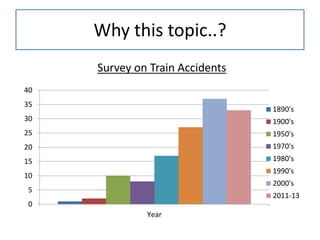
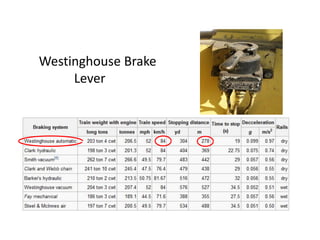
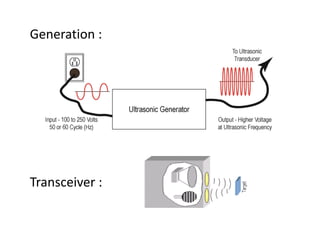
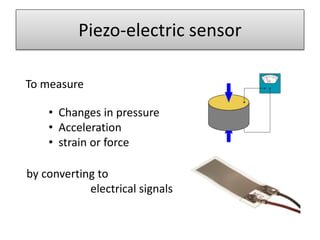
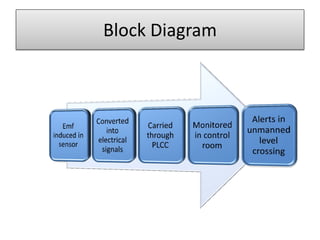
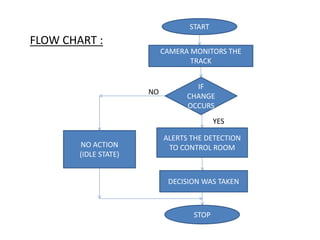
The document discusses an automatic train collision and accident avoidance system, highlighting the need for automated braking, real-time train monitoring, and an alert system using pattern recognition. It provides an overview of historical rail accidents and emphasizes the technology's potential to significantly reduce collision rates. Proposed solutions include installing ultrasonic sensors and implementing image pattern recognition to detect obstacles and alert control personnel.