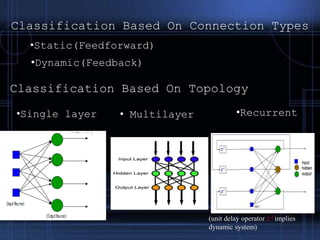
This document provides an introduction to neural networks, including their basic components and types. It discusses neurons, activation functions, different types of neural networks based on connection type, topology, and learning methods. It also covers applications of neural networks in areas like pattern recognition and control systems. Neural networks have advantages like the ability to learn from experience and handle incomplete information, but also disadvantages like the need for training and high processing times for large networks. In conclusion, neural networks can provide more human-like artificial intelligence by taking approximation and hard-coded reactions out of AI design, though they still require fine-tuning.