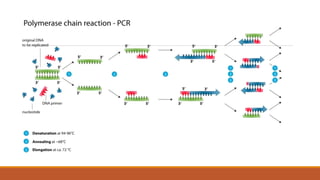
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is an in vitro technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample in the presence of DNA polymerase, primers that flank the target region, and dNTPs. Each cycle doubles the amount of target DNA, exponentially amplifying the target region up to millions of copies. PCR is widely used in medical research, forensics, and other applications to generate numerous copies of a specific DNA segment.



![REQUIREMENTS FOR PCR
DNA TEMPLATE – which contain region to amplify
DNA POLYMERASE – enzyme which synthesizes new dna strands –Taq Polymerase
[heat resistant] from Thermis aquaticus
DNA PRIMER – Intiate DNA synthesis
dNTPs -- deoxynucleotide triphosphates -the building blocks from which the DNA
polymerase synthesizes a new DNA strand
BUFFER SOLUTION -- providing a suitable chemical environment for optimum activity
and stability of the DNA polymerase
BIVALENT CATIONS – mainly Mg or Mn ions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/polymerasechainreaction-190428070106/85/Polymerase-chain-reaction-4-320.jpg)