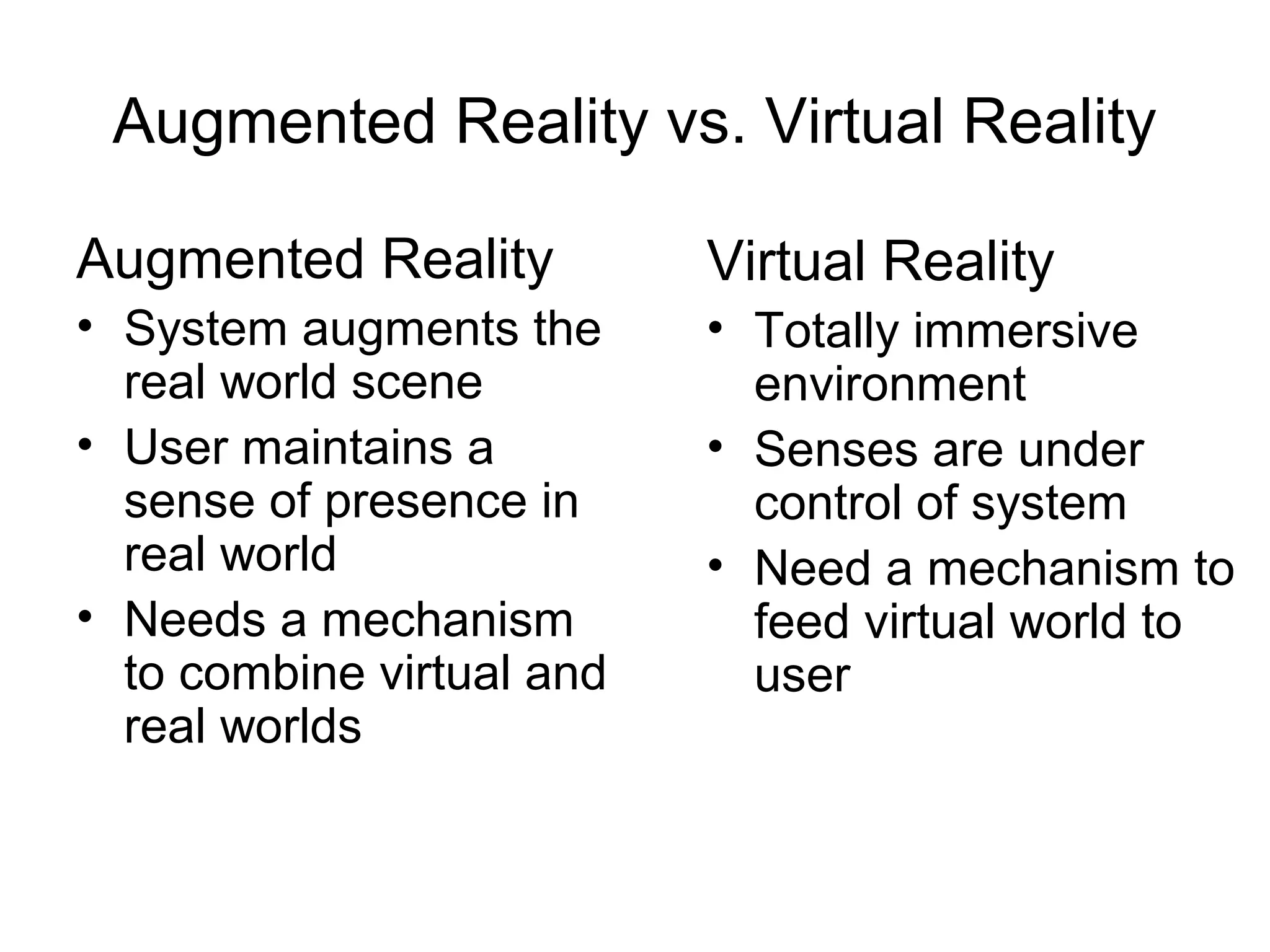
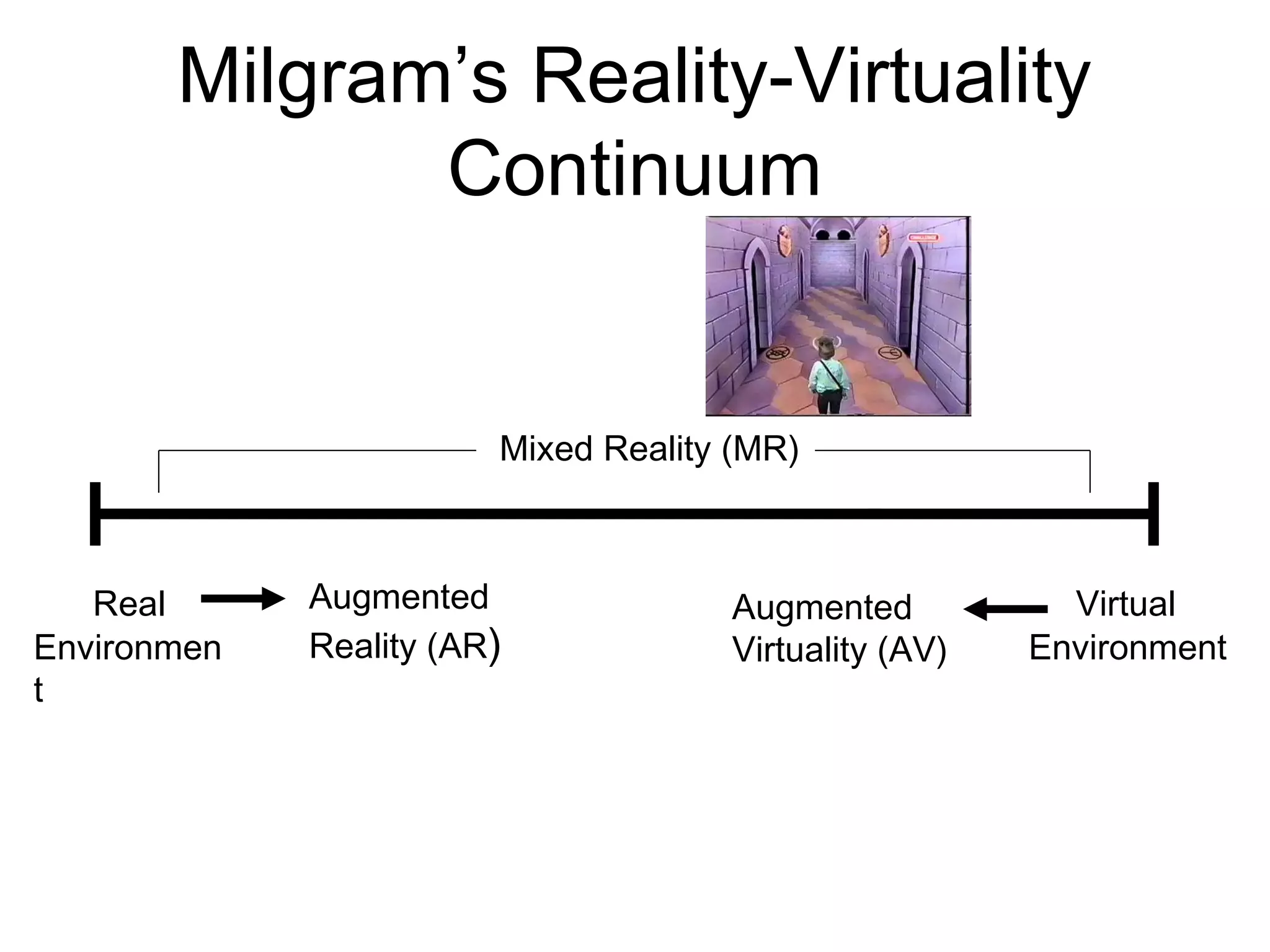
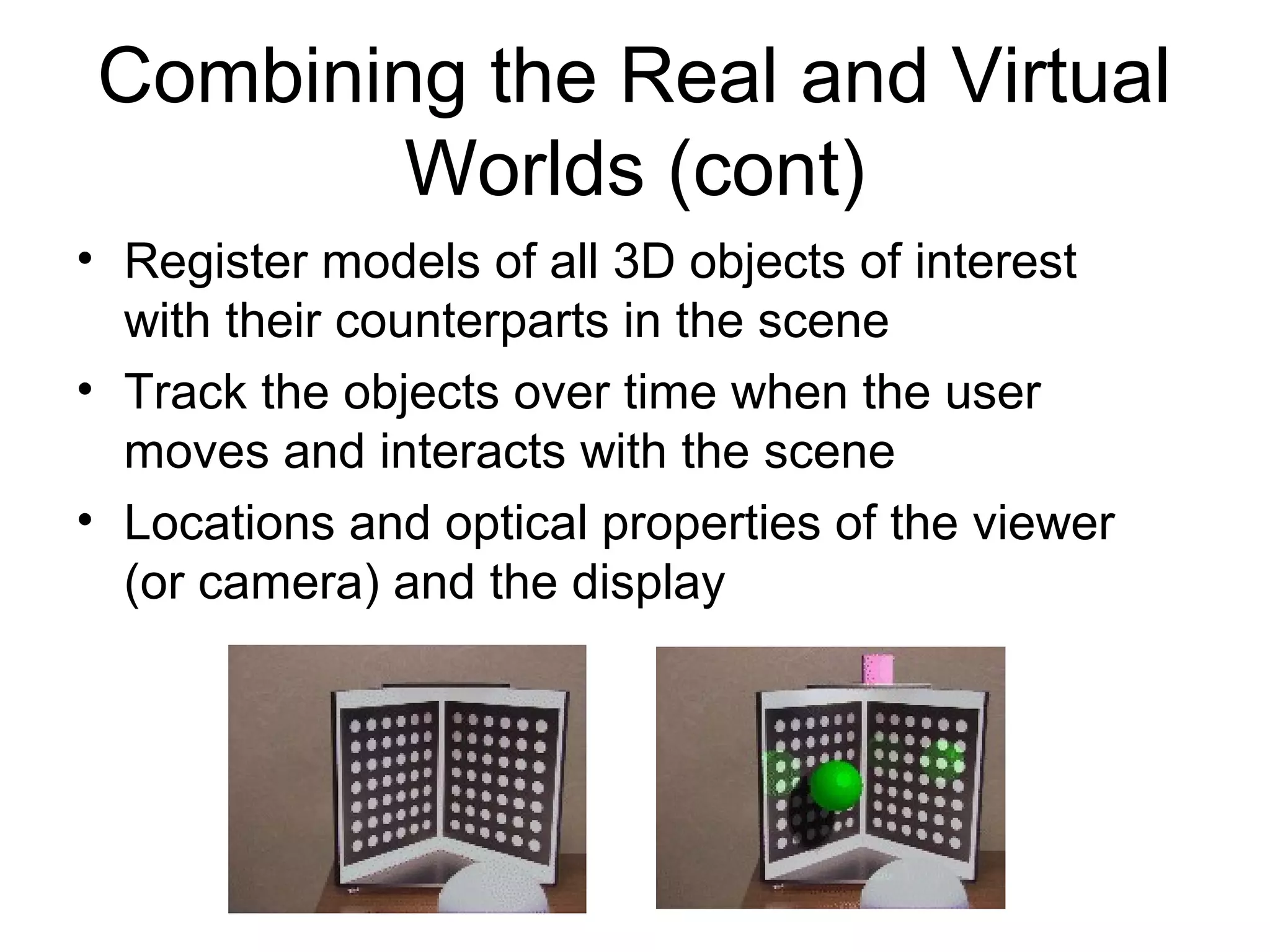
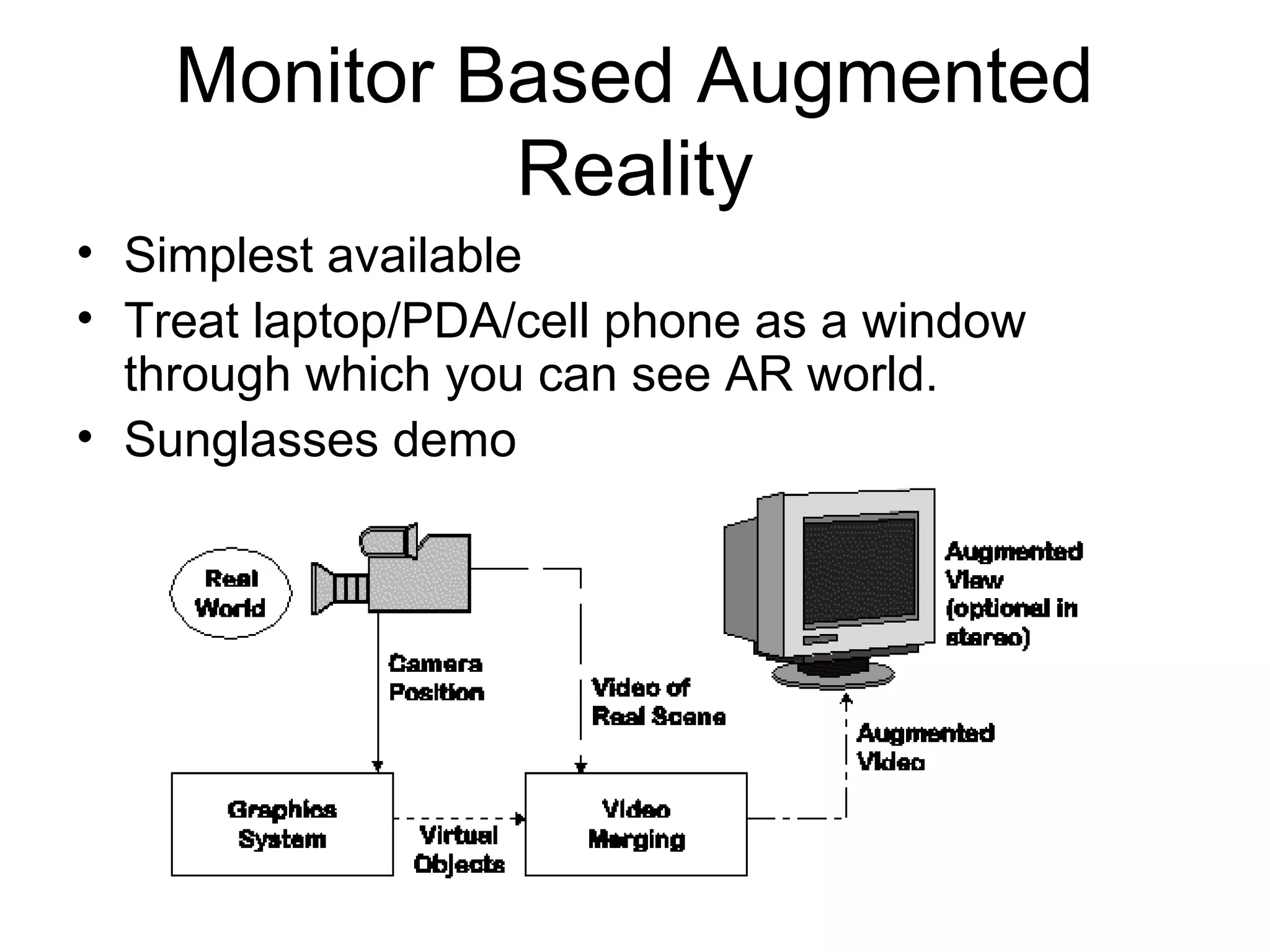
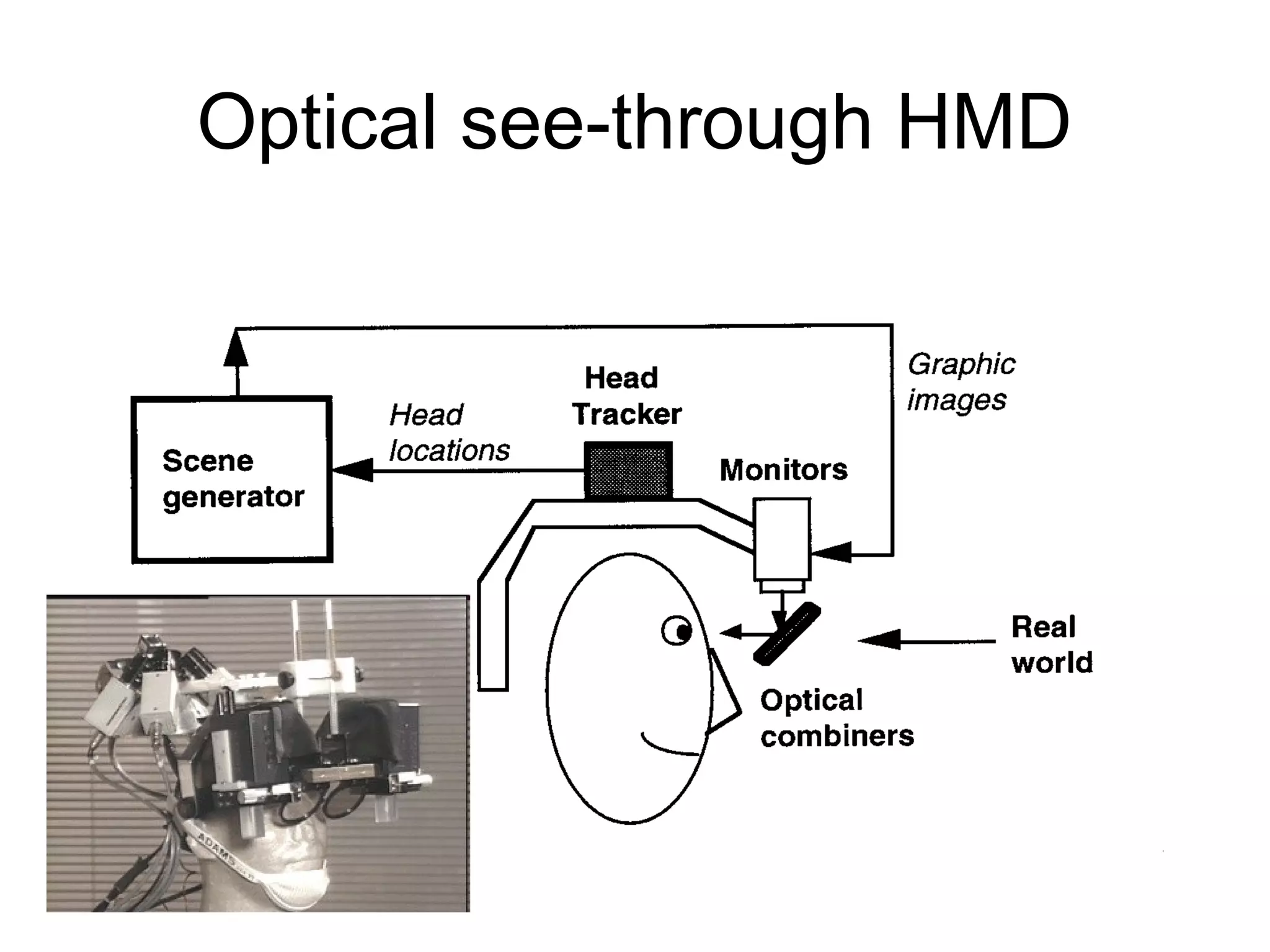
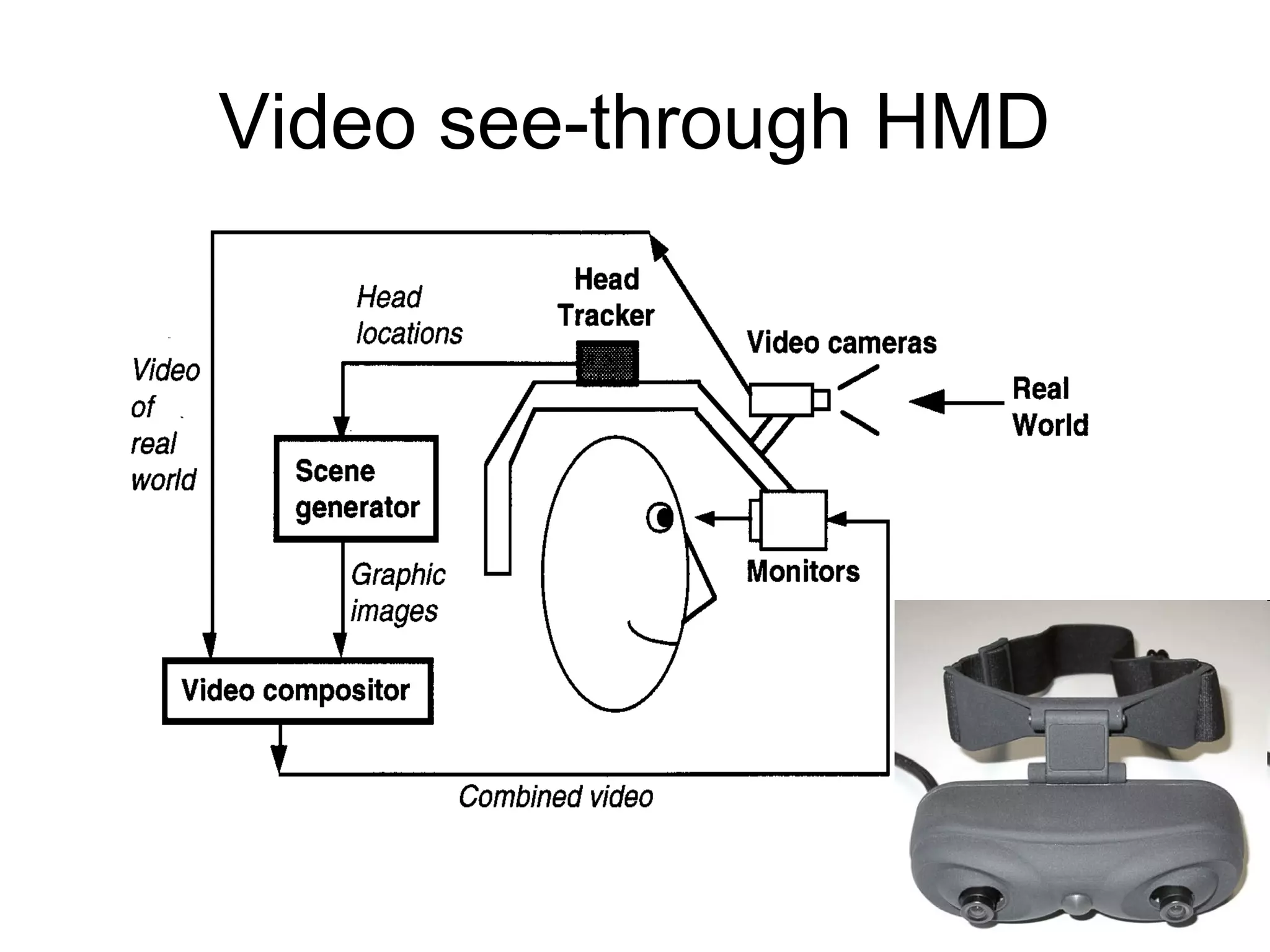
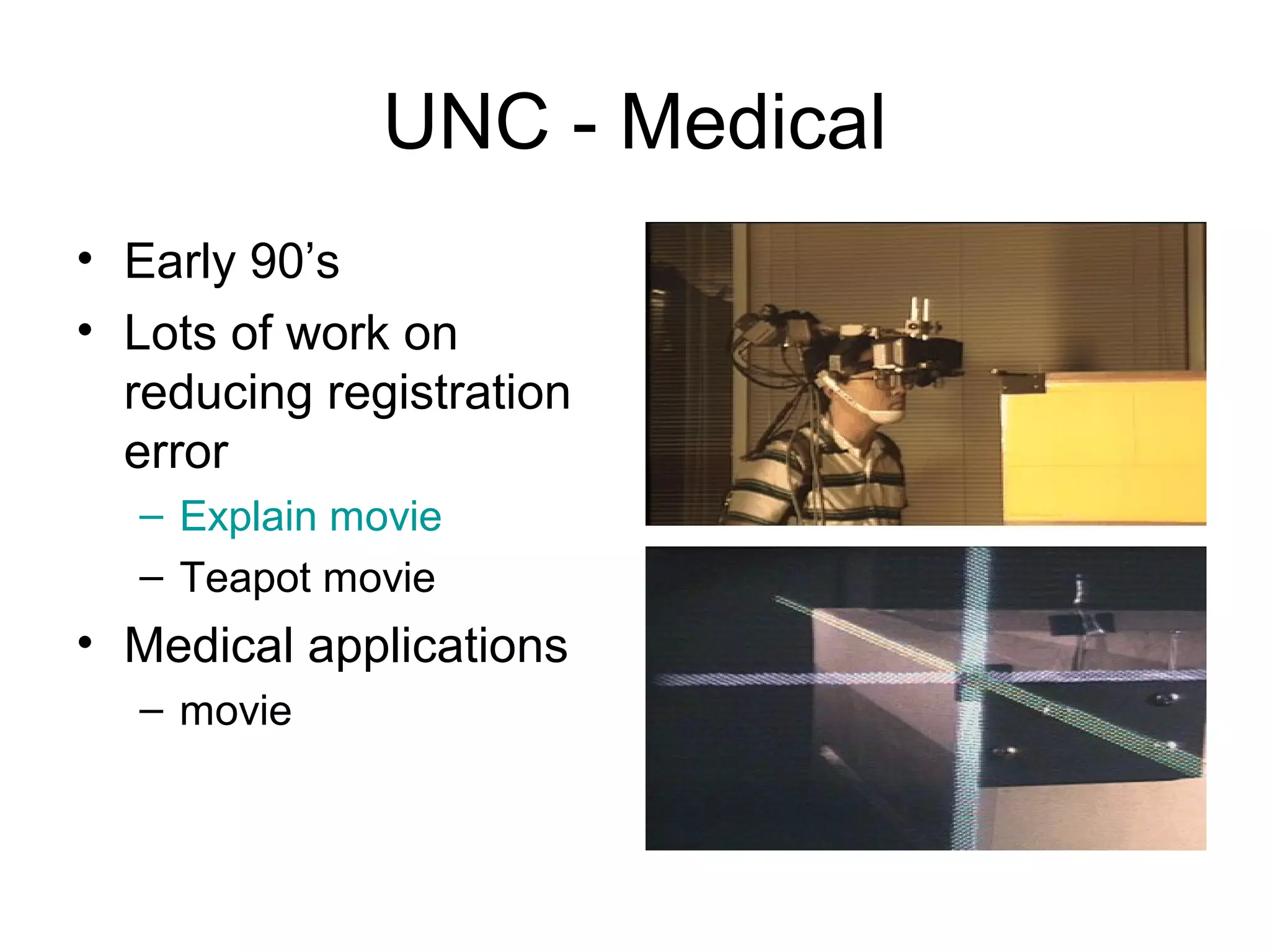
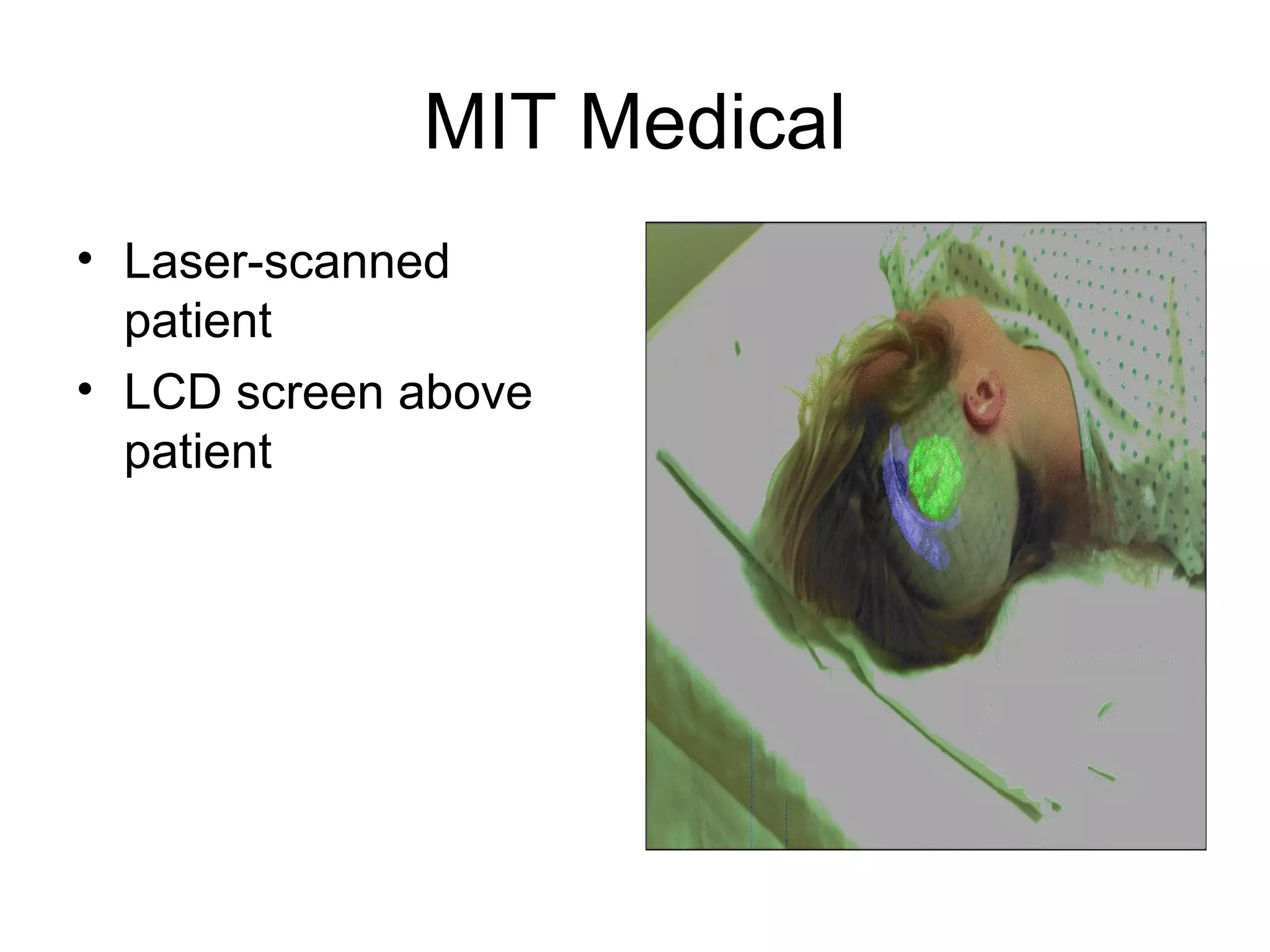
This document discusses augmented reality (AR) and its key concepts. It defines AR as a combination of real and virtual scenes that augments the real scene with additional computer-generated information. The document contrasts AR with virtual reality and discusses various AR display technologies including monitor-based, video see-through head-mounted displays, and optical see-through head-mounted displays. It also outlines some early applications of AR in areas like maintenance, medical, instruction, and gaming. Overall the document provides a high-level overview of AR, its definition, differences from virtual reality, display technologies, and early applications.