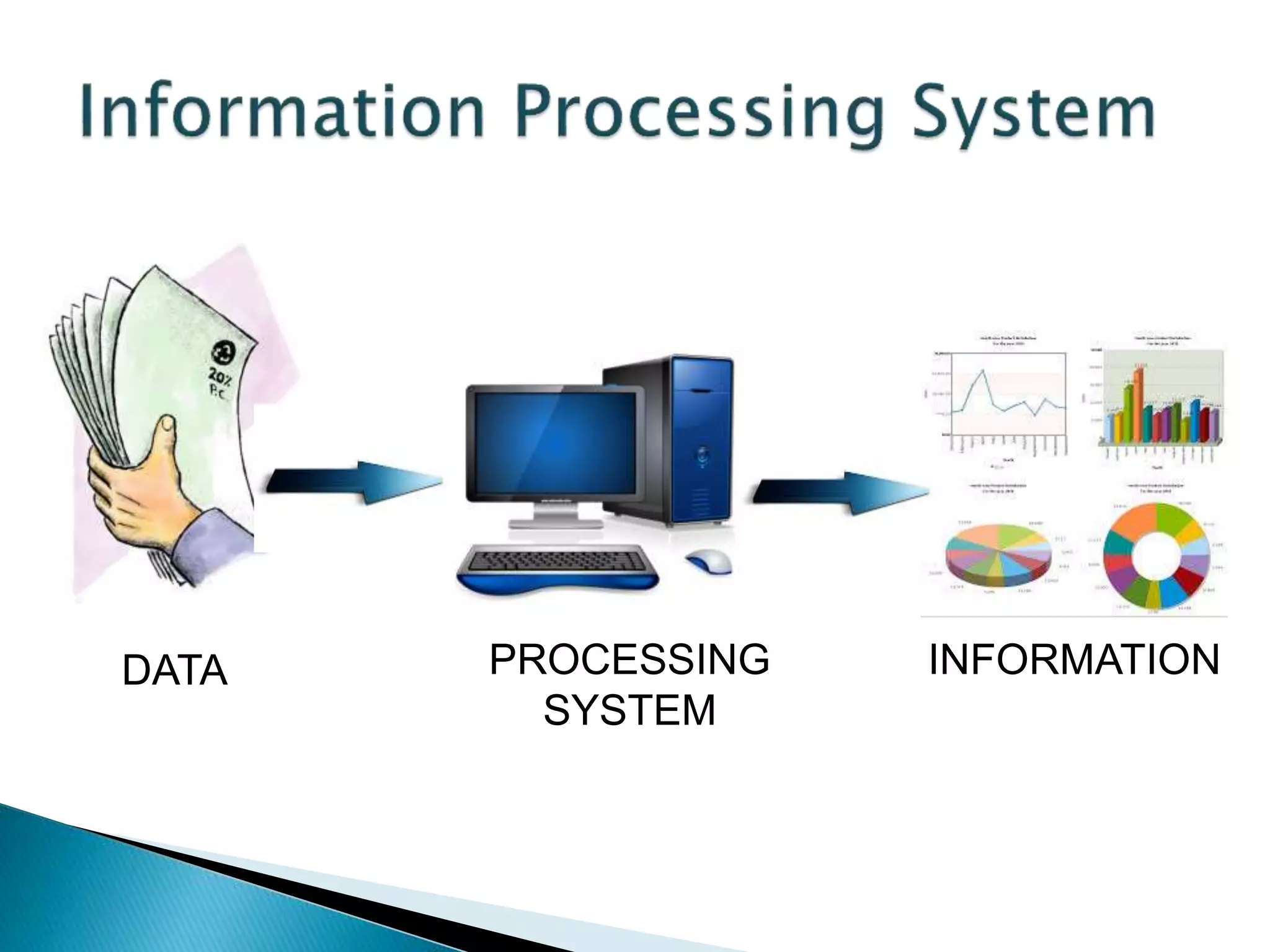
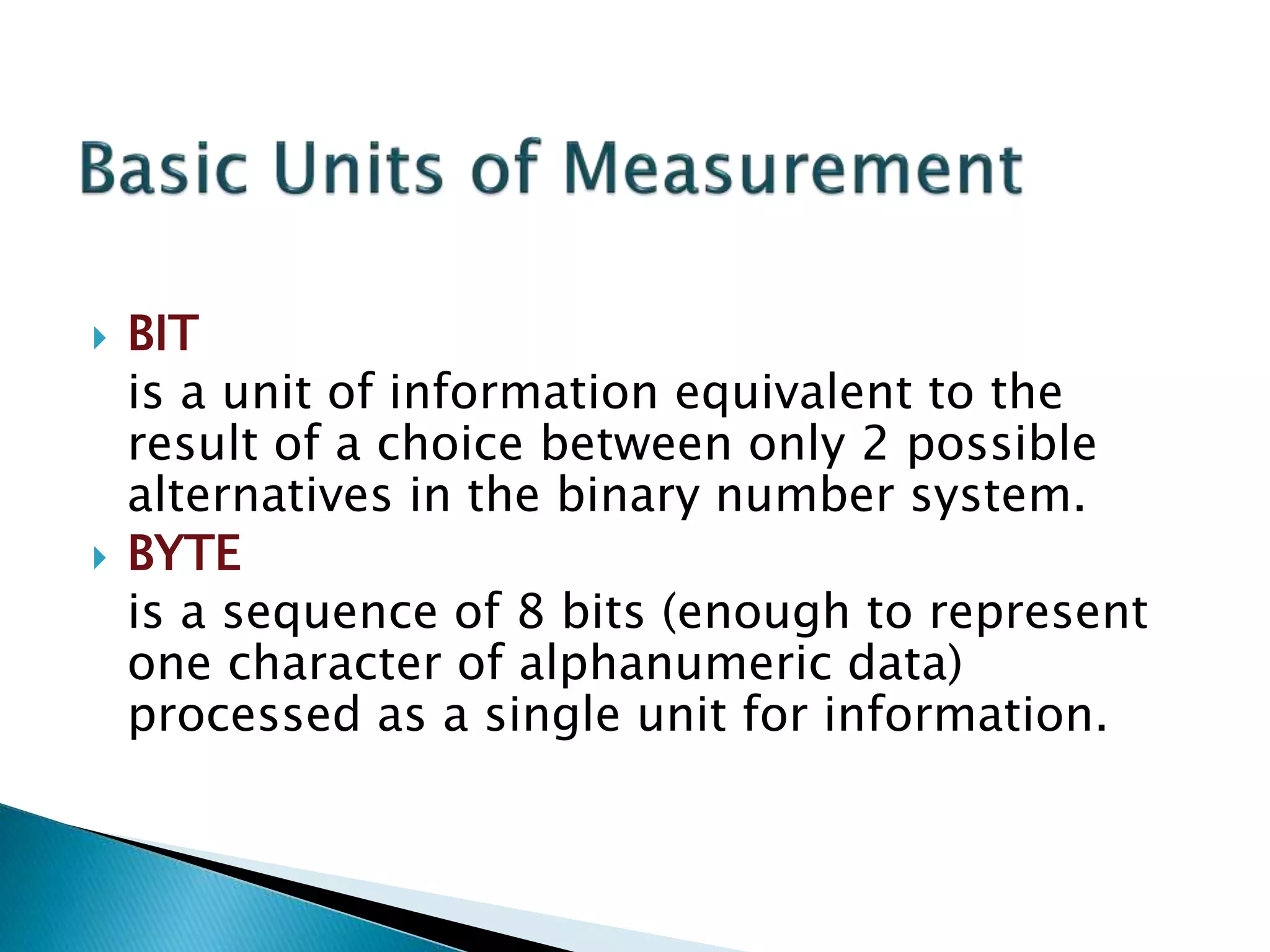
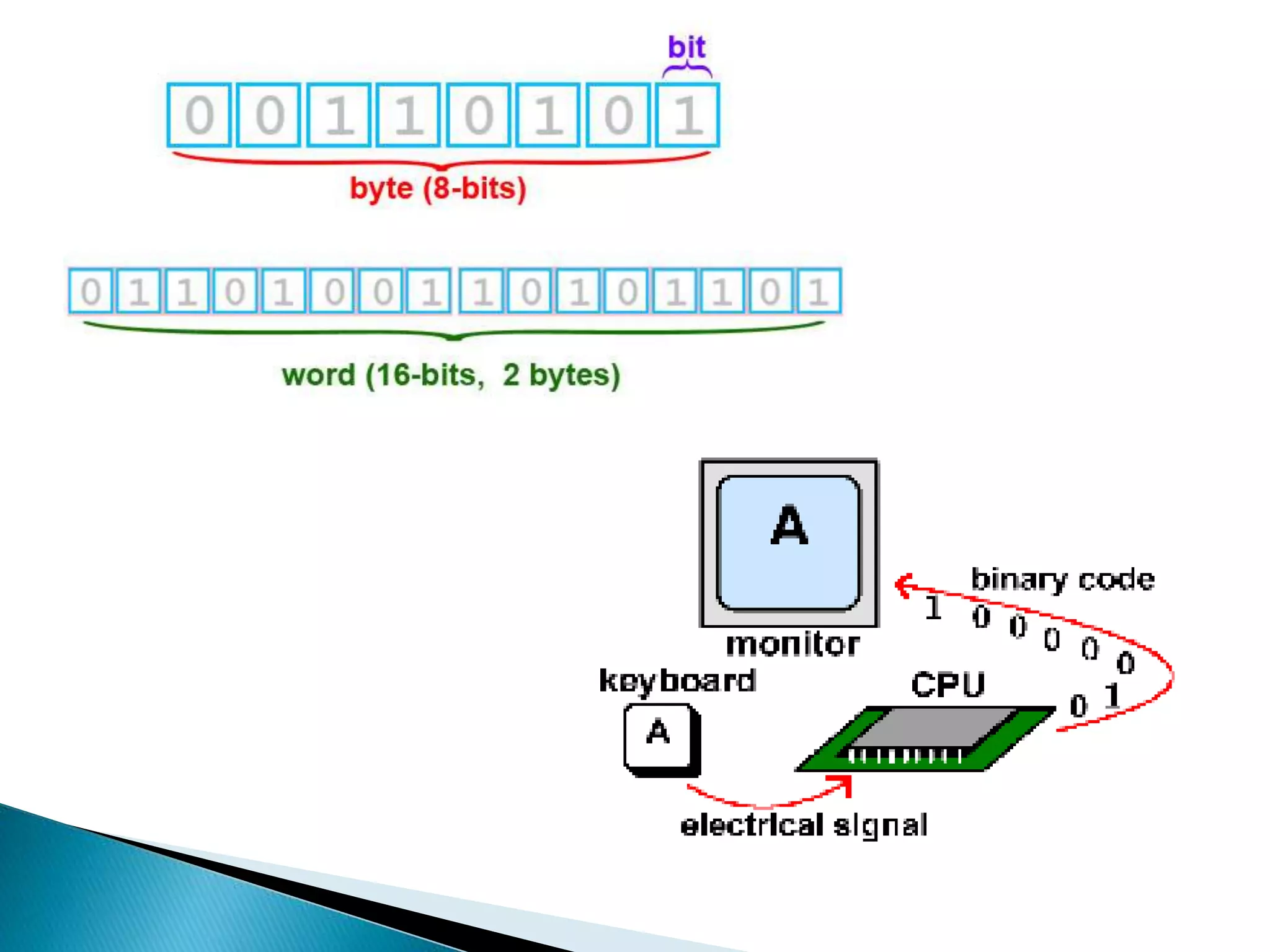
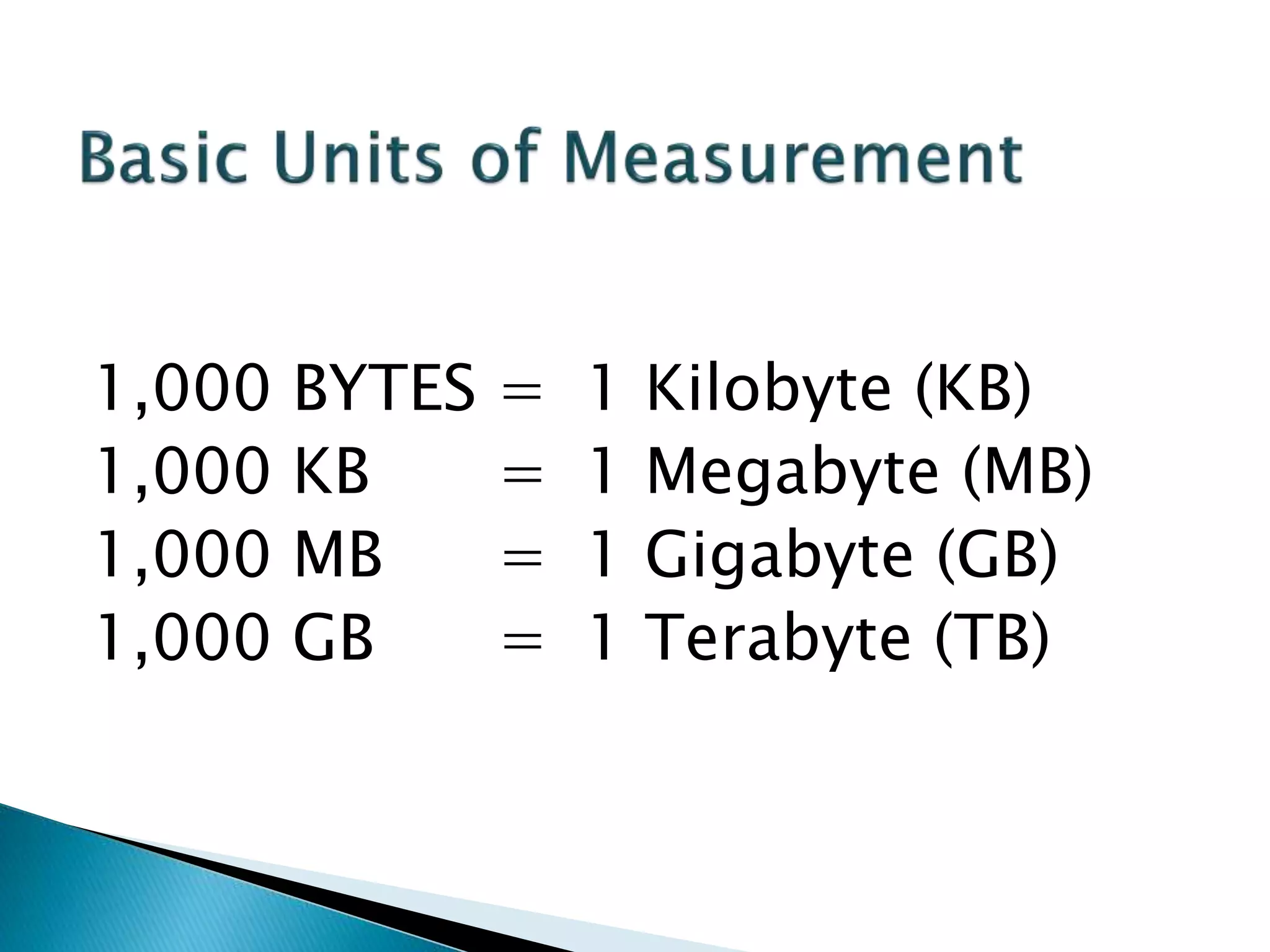
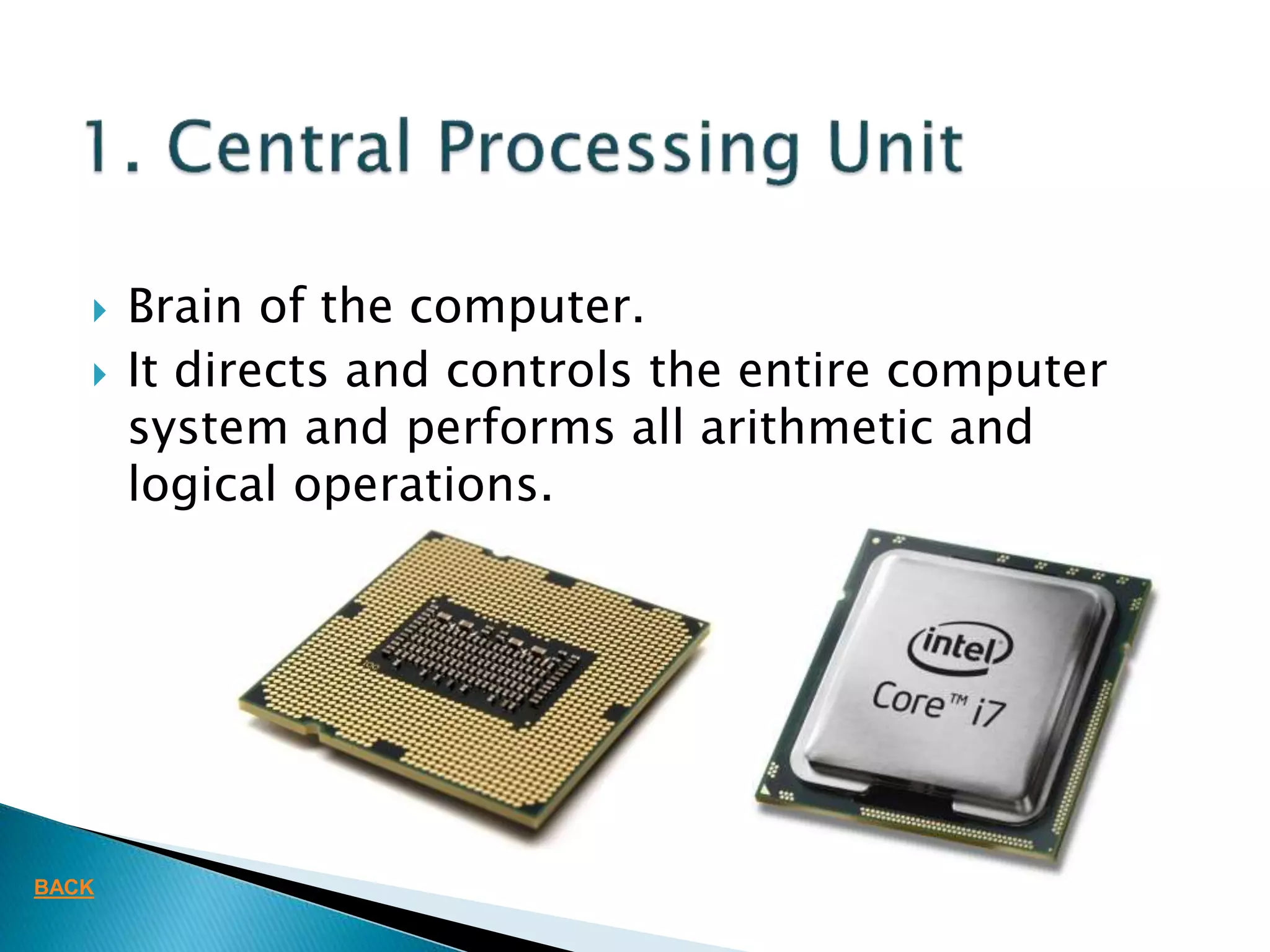
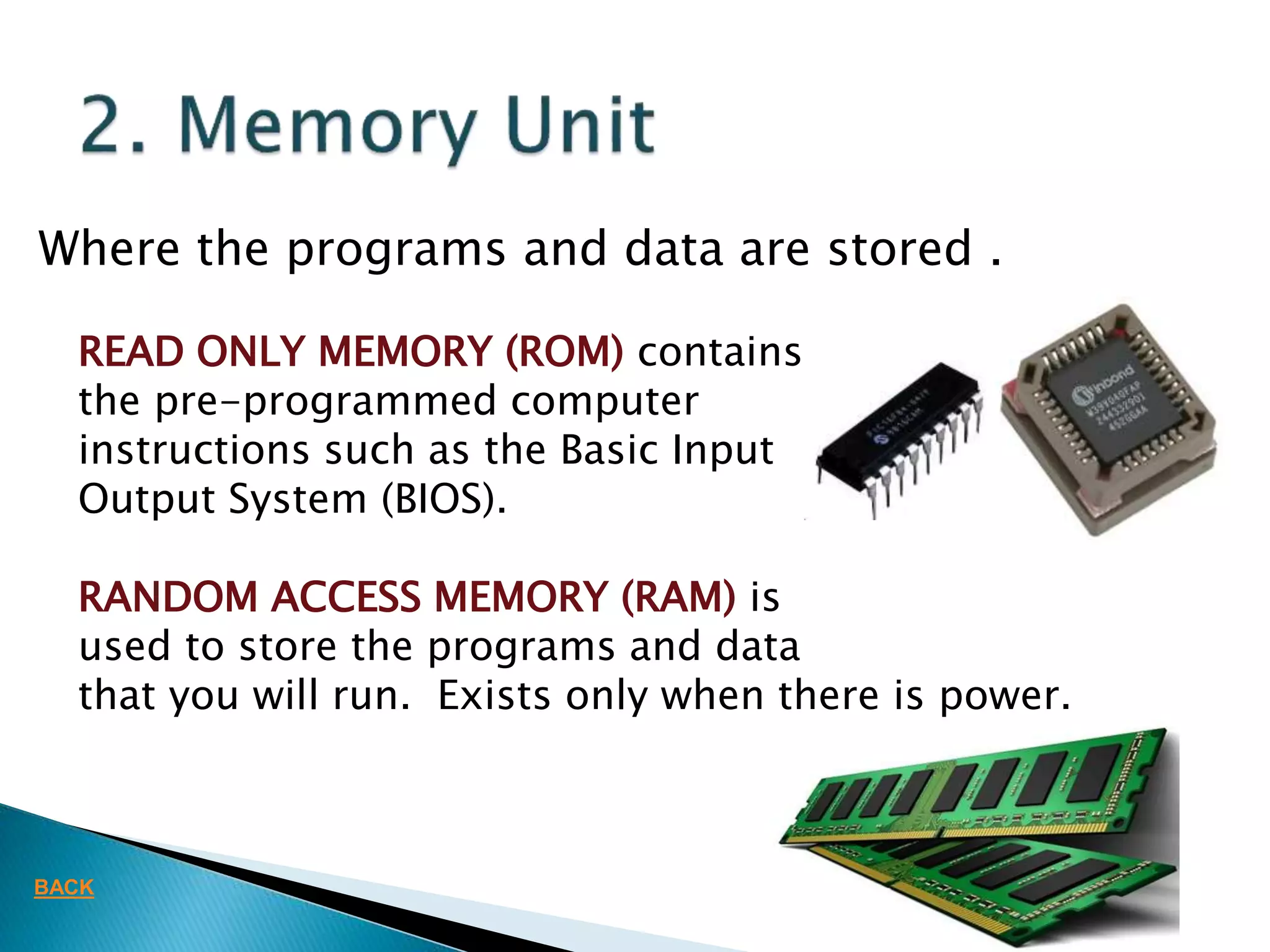
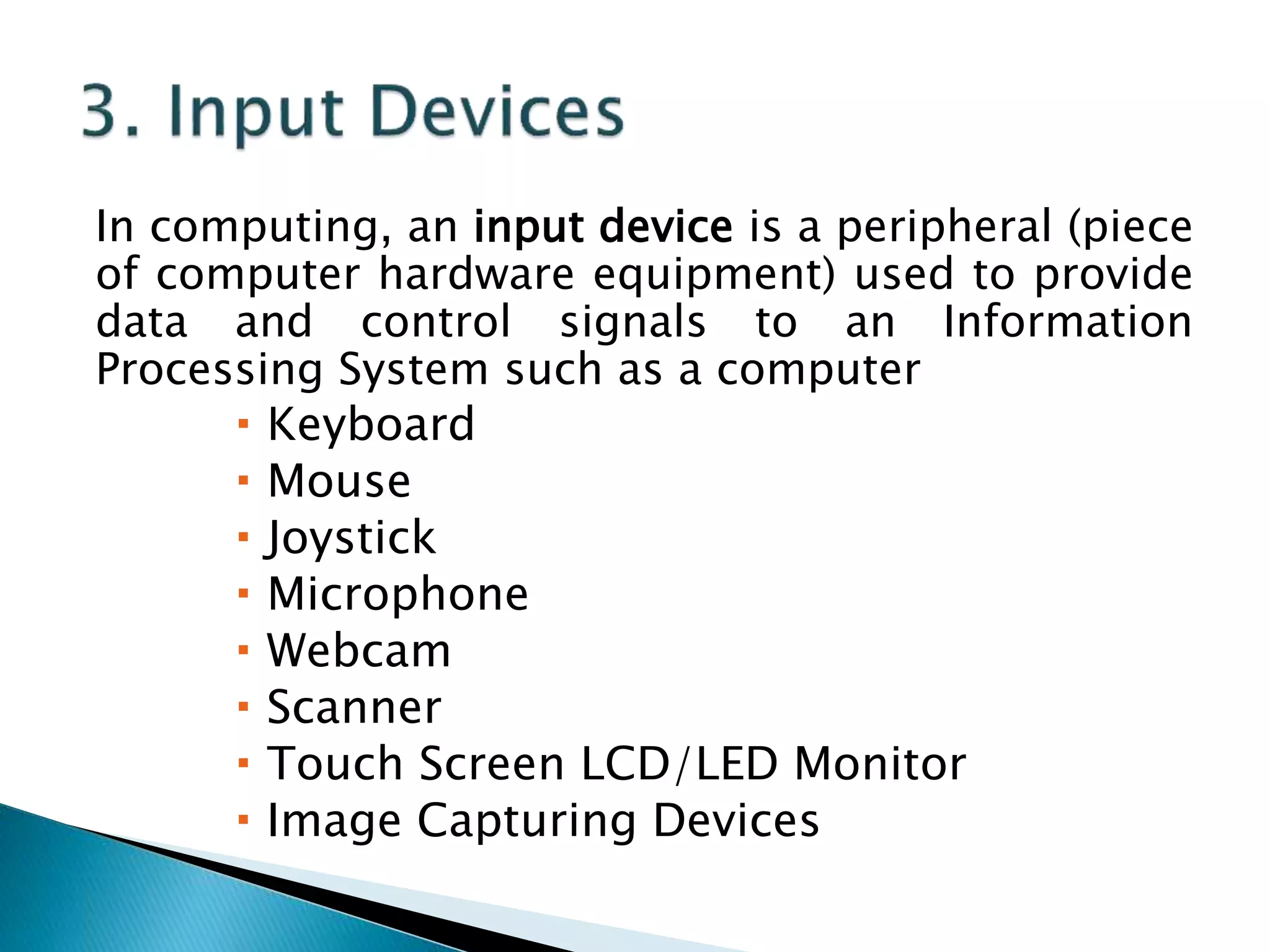
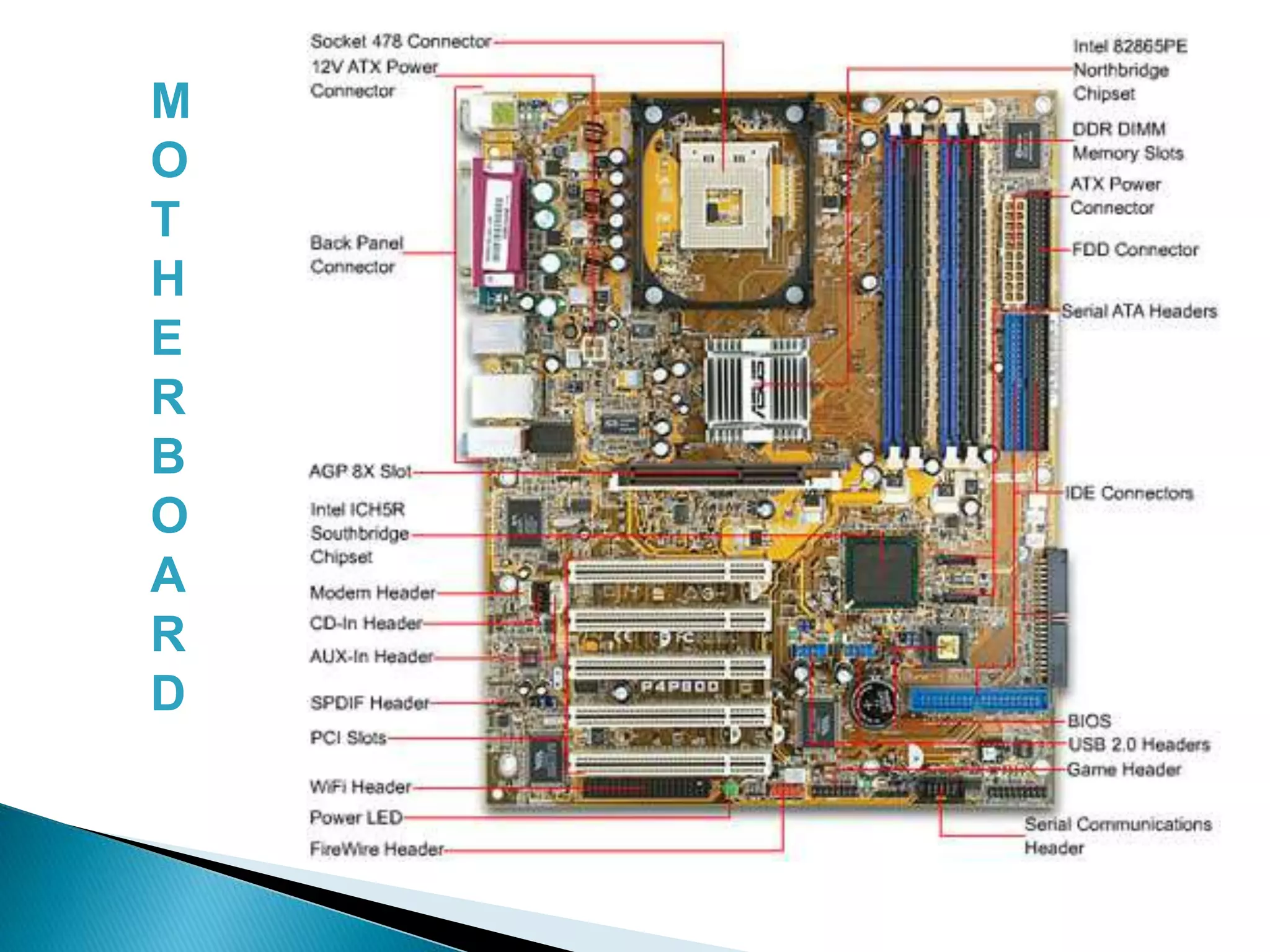
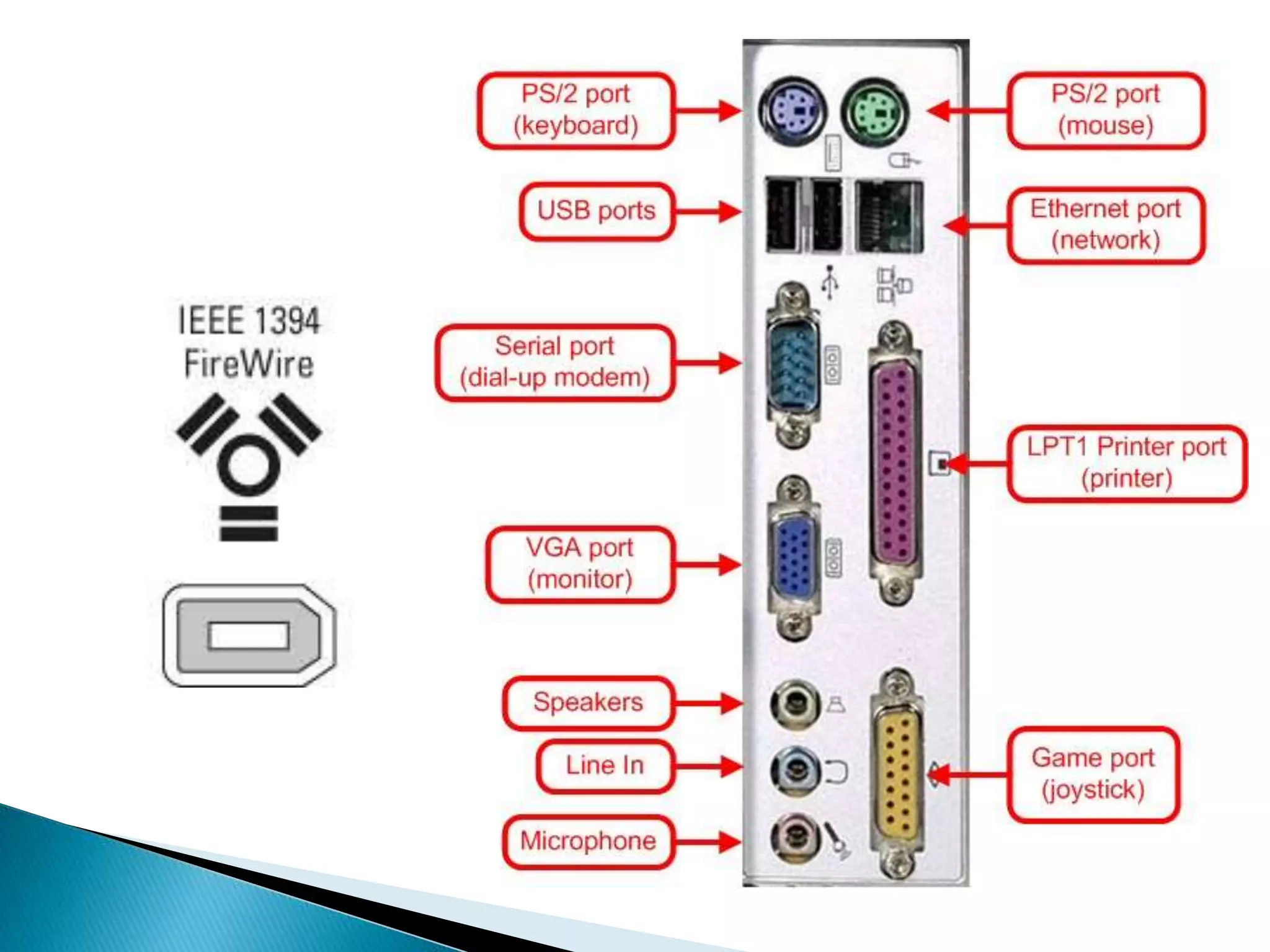
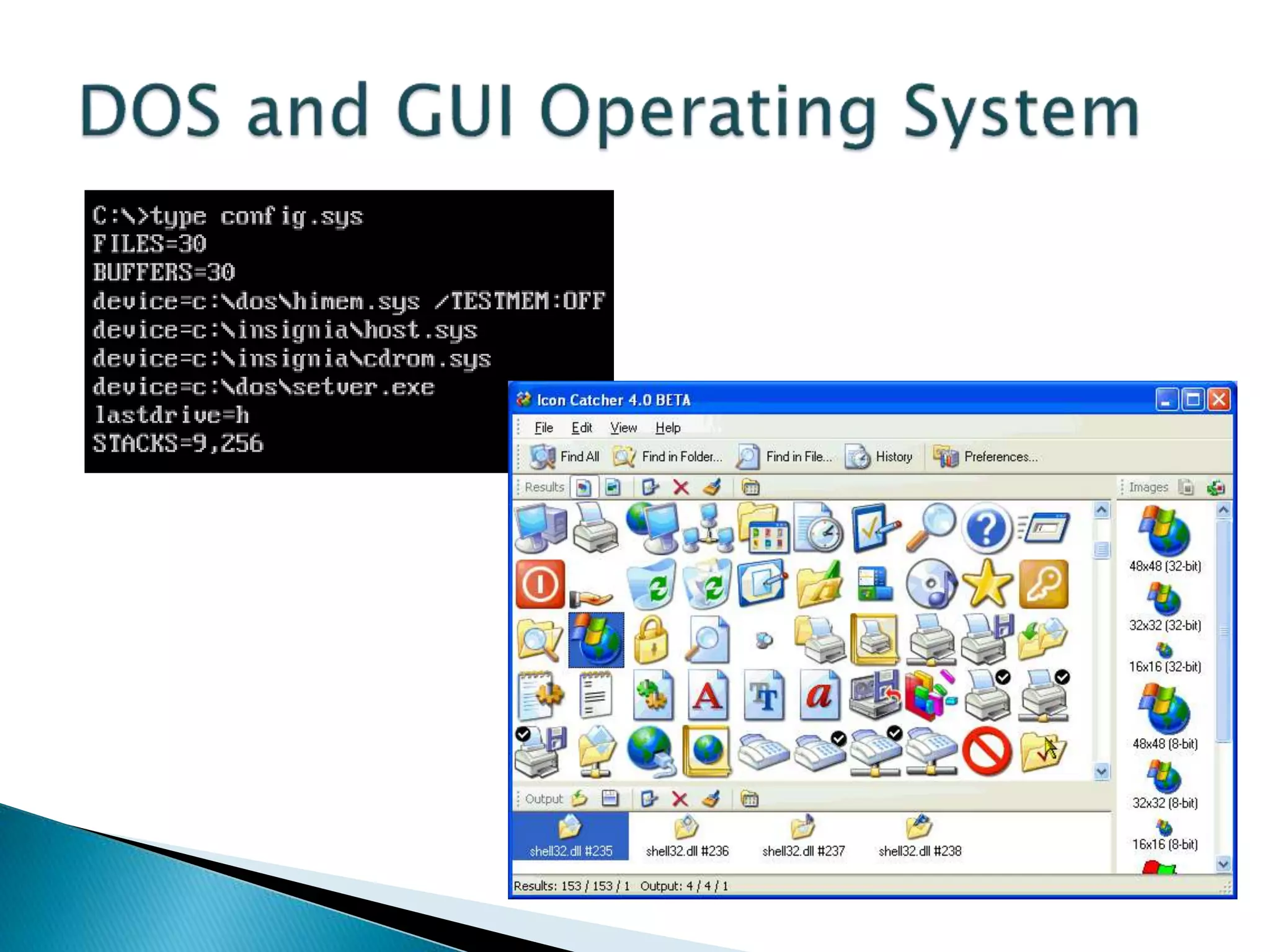
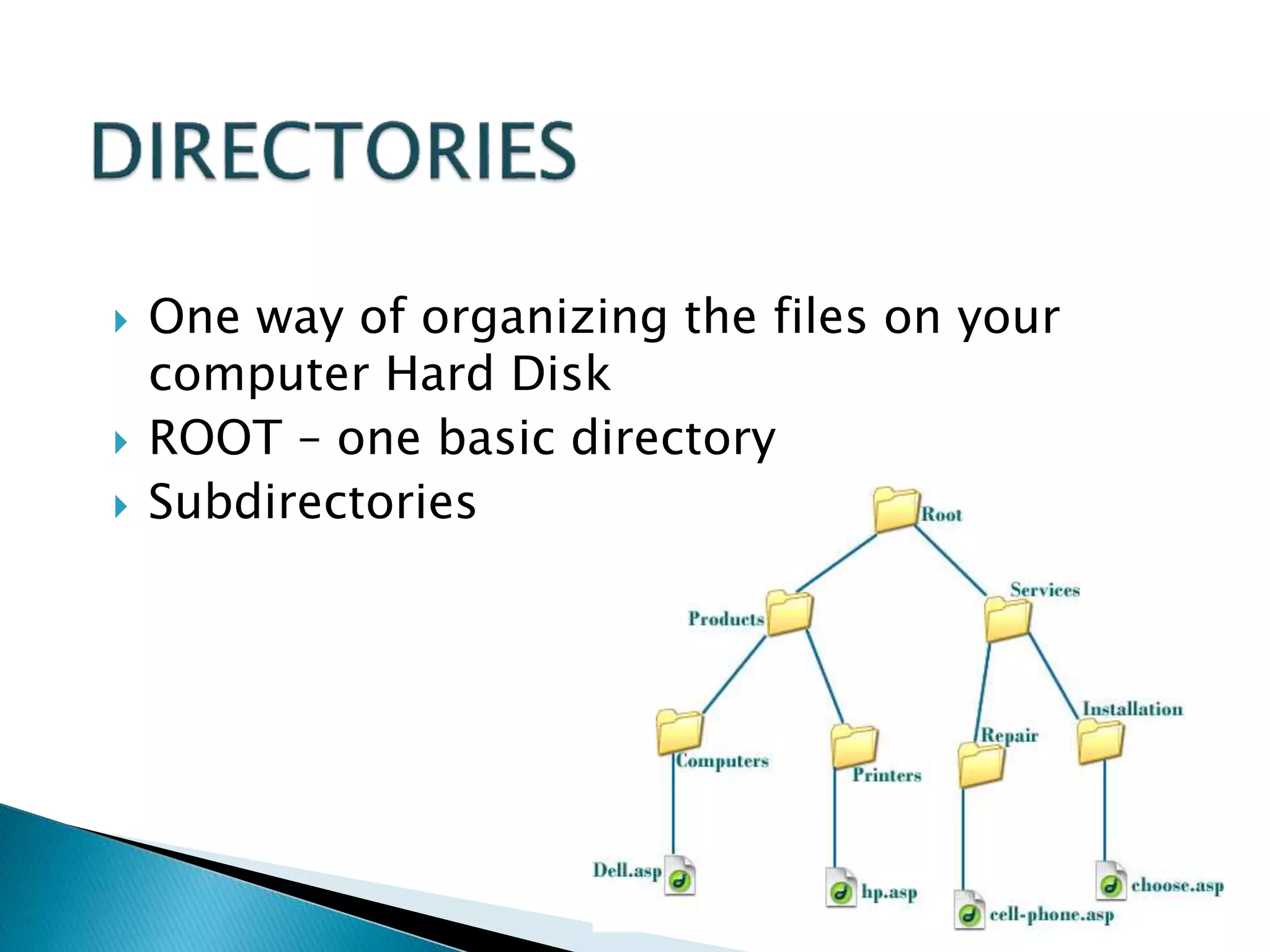
This document defines key concepts related to computers and data processing. It explains that data is raw facts while information is processed data presented meaningfully. Computers accept and process data to transform it into information by following a set of instructions. Hardware refers to tangible computer components while software tells the computer how to operate. The document also outlines different types of computers, data storage units, input/output devices, and other basic computer parts and concepts.