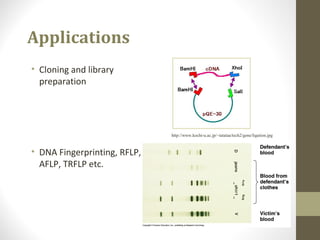
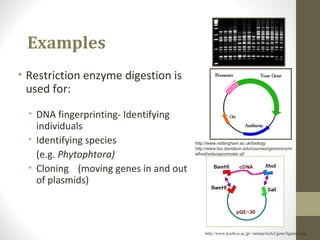
The document discusses the structure and function of DNA, focusing on the role of nucleases, particularly restriction enzymes that cut DNA at specific sequences. It outlines the use of restriction enzymes in applications like cloning, DNA fingerprinting, and genetic analysis. Additionally, it explains digestion procedures, gel electrophoresis for fragment separation, and the distinction between endonucleases and exonucleases.


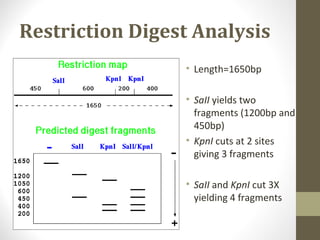
![Restriction Digest Analysis
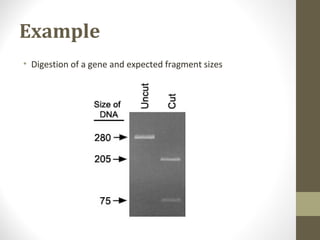
• Aim: the digested fragments must be separated and identified.
• Fragments are separated by agarose gel electrophoresis.
[Agarose is a large polysaccharide].
• Gel electrophoresis: your DNA will move through spaces in
agarose against a current
• DNA has a negative charge and will migrate towards the
cathode](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/restrictiondigestionemachuka-190213133943/85/Restriction-digestion-7-320.jpg)