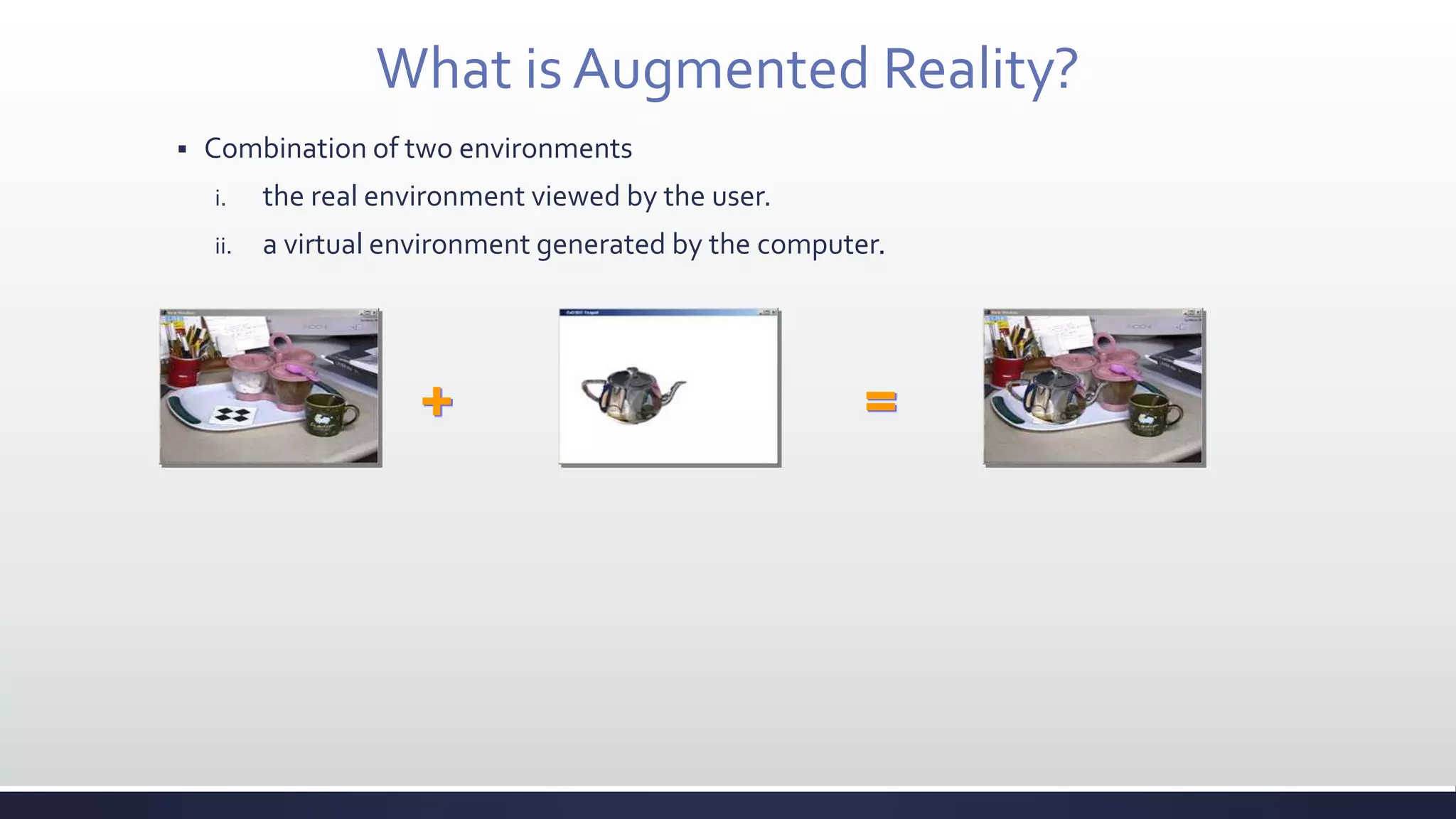
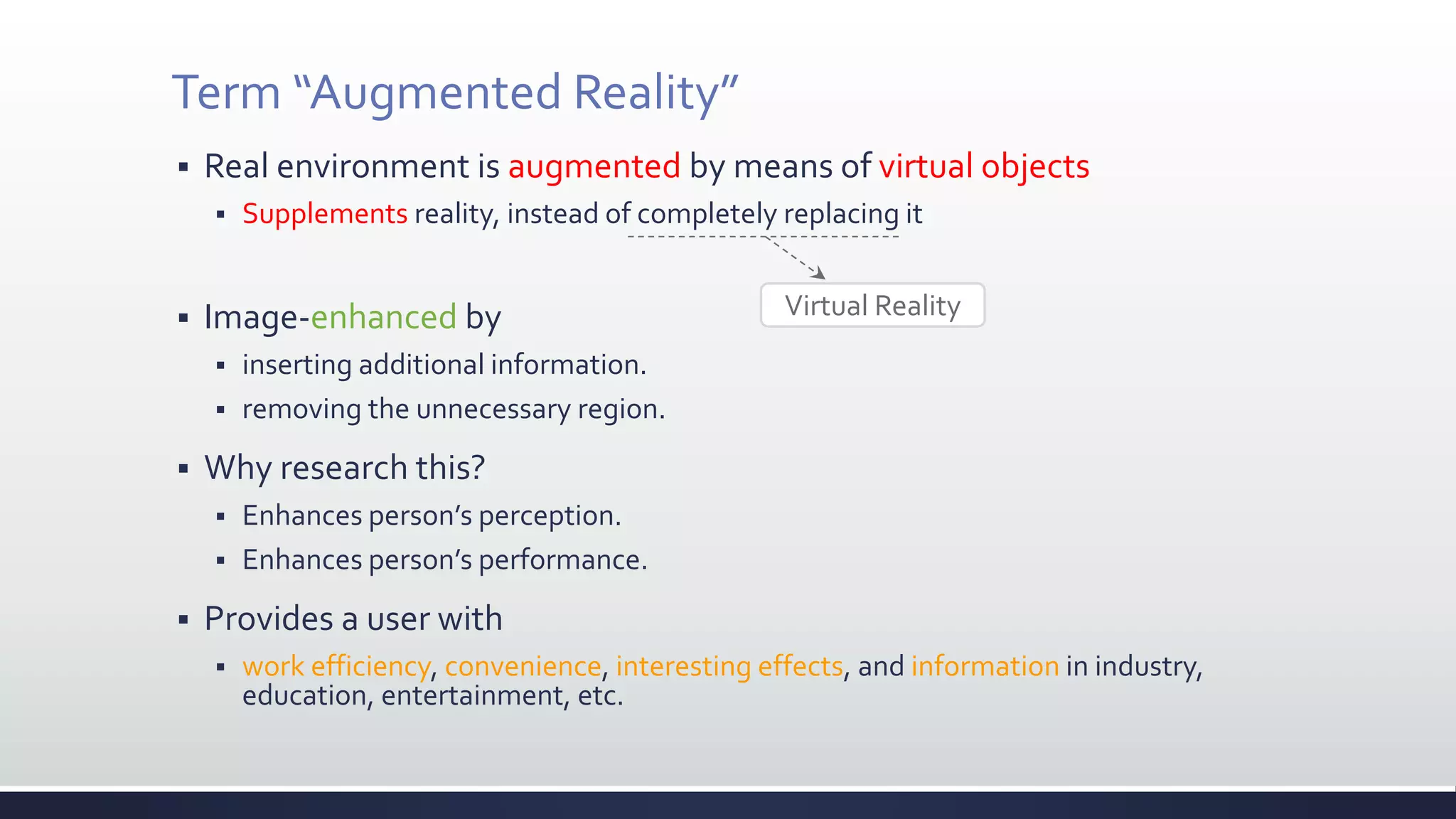
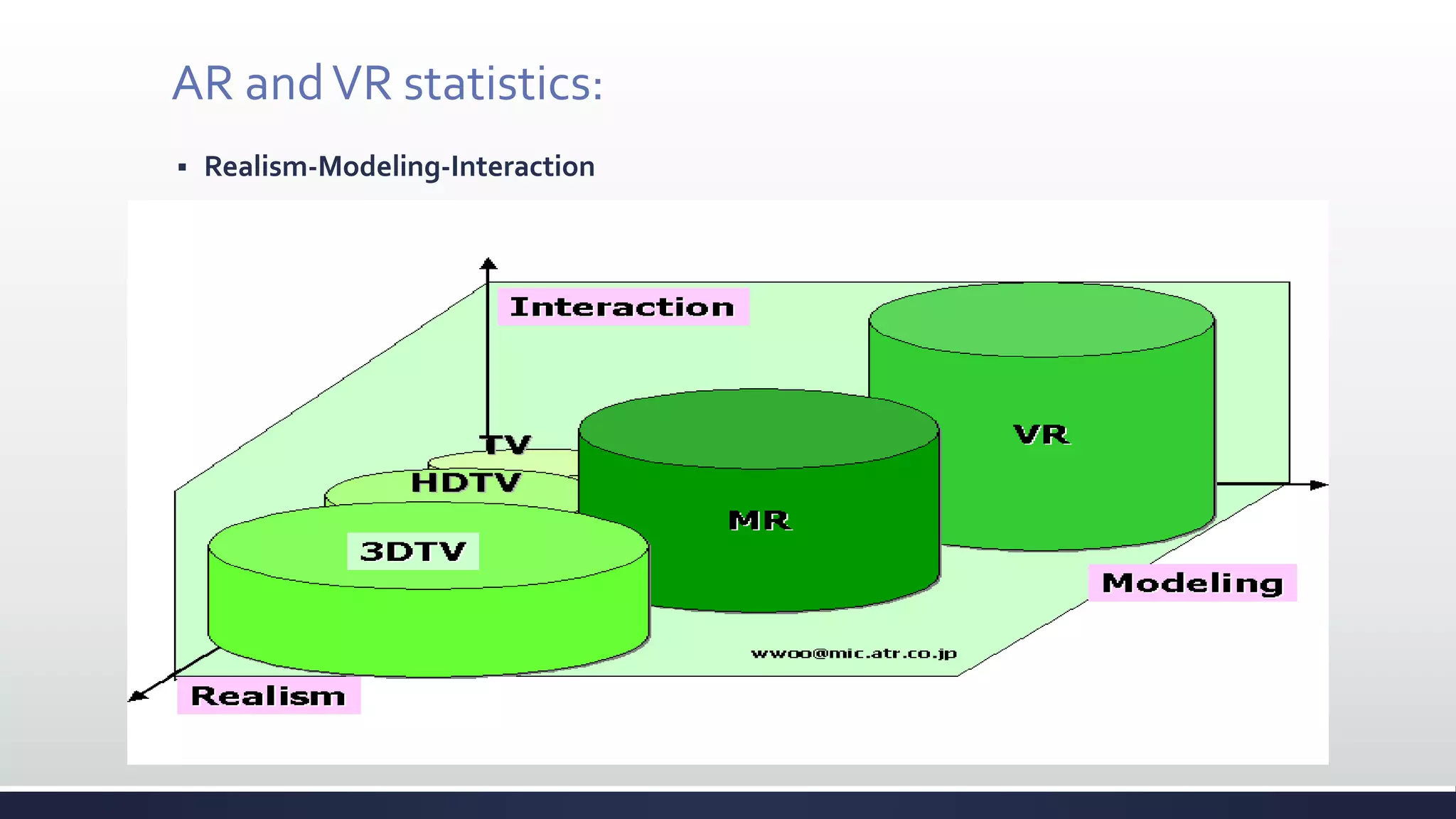
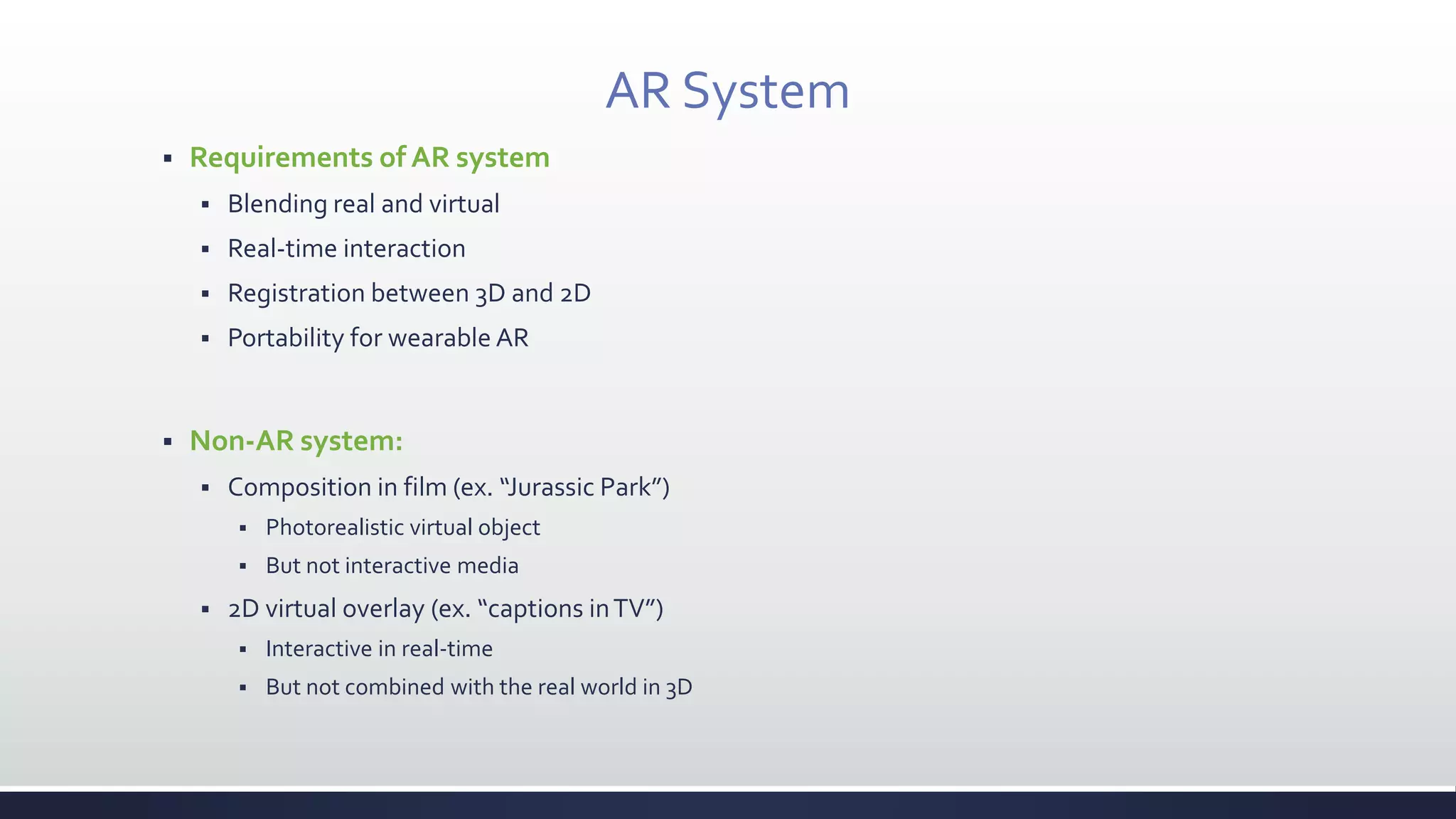
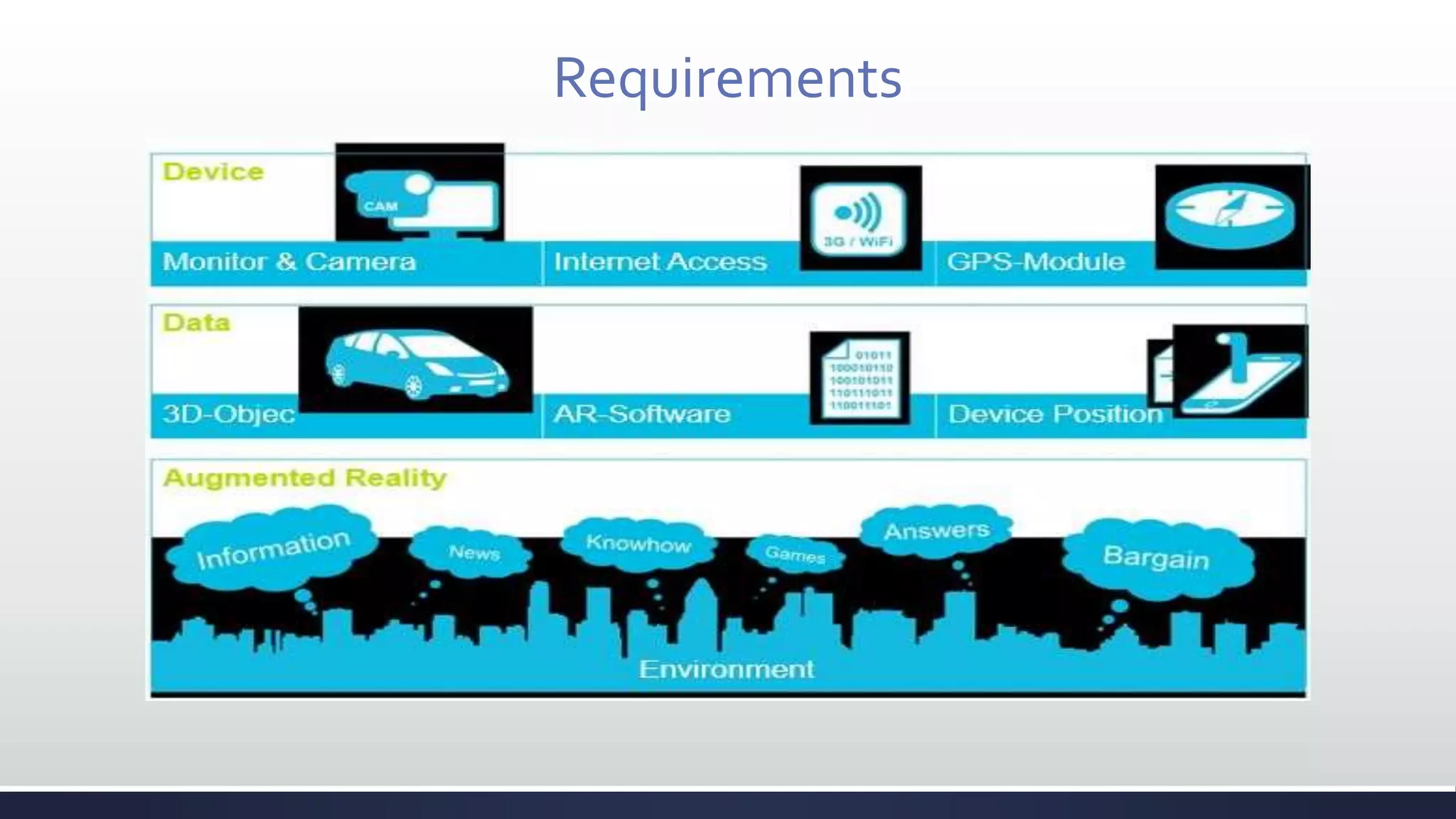
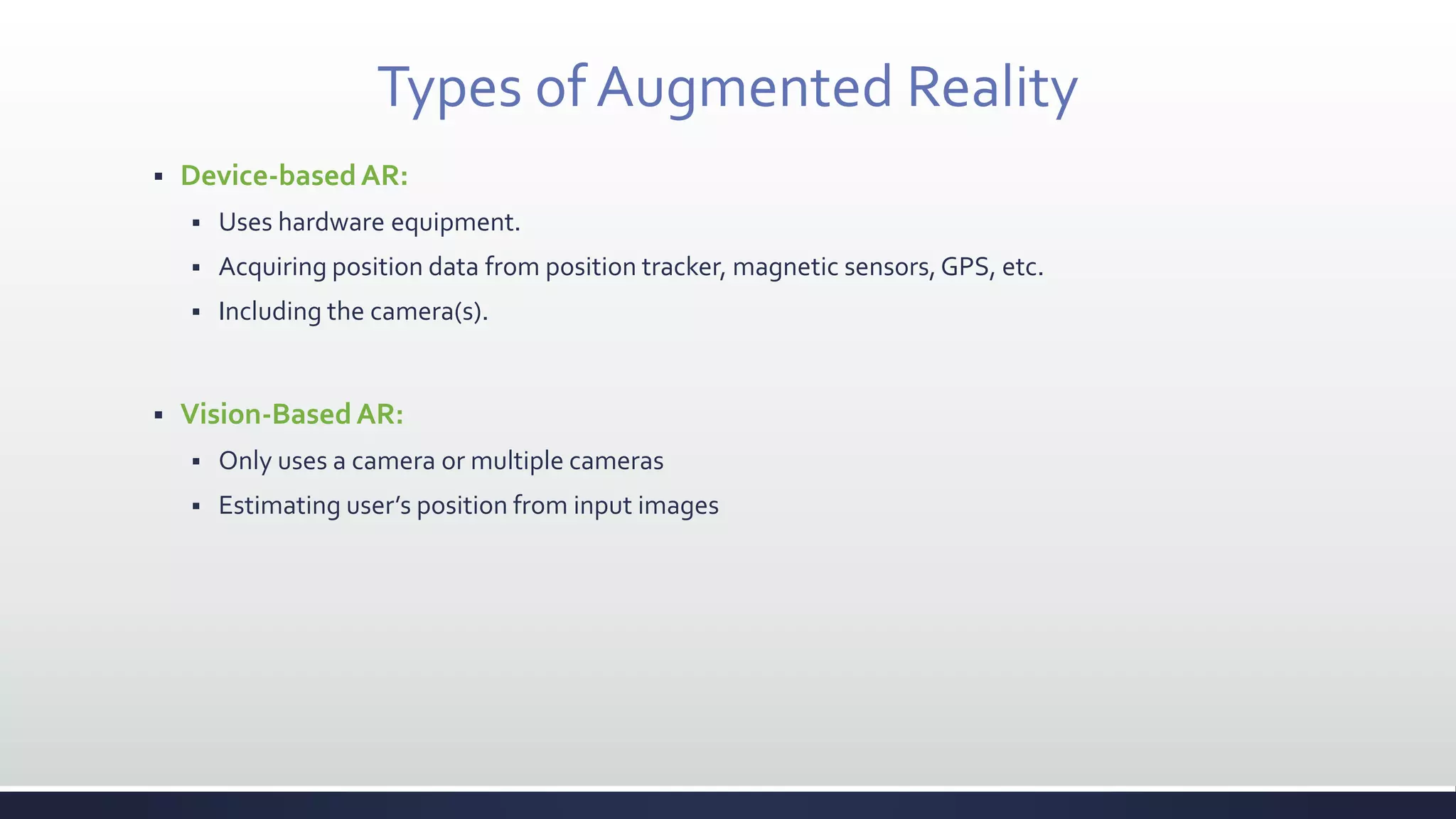
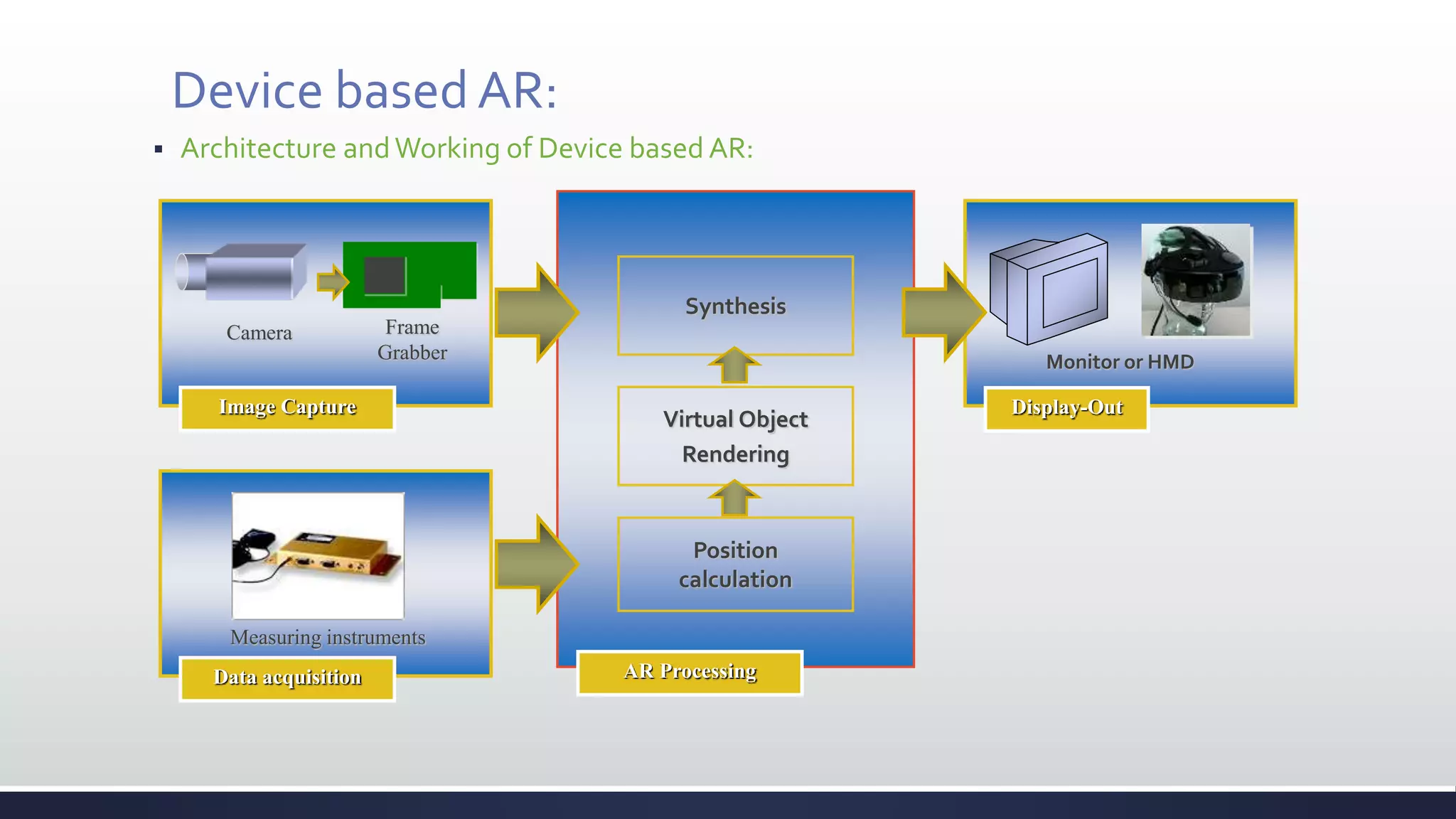
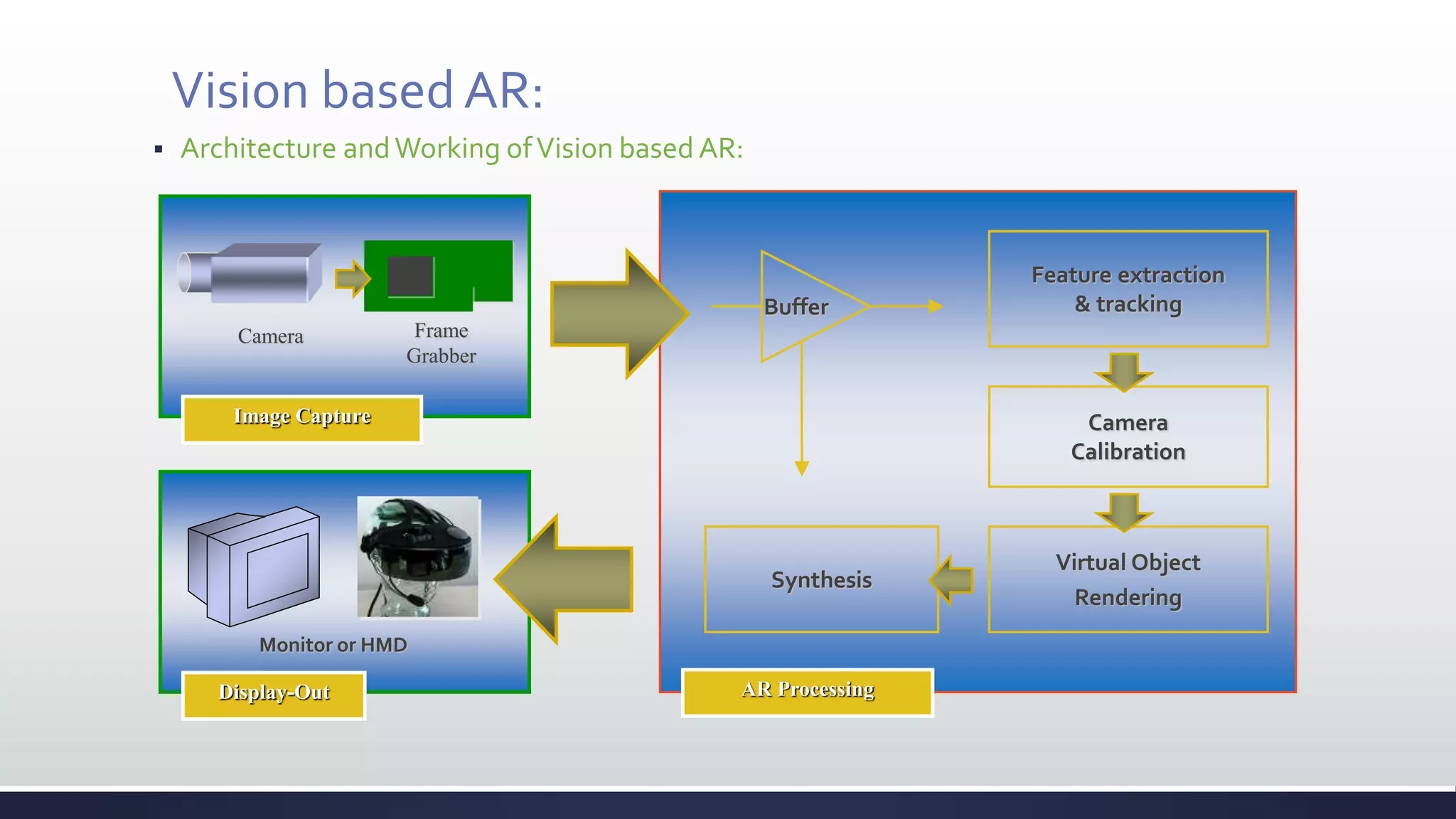
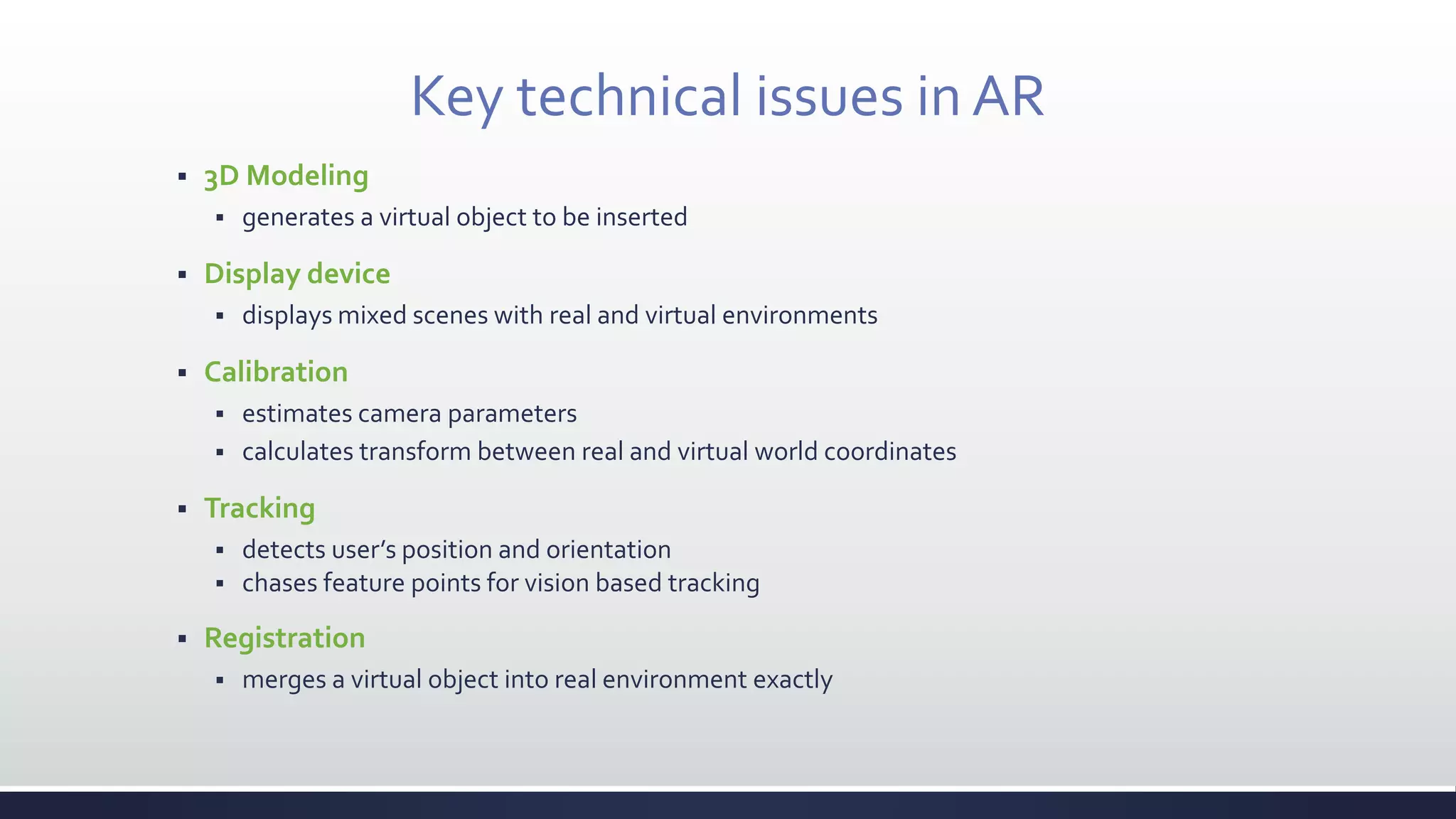
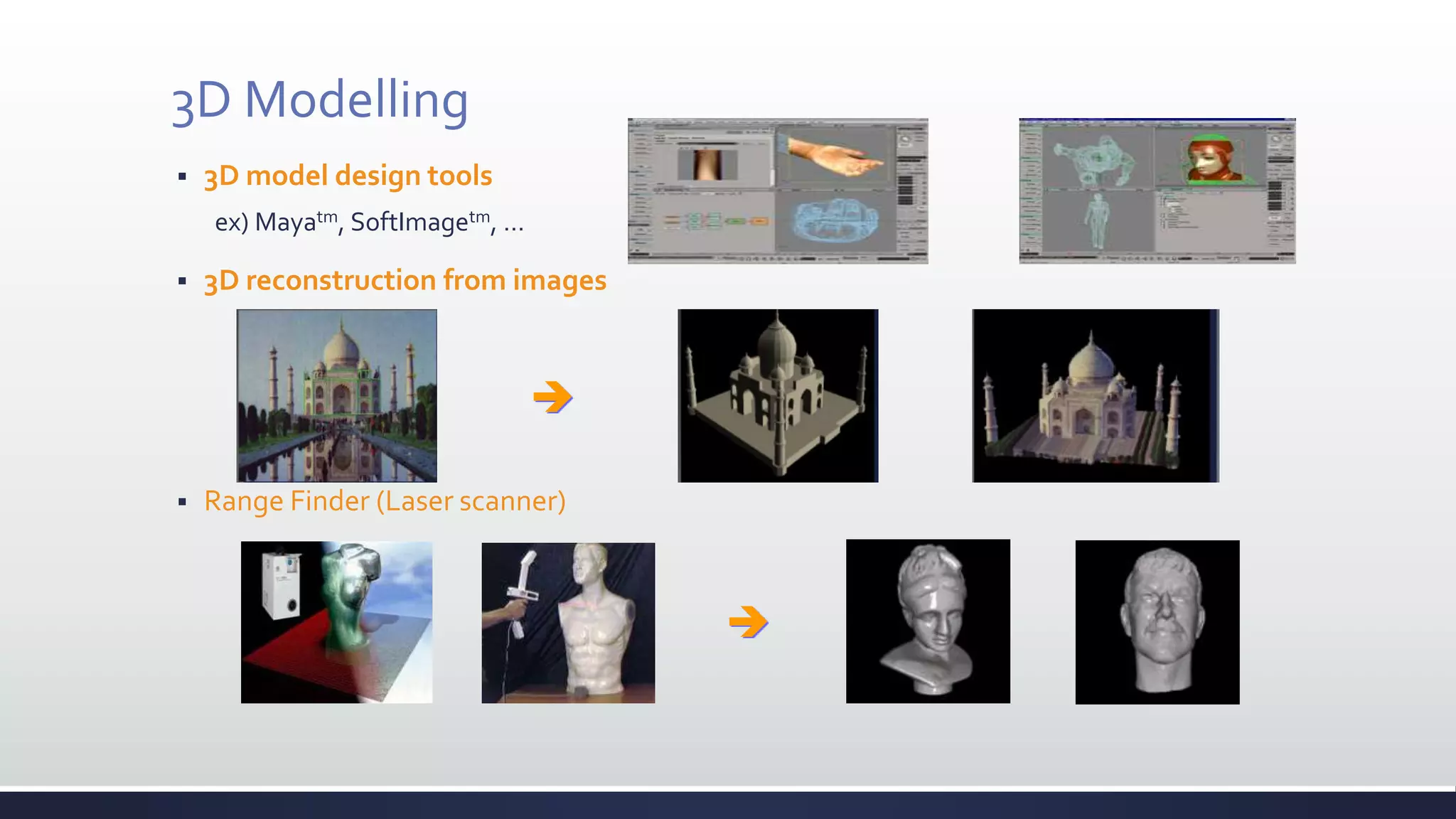
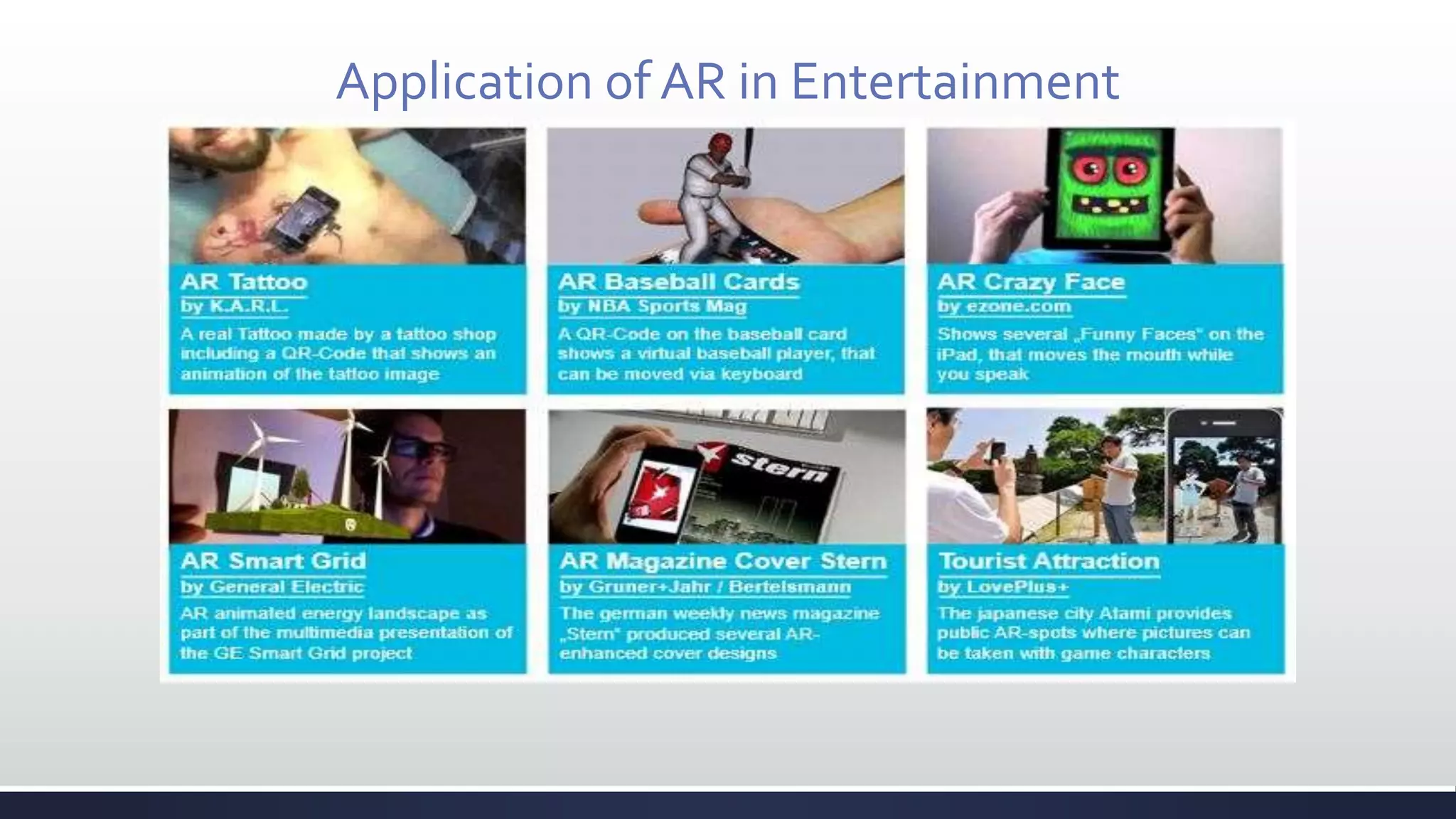
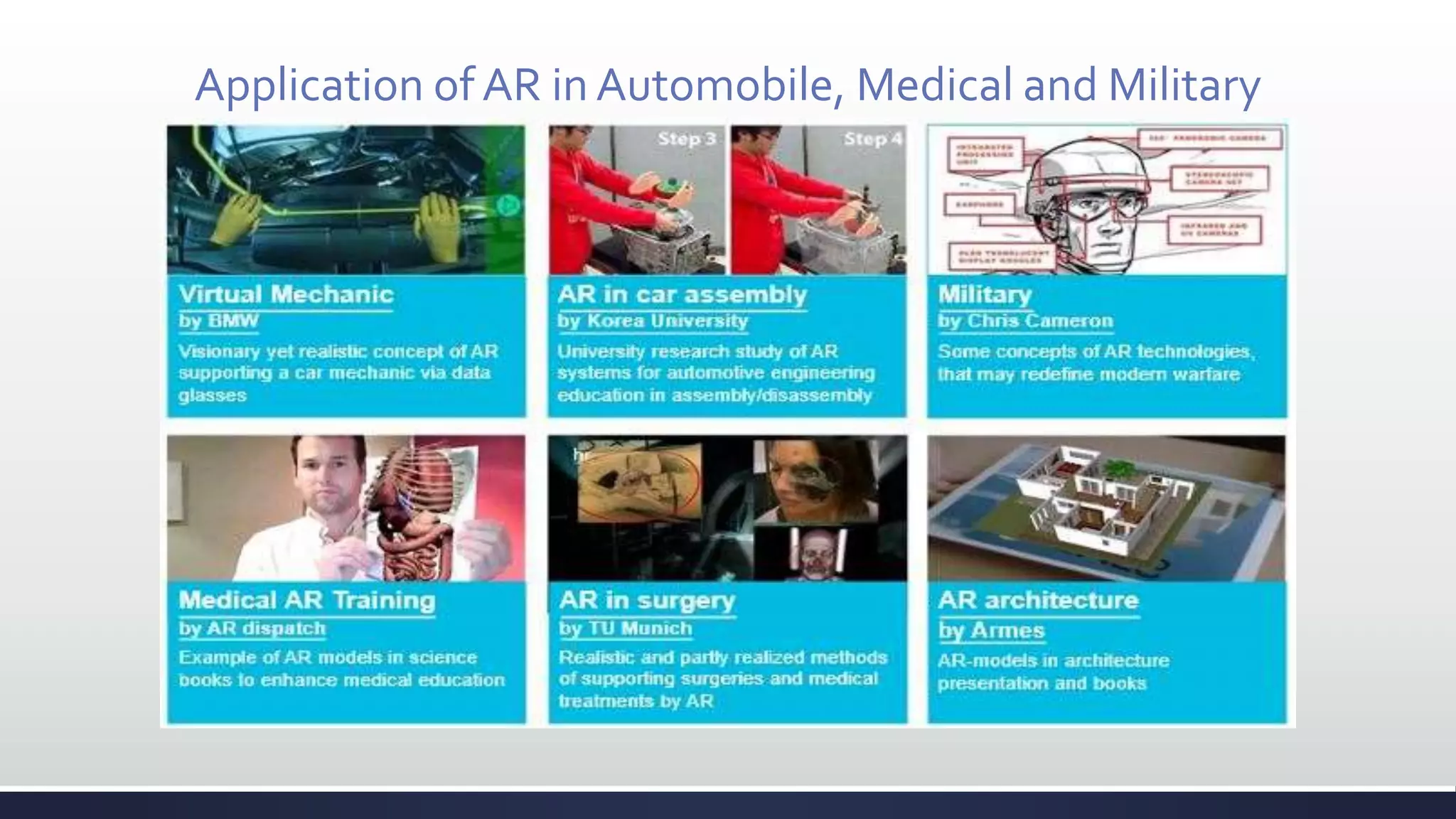
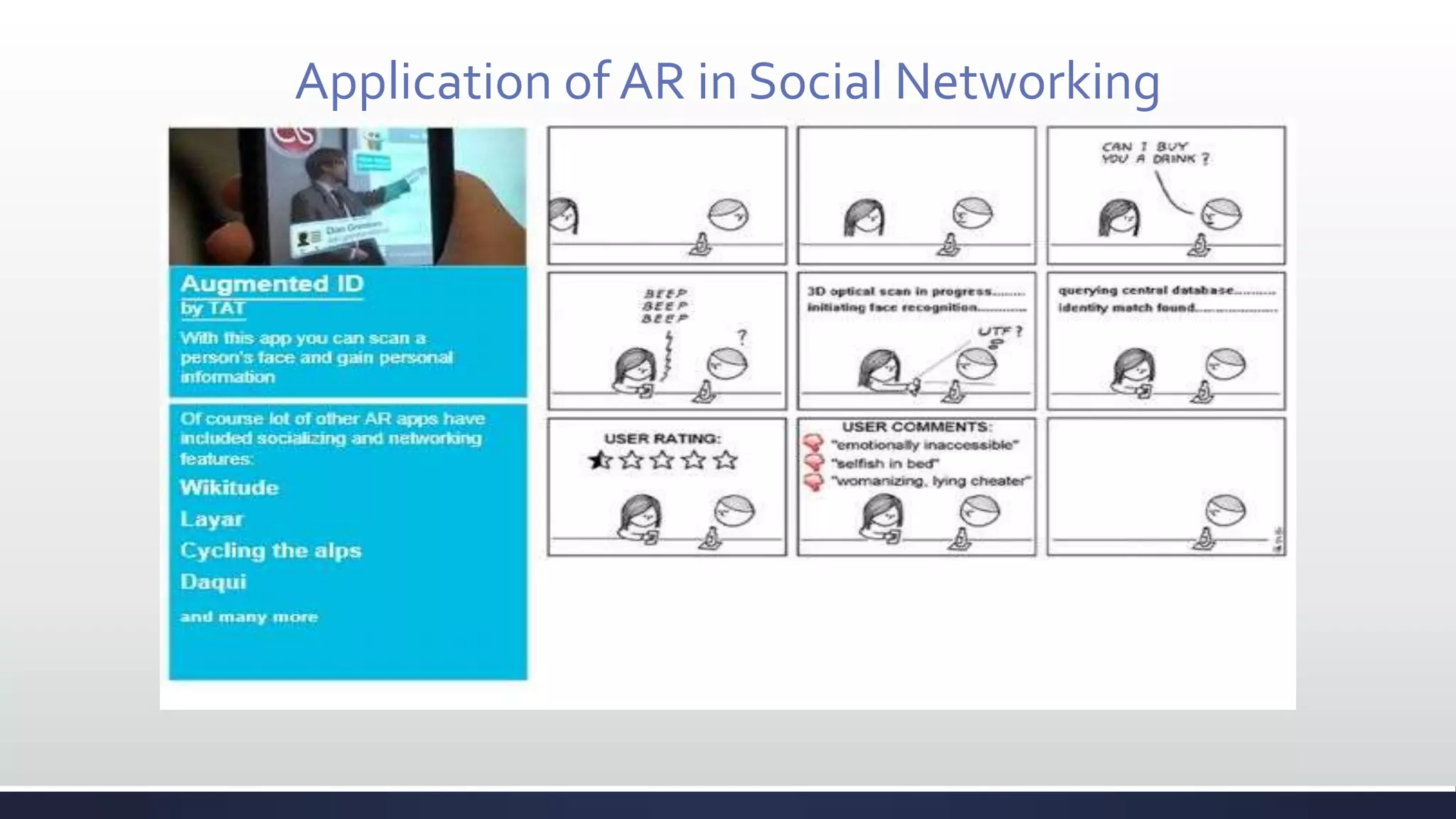
This document discusses augmented reality (AR), which combines the real world with virtual objects. It defines AR, distinguishes it from virtual reality by noting AR inserts virtual objects into the real environment rather than fully immersing the user. The document outlines the key components of an AR system including requirements for blending real and virtual environments, types of AR systems, and technical issues like tracking, registration, and display. It concludes by describing various applications of AR in fields like entertainment, marketing, automobiles, games, navigation, and more.