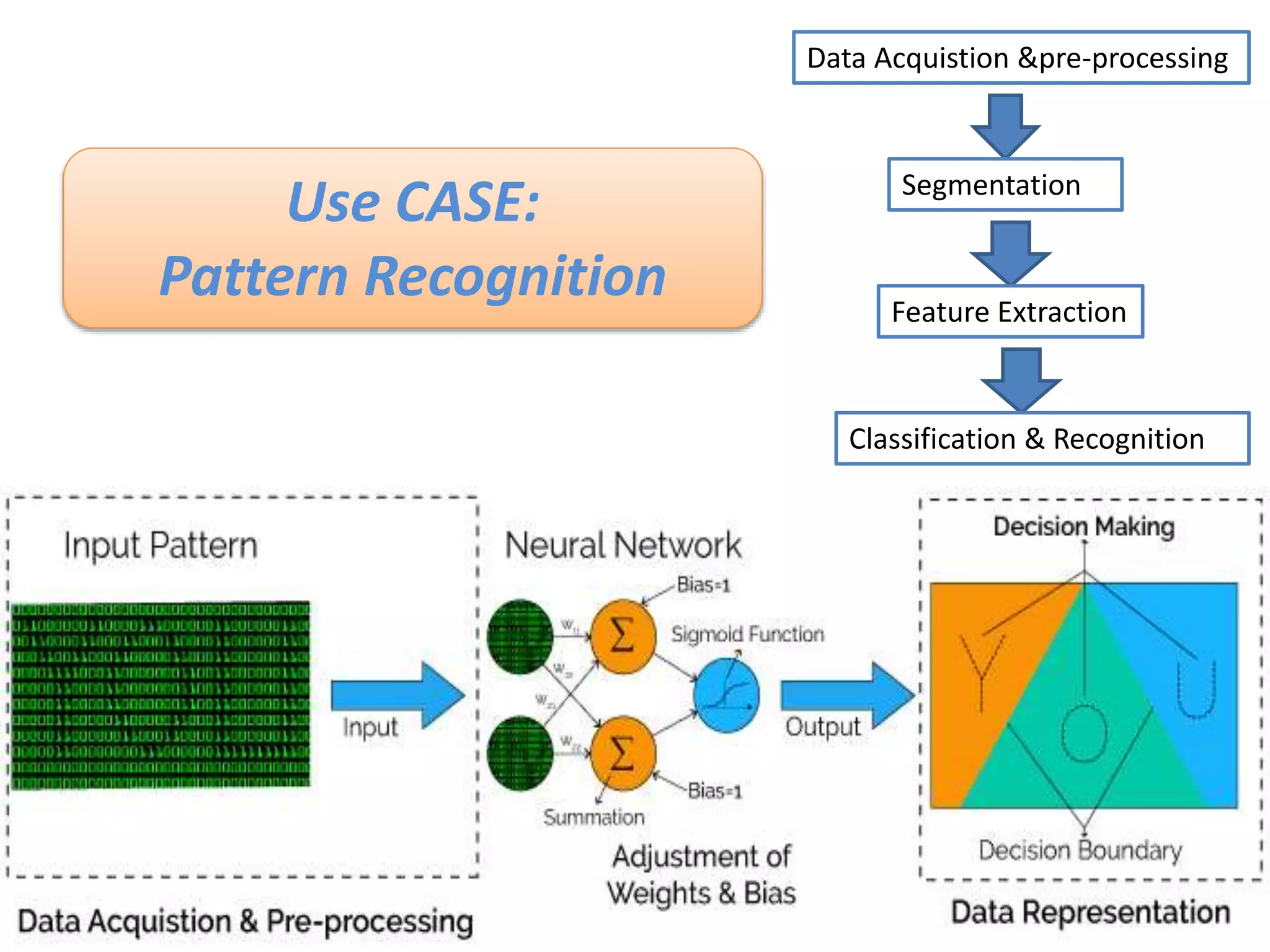
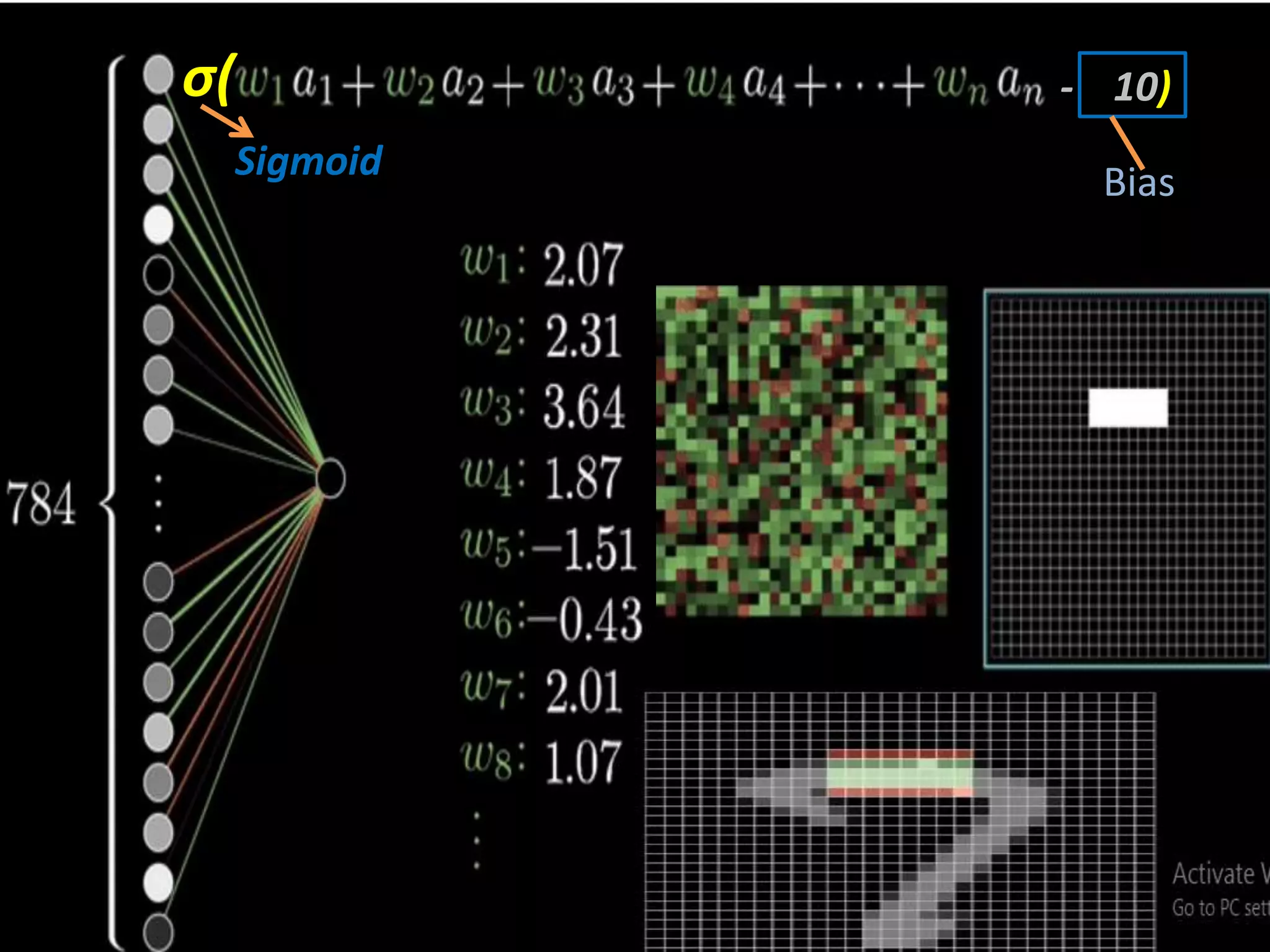
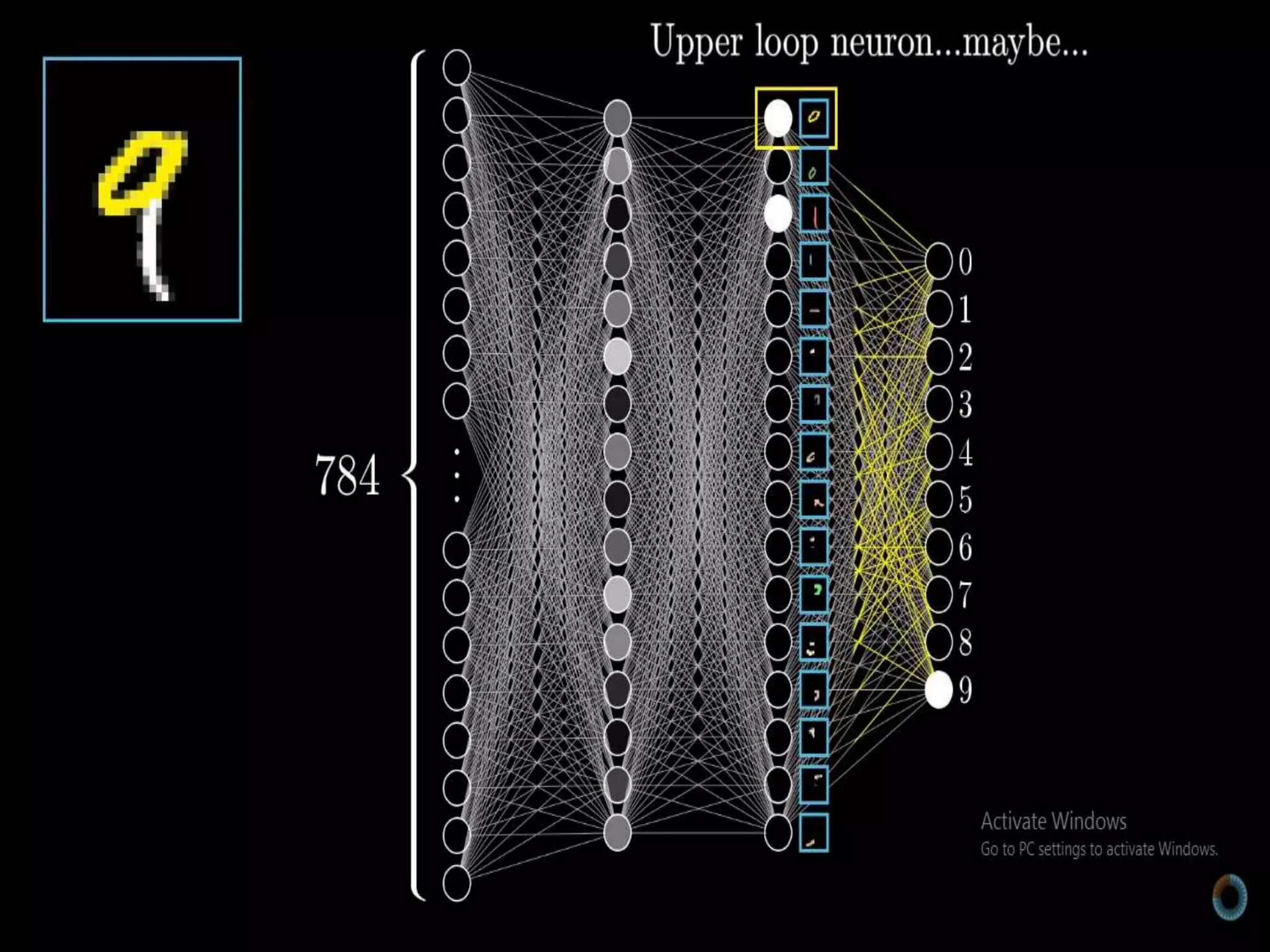
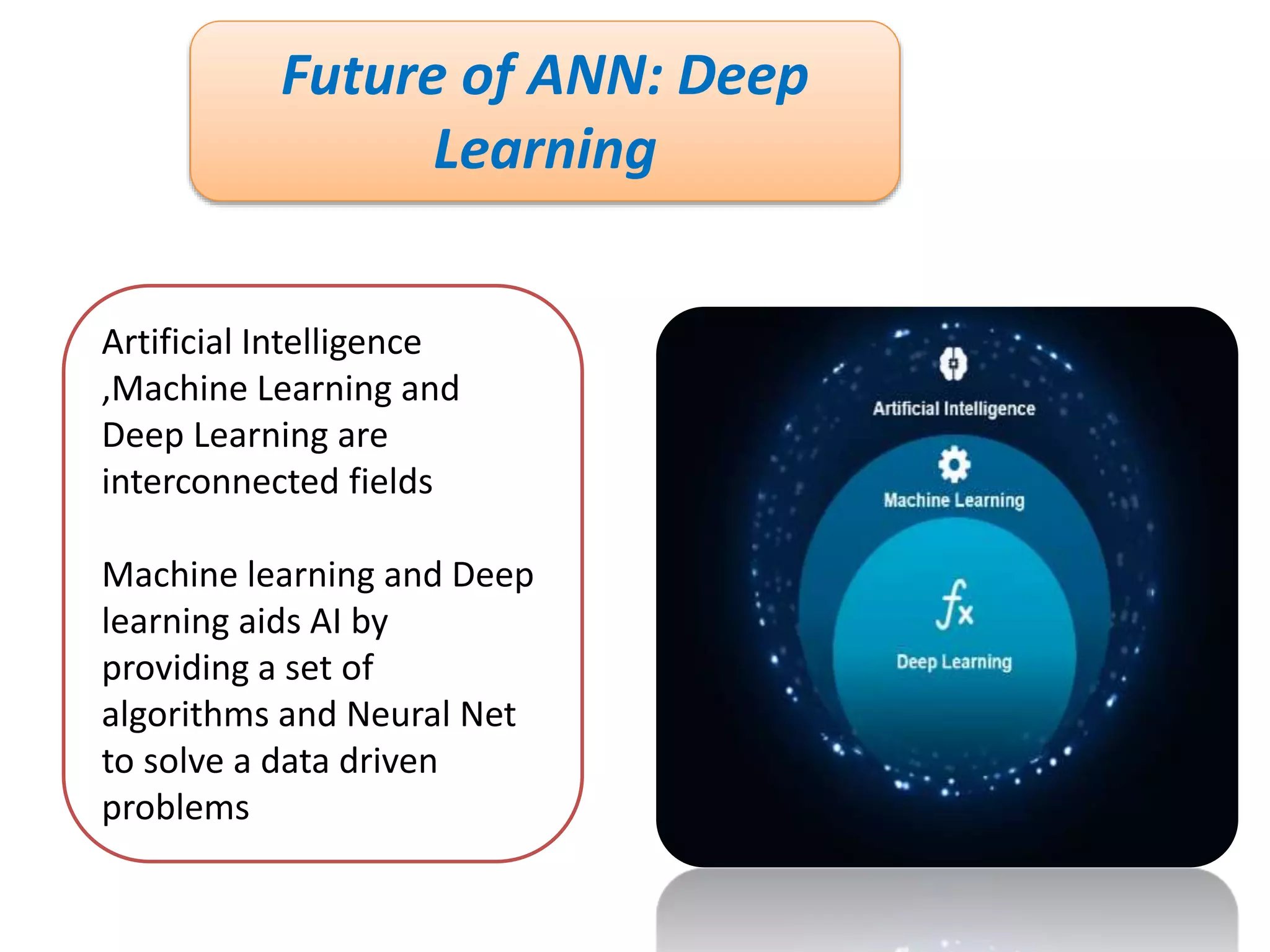
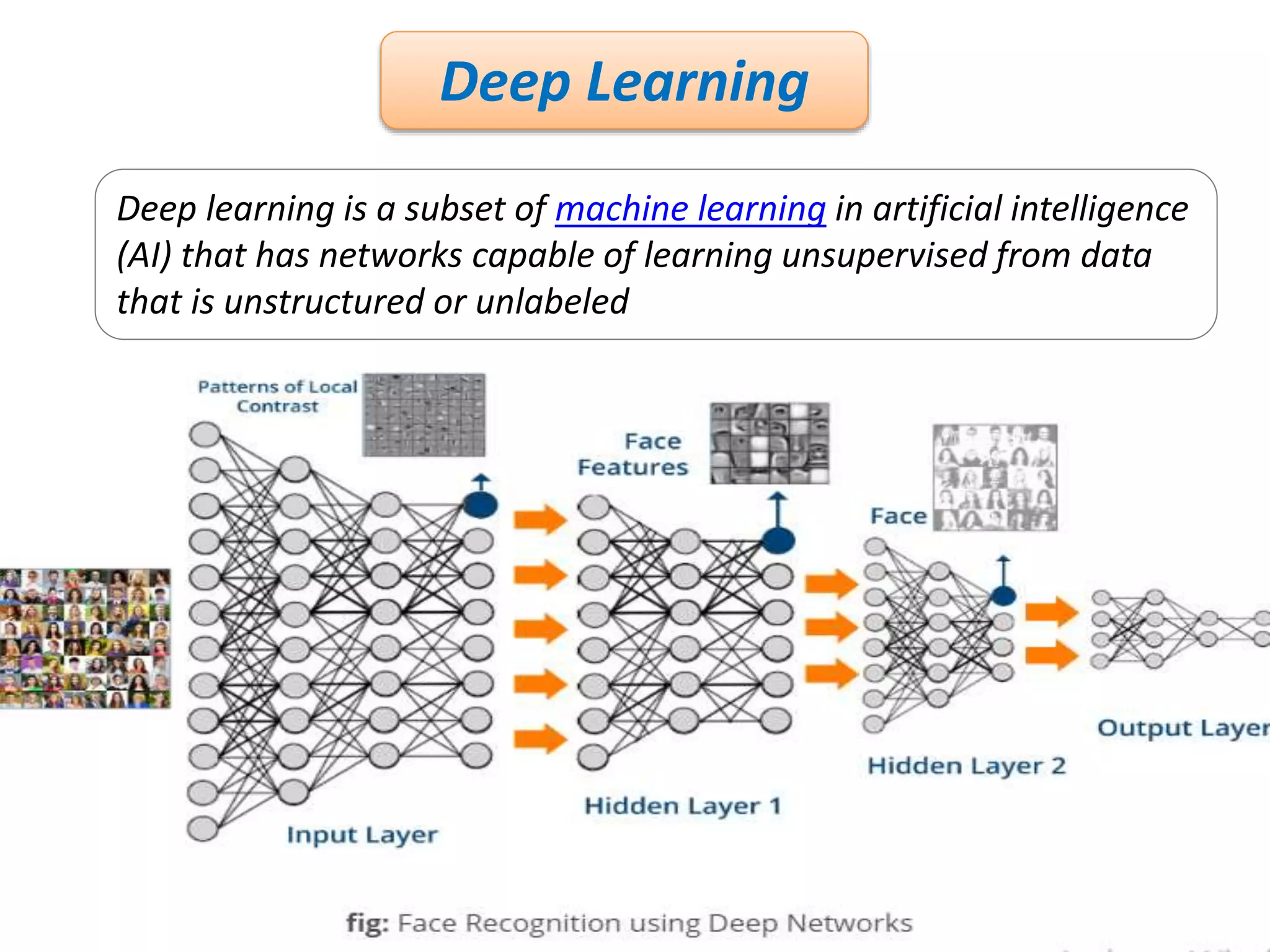
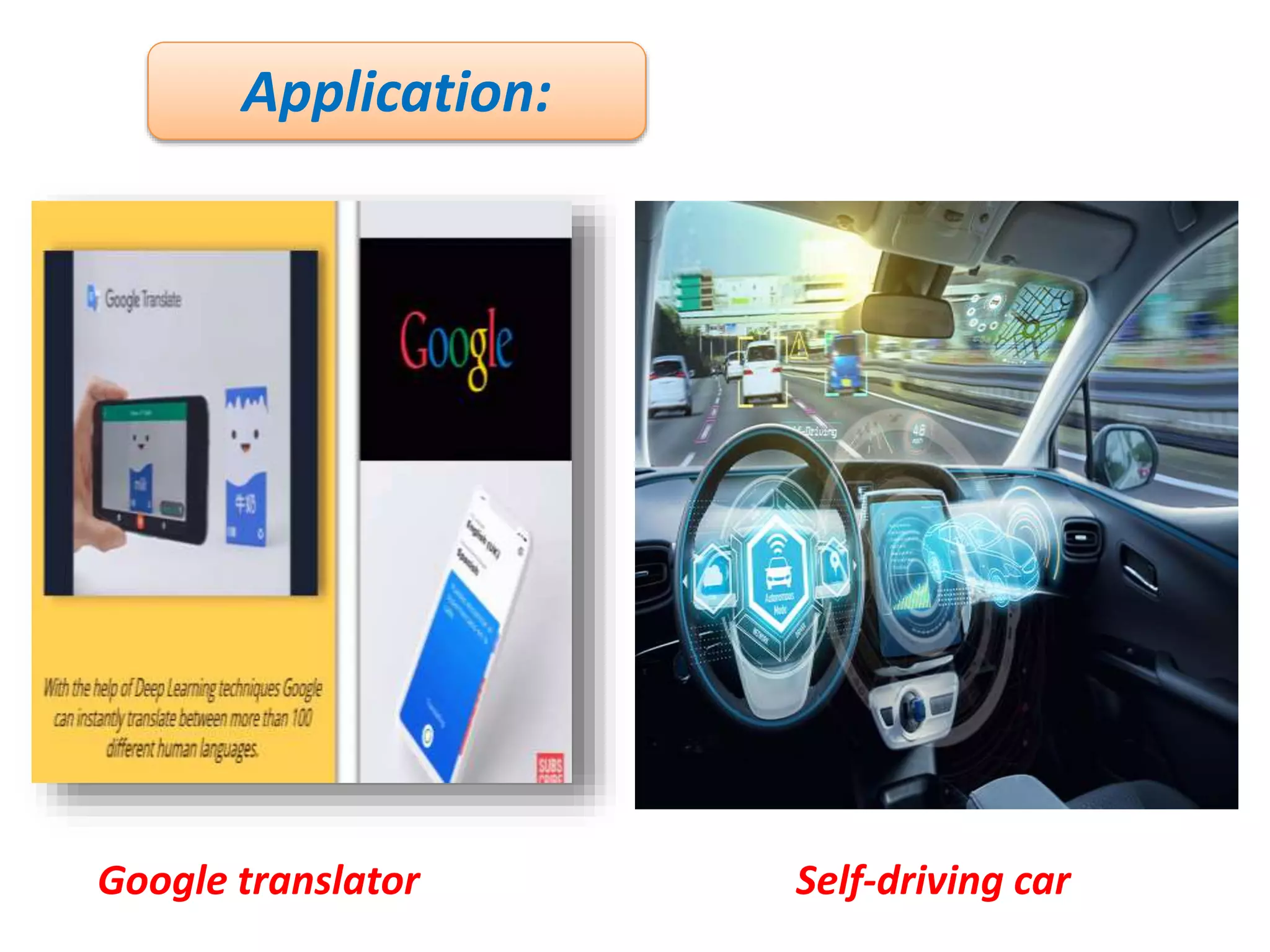
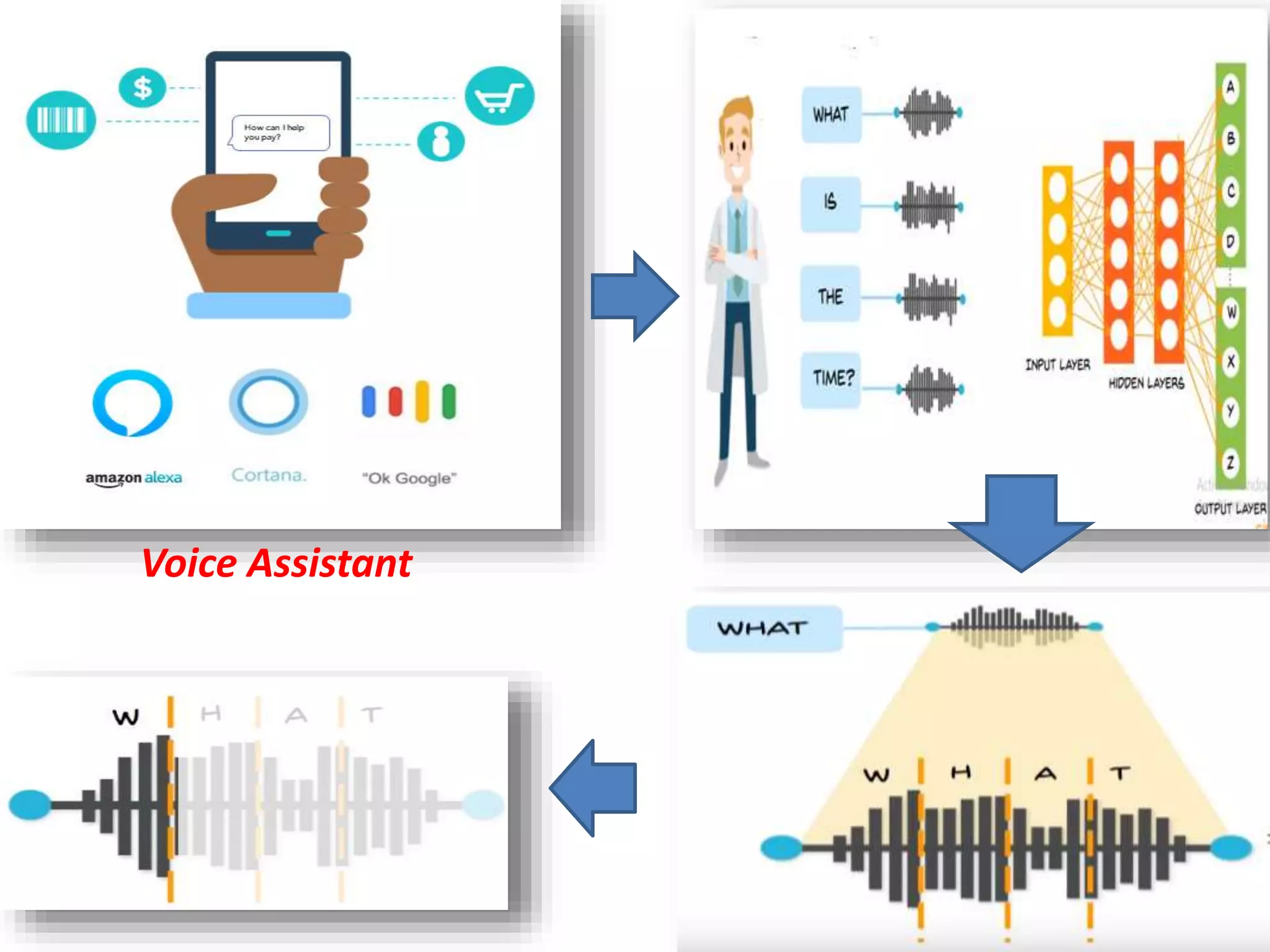
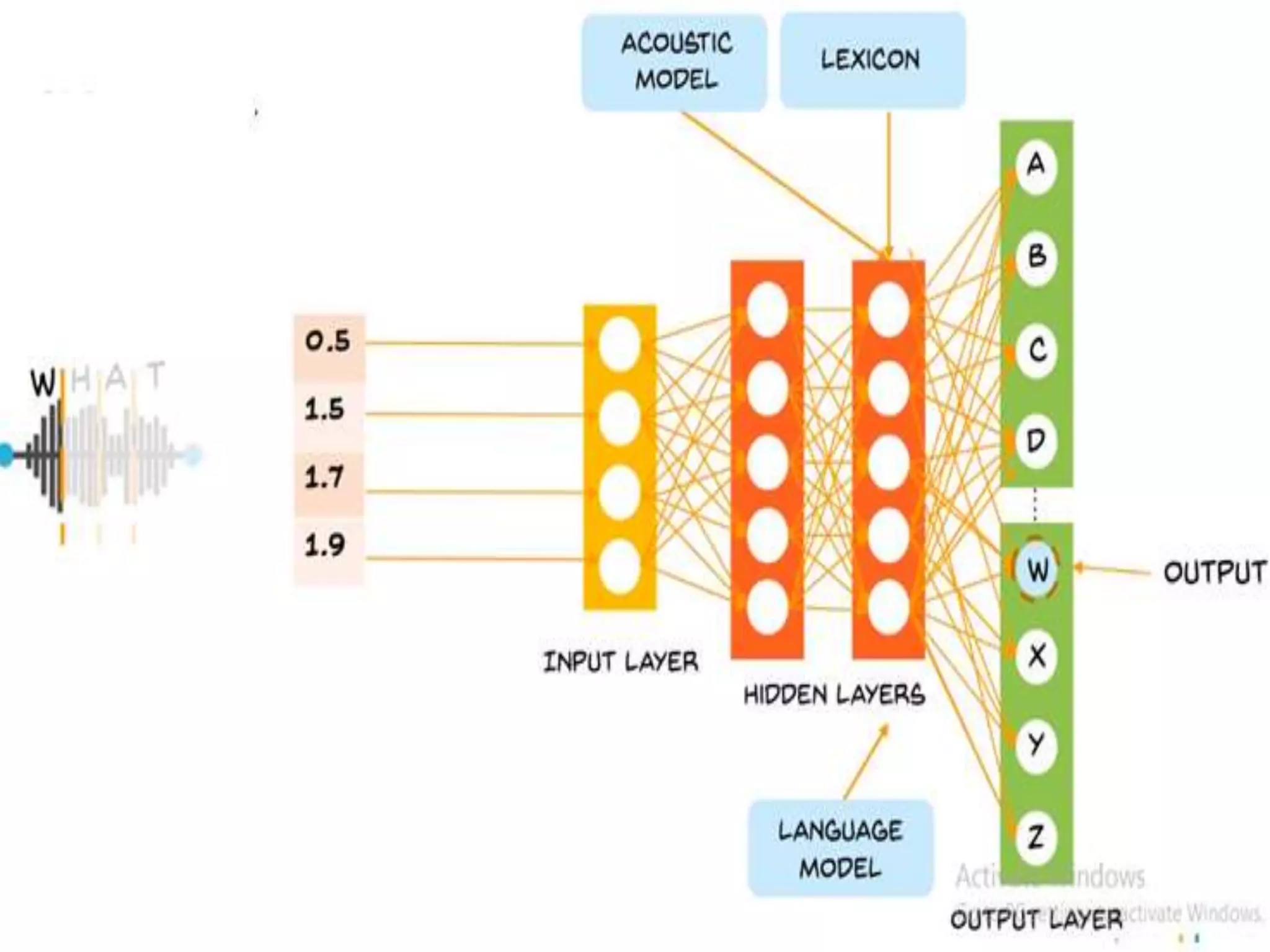
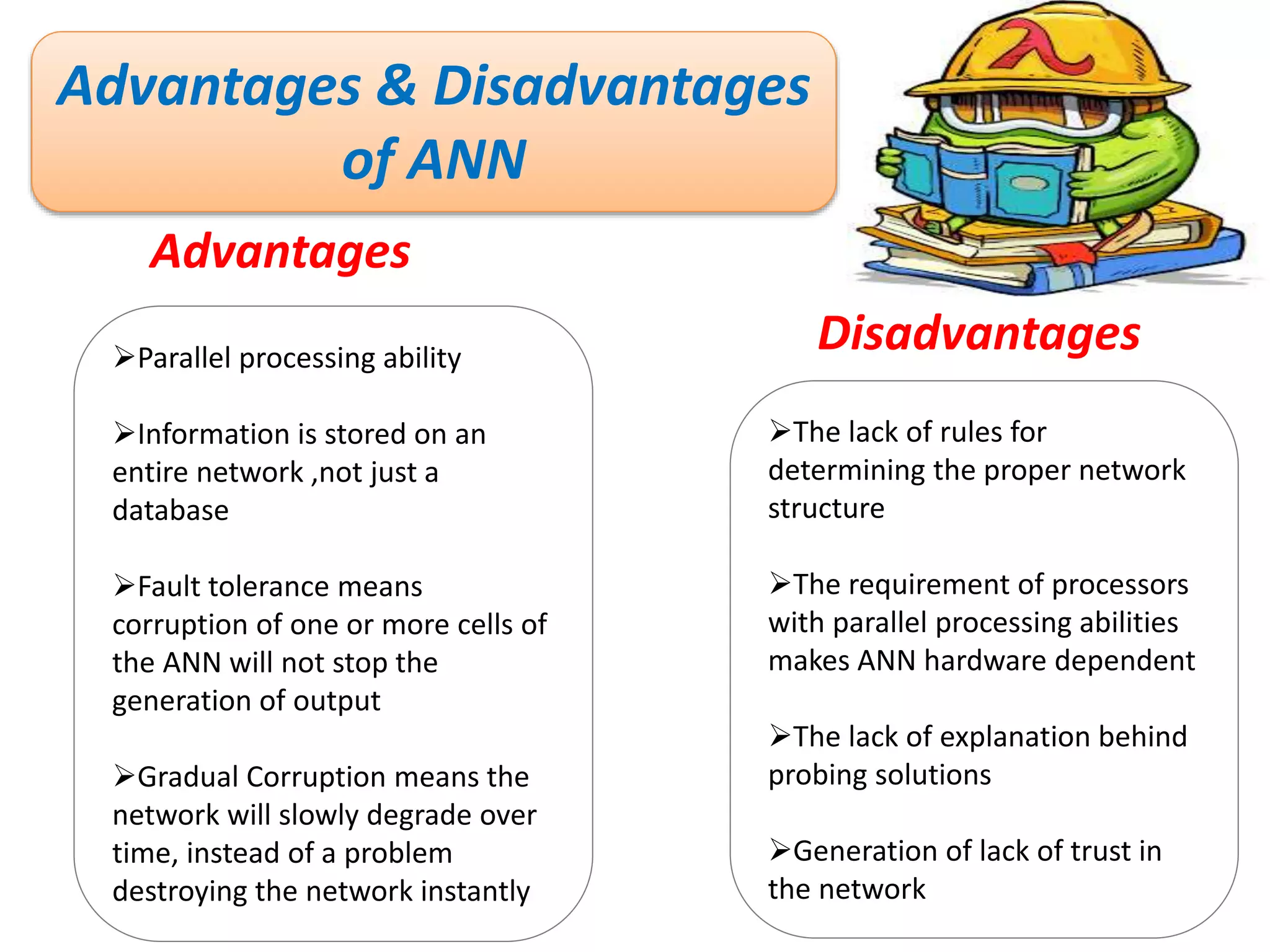
The document discusses Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), exploring their structure, function, and comparison with biological neurons. It covers topics such as perceptrons, feedforward neural networks, the backpropagation algorithm, and deep learning applications, along with advantages and disadvantages of ANNs. The document aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ANNs and their future in machine learning and artificial intelligence.