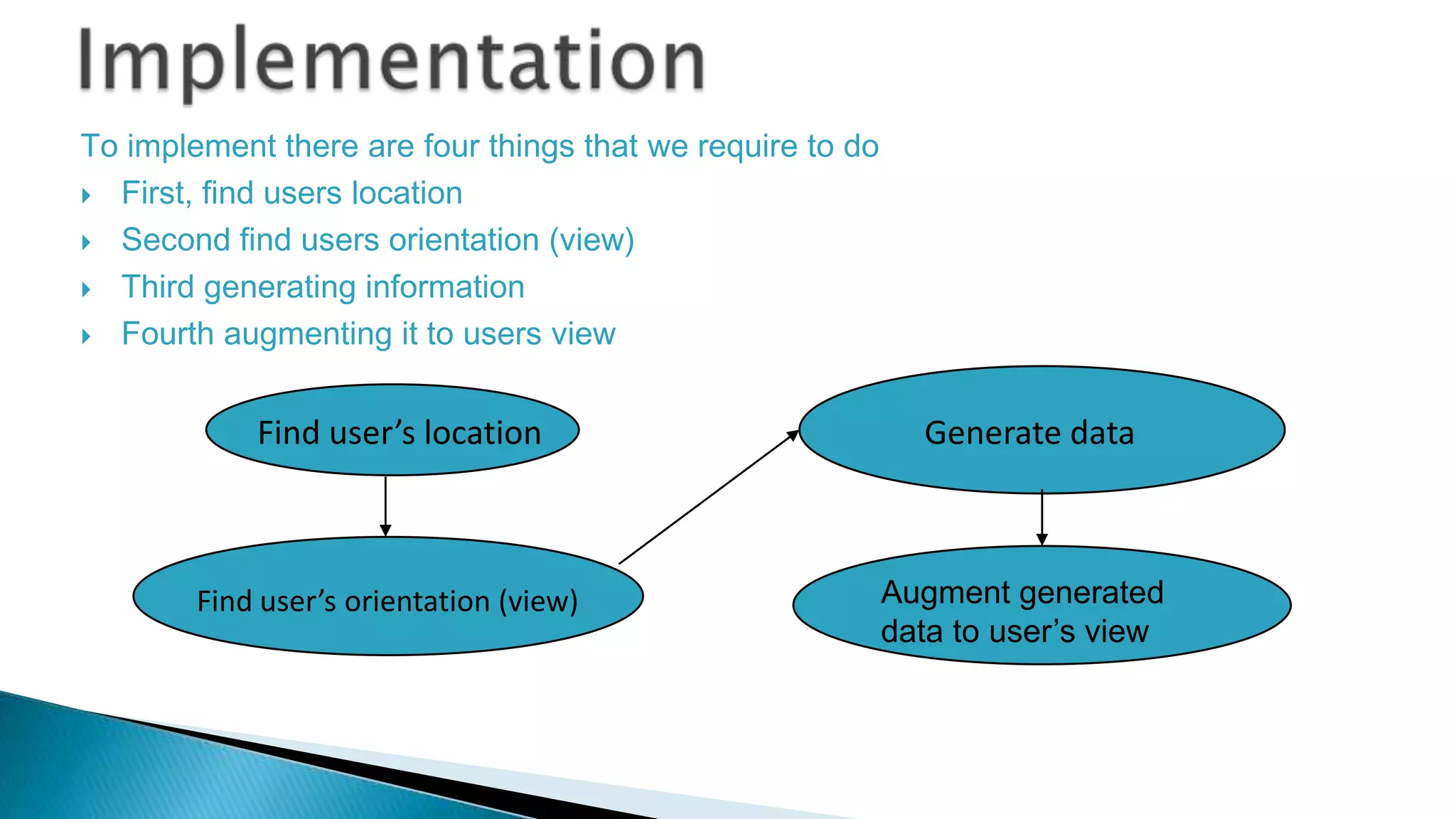
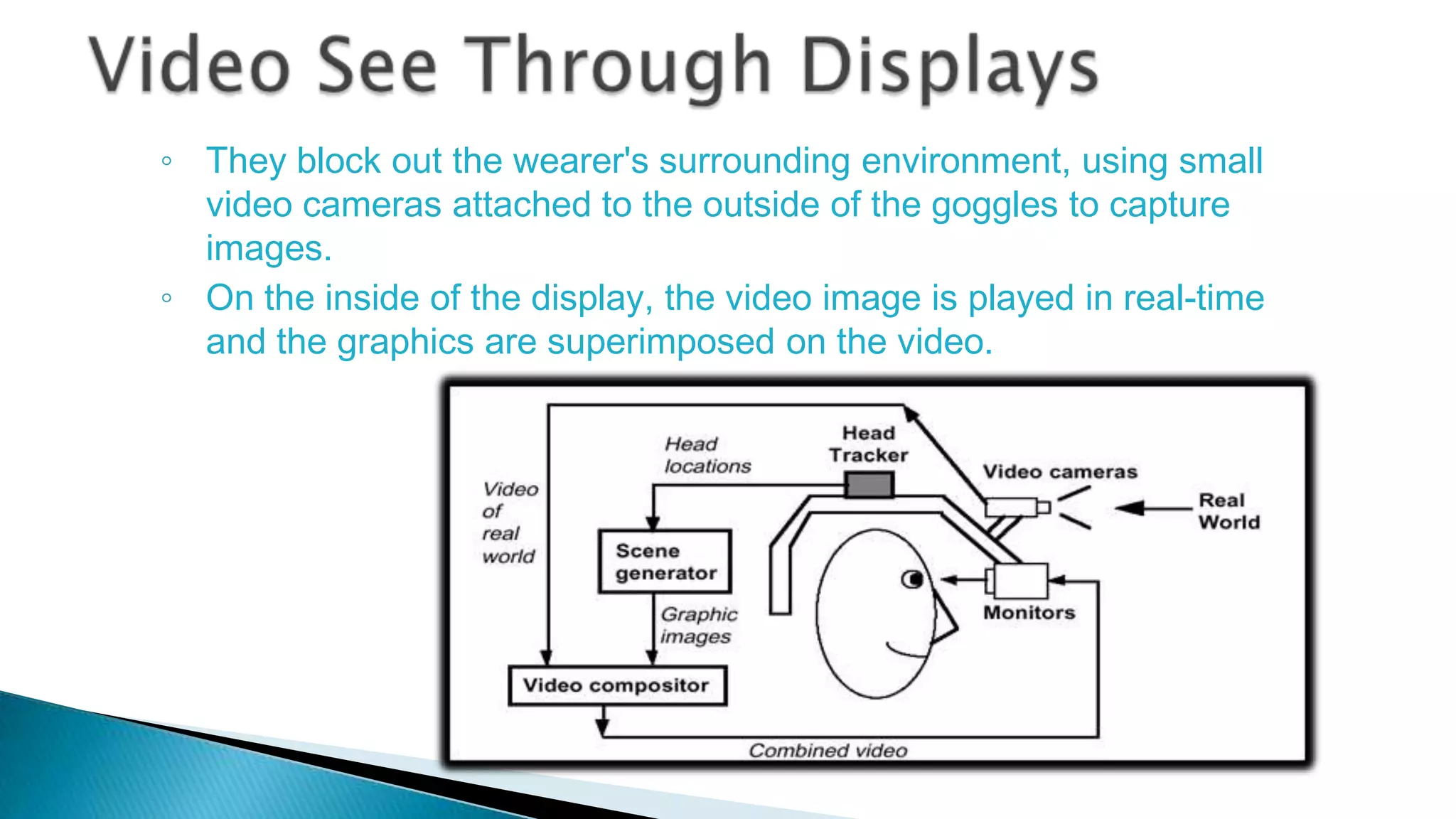
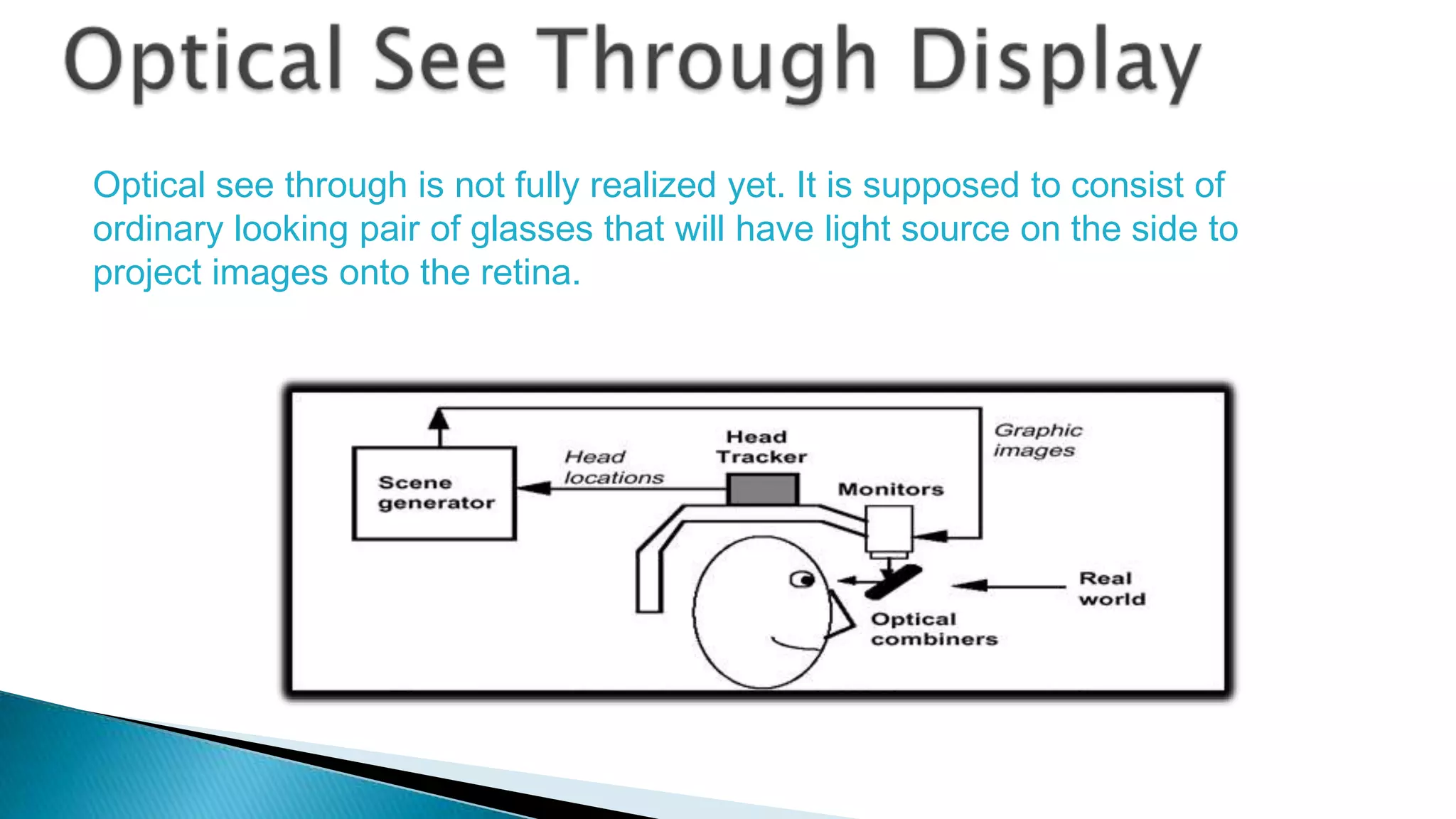
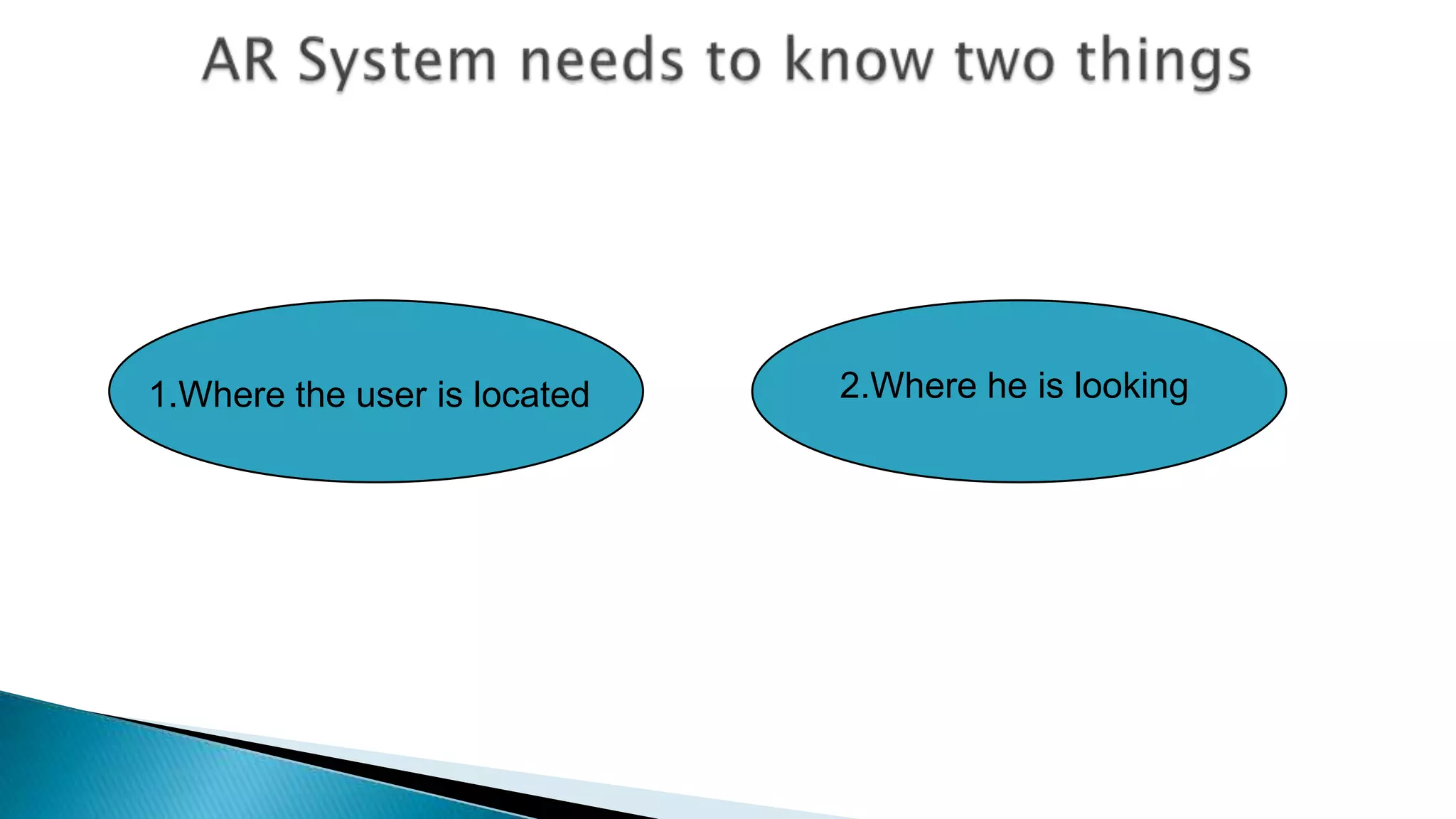
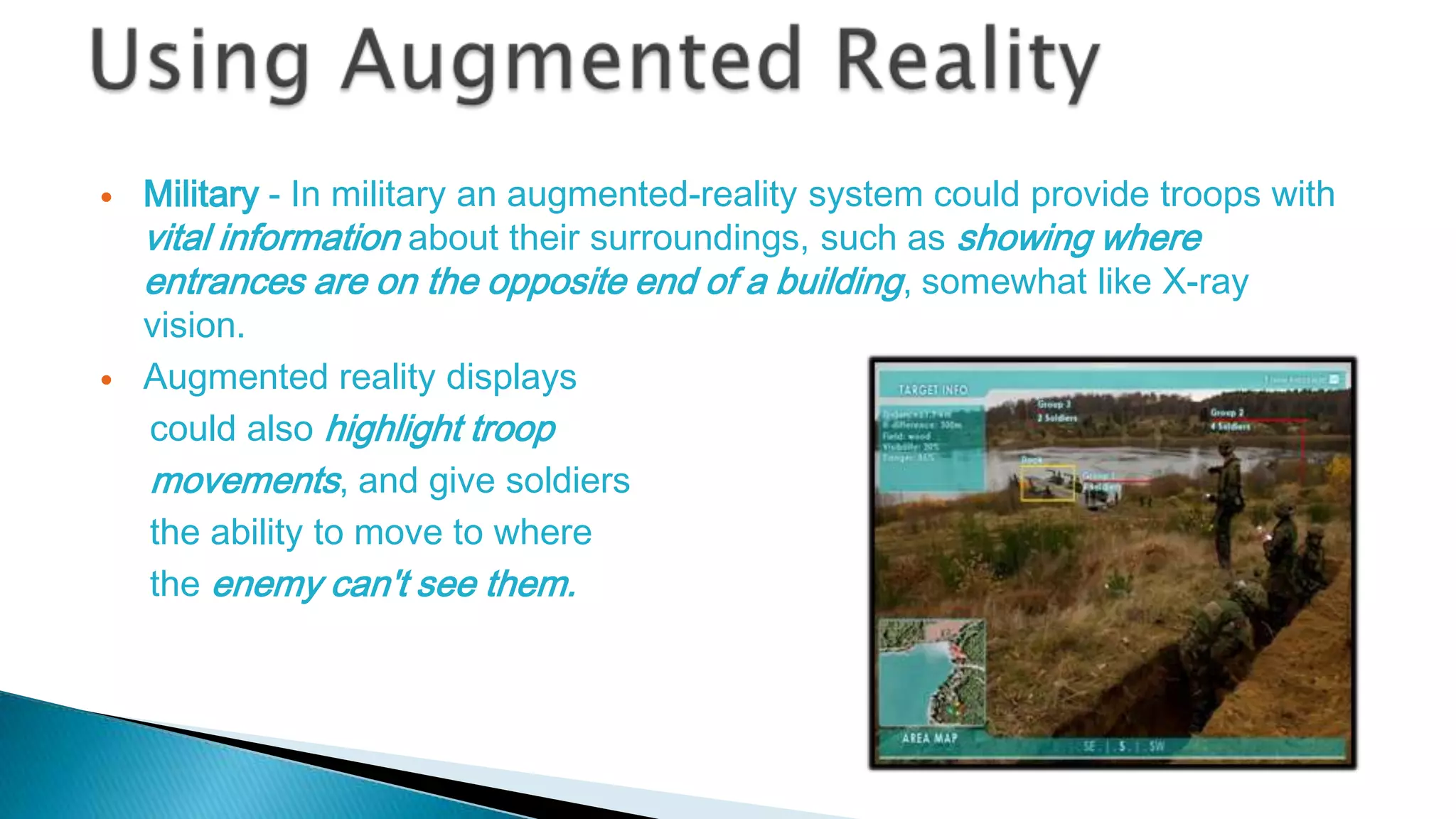
The document discusses augmented reality (AR) as an interactive system that blends real and virtual worlds, emphasizing the technology's potential applications in various fields such as education, military, and gaming. It outlines the components required for AR systems, including displays, tracking systems, and mobile computing, while also addressing current limitations and challenges such as accurate location tracking. The document concludes that with advancements in technology, AR could significantly transform how we experience our surroundings.