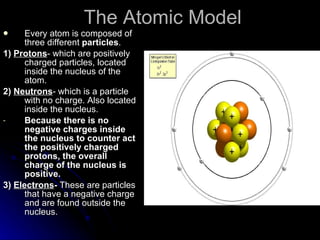
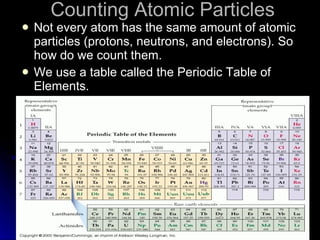
This document provides an overview of key concepts about atoms, matter, and the structure of atoms. It defines atoms as the building blocks of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space, and can exist as solids, liquids or gases. Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus. The number of protons determines the element. Atoms can combine to form compounds or mixtures. Compounds can only be separated through chemical means while mixtures can be separated physically or chemically.