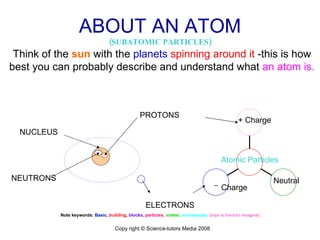
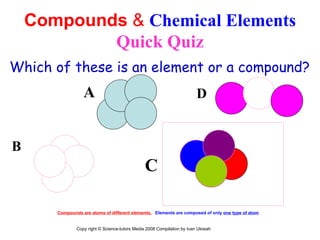
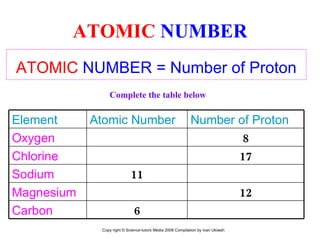
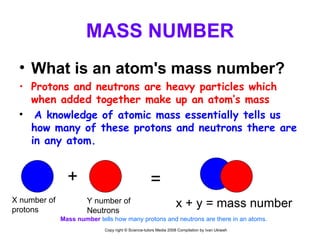
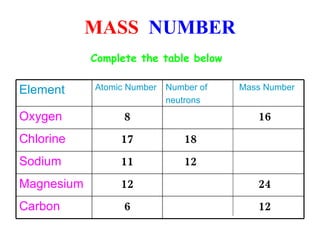
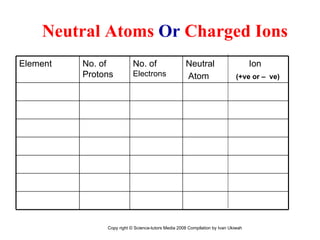
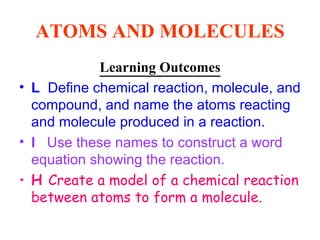
The document is a presentation about atoms and elements, detailing the structure of atoms, including protons, neutrons, and electrons, as well as the distinction between chemical elements and compounds. It explains concepts like atomic number, mass number, and the neutrality of atoms in terms of protons and electrons. Additionally, it covers topics related to chemical reactions, specifically the formation of metal oxides and experimental procedures for safely demonstrating these reactions.