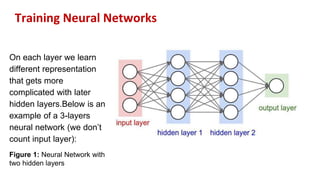
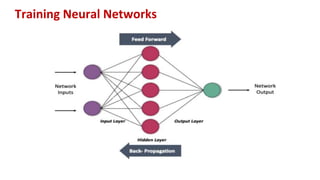
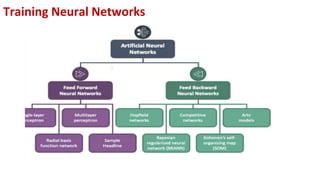
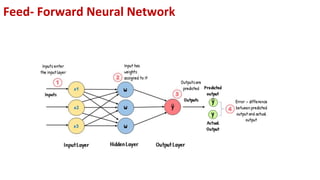
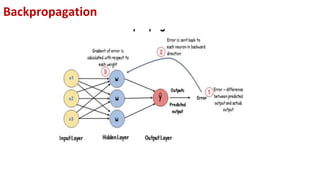
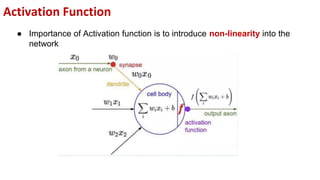
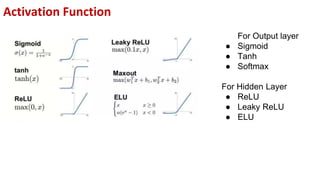
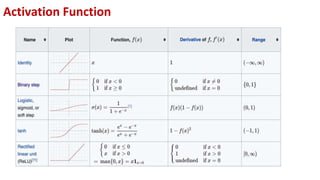
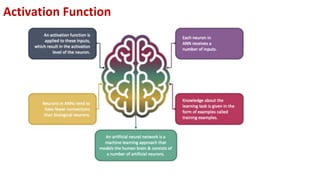
This document provides an overview of training neural networks through forward and backpropagation. It discusses how training involves adjusting weights and biases to minimize loss between predicted and actual outputs. The process includes forward propagation to make predictions, calculating loss, then backpropagating errors to update weights and biases in a way that reduces loss, repeating over multiple epochs. Activation functions and common types are also summarized.