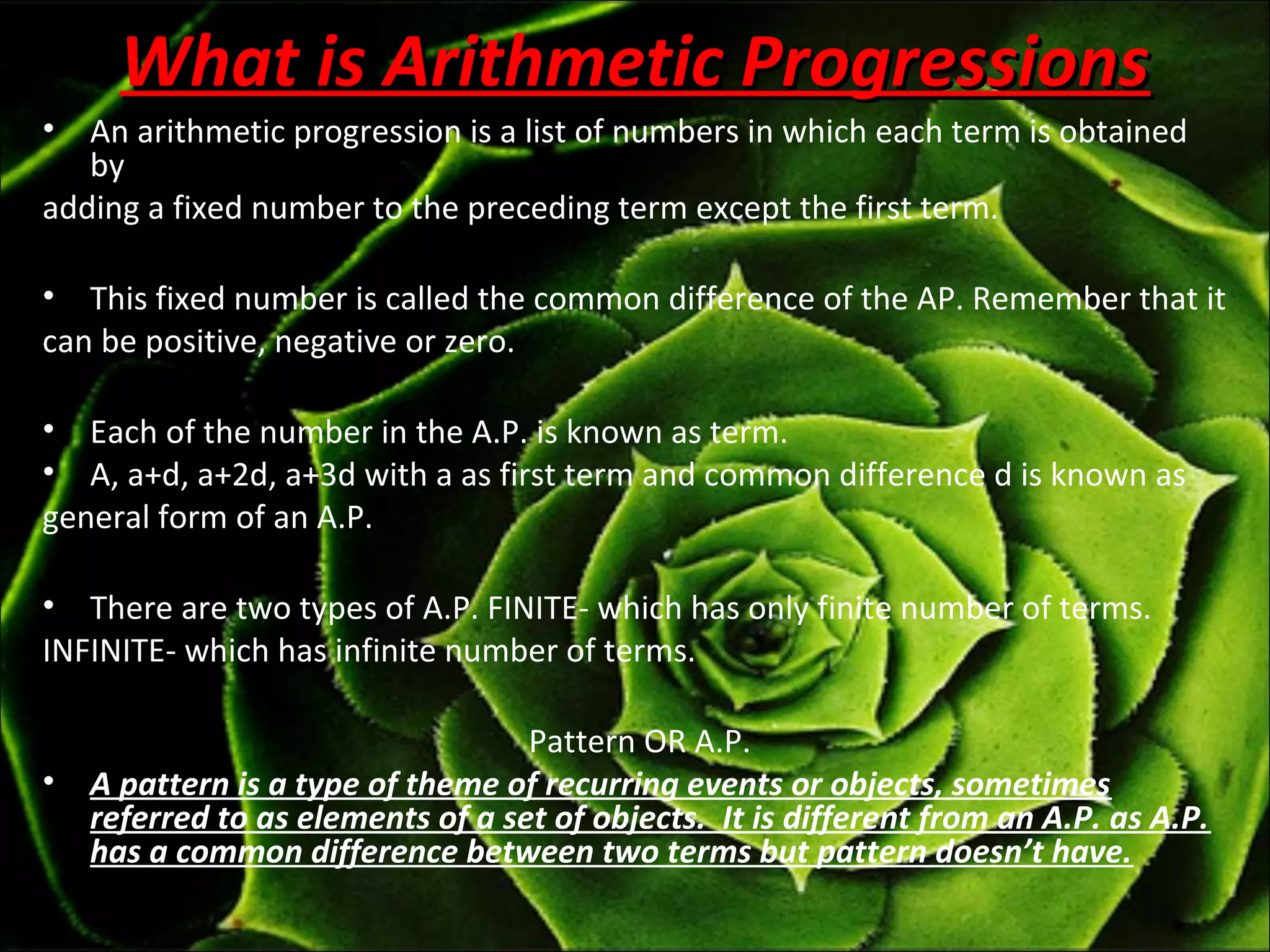
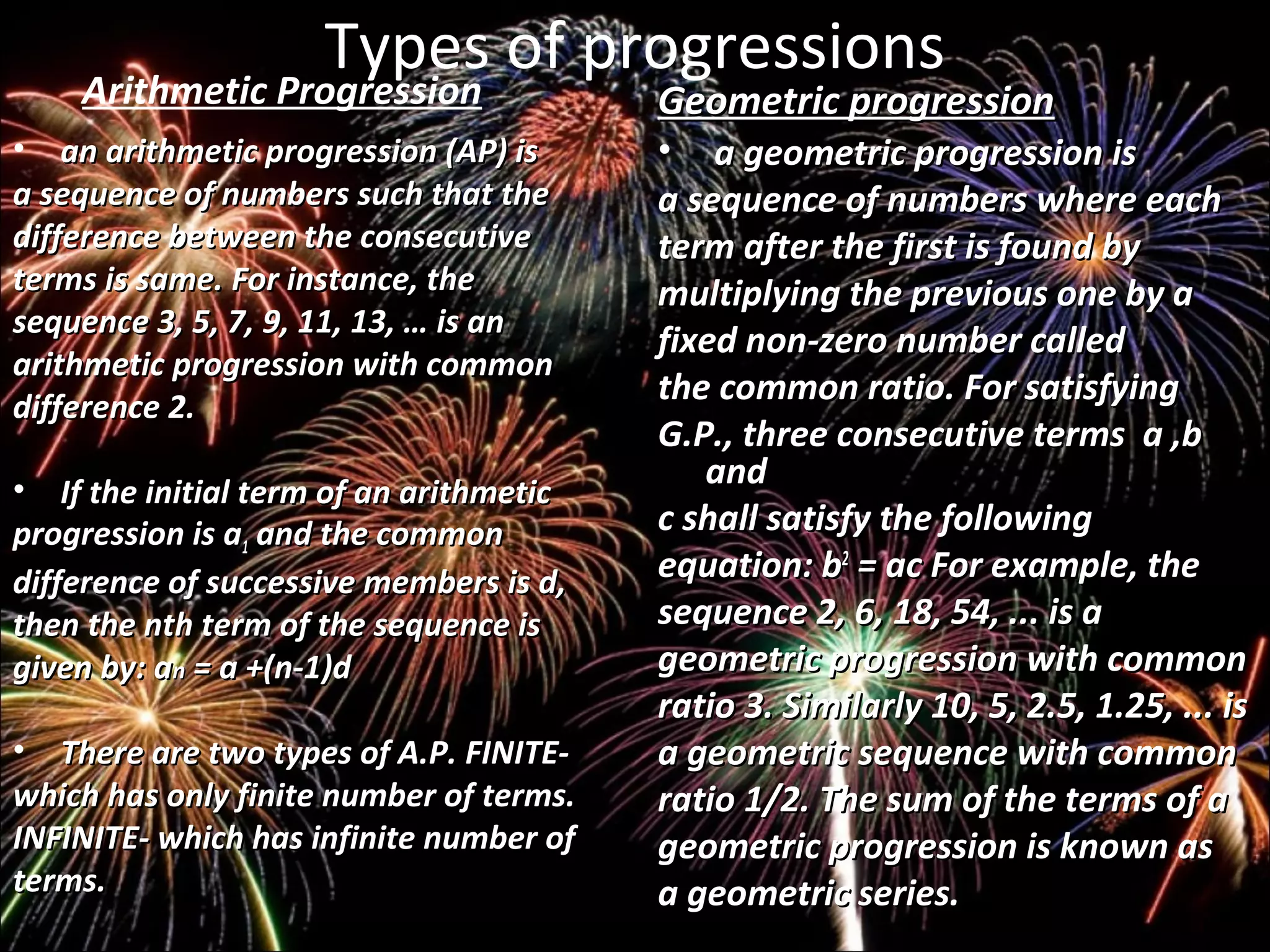
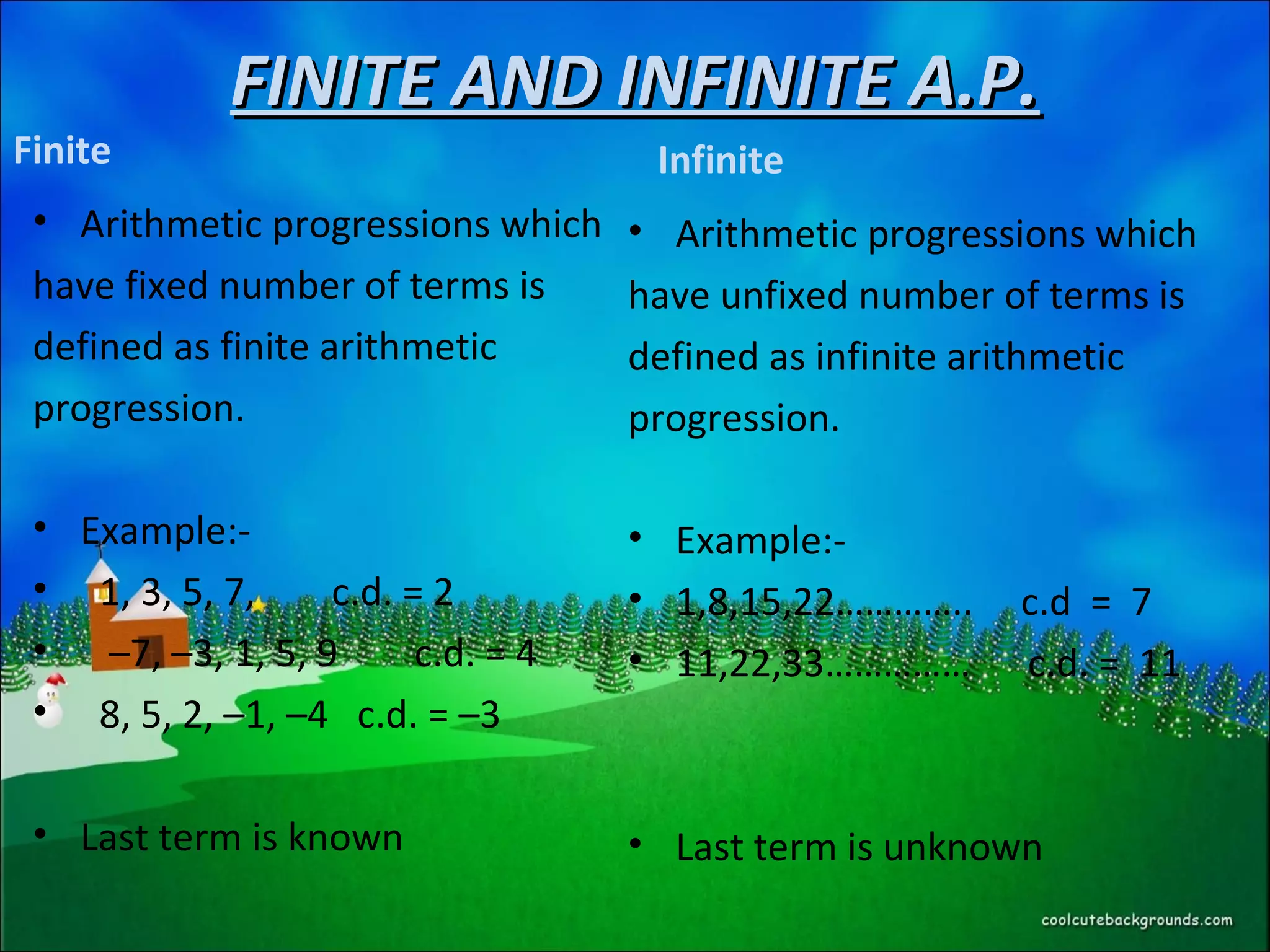
An arithmetic progression is a sequence of numbers where each term after the first is calculated by adding a fixed number, called the common difference, to the previous term. The nth term can be calculated as an = a + (n - 1)d, where a is the first term and d is the common difference. An arithmetic progression can be either finite, with a fixed number of terms, or infinite, with an unlimited number of terms. The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression is given by Sn = n/2(2a + (n-1)d).


![FORMULAS IN THE CHAPTERFORMULAS IN THE CHAPTER
• aan = a +(n-1)dn = a +(n-1)d
• SSn =n/2[2a+(n-1)d]n =n/2[2a+(n-1)d]
OROR
• SSnn= (a+a= (a+ann))
The sum of first n positive integer isThe sum of first n positive integer is
given bygiven by
• ssnn=n(n+1)/2=n(n+1)/2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arthmeticprogression-130822000818-phpapp01/75/CBSE-Class-XI-Maths-Arthmetic-progression-6-2048.jpg)

![Derivation of SDerivation of Snn
S = a + (a + d ) + (a + 2d) + . . . + [a + (n – 1) d ] ............................................... (1)
Rewriting the terms in reverse order, we have
S = [a + (n – 1) d] + [a + (n – 2) d ] + . . . + (a + d) + a ........................................(2)
On adding (1) and (2), term-wise. we get
2S =[2a +(n-1)d] + [2a +(n-1)d] + …….[2a +(n-1)d] + [2a +(n-1)d [n times]
or, 2S = n [2a + (n – 1) d ] (Since, there are n terms)
or, S = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d ]
So, the sum of the first n terms of an AP is given by
S = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d ]
i.e., S =n/2 (a + an ) ………………………………………………………………… (3)
Now, if there are only n terms in an AP, then an = l, the last term. From (3), we see that
S =n/2 (a + l )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arthmeticprogression-130822000818-phpapp01/75/CBSE-Class-XI-Maths-Arthmetic-progression-8-2048.jpg)

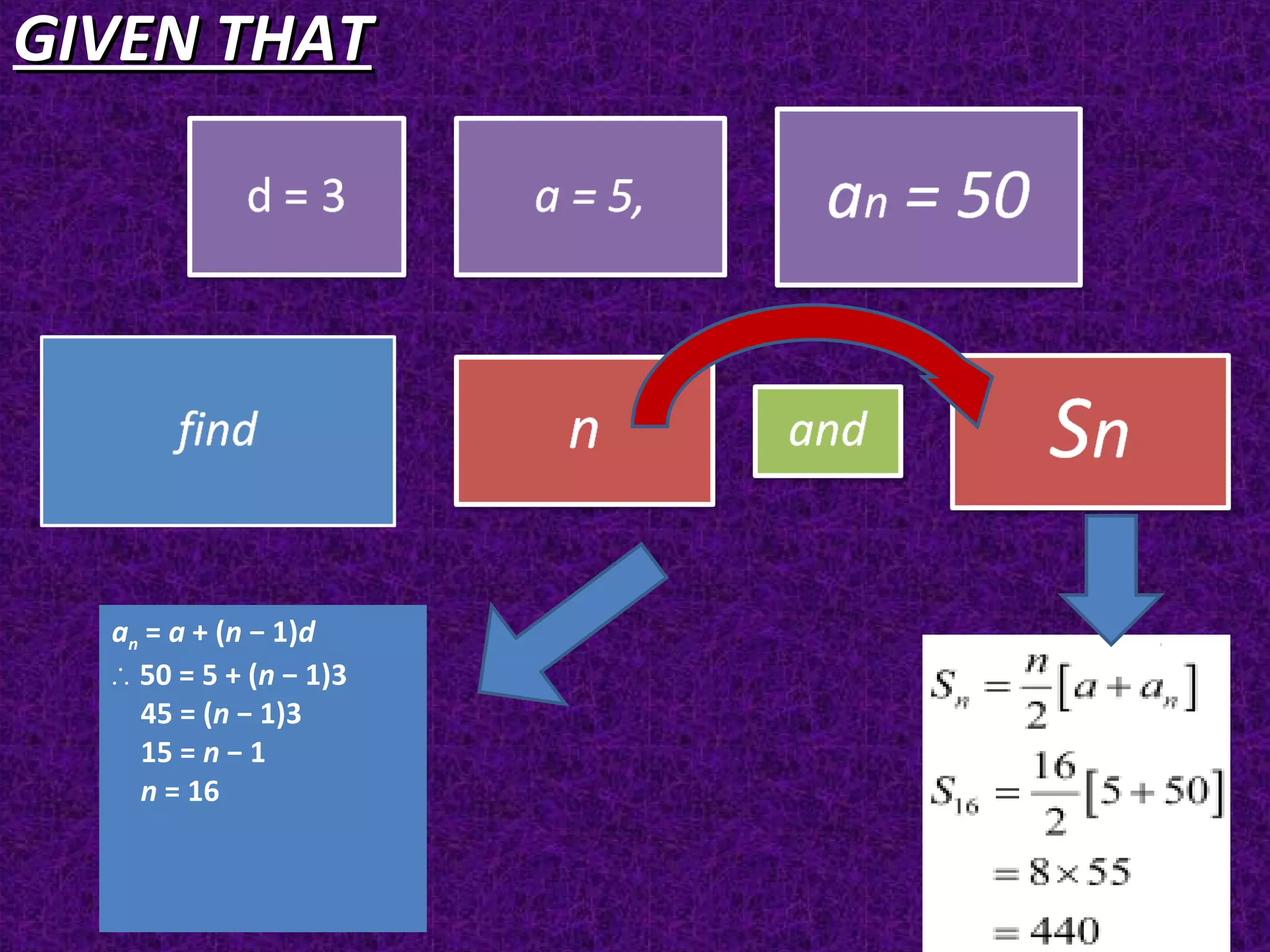
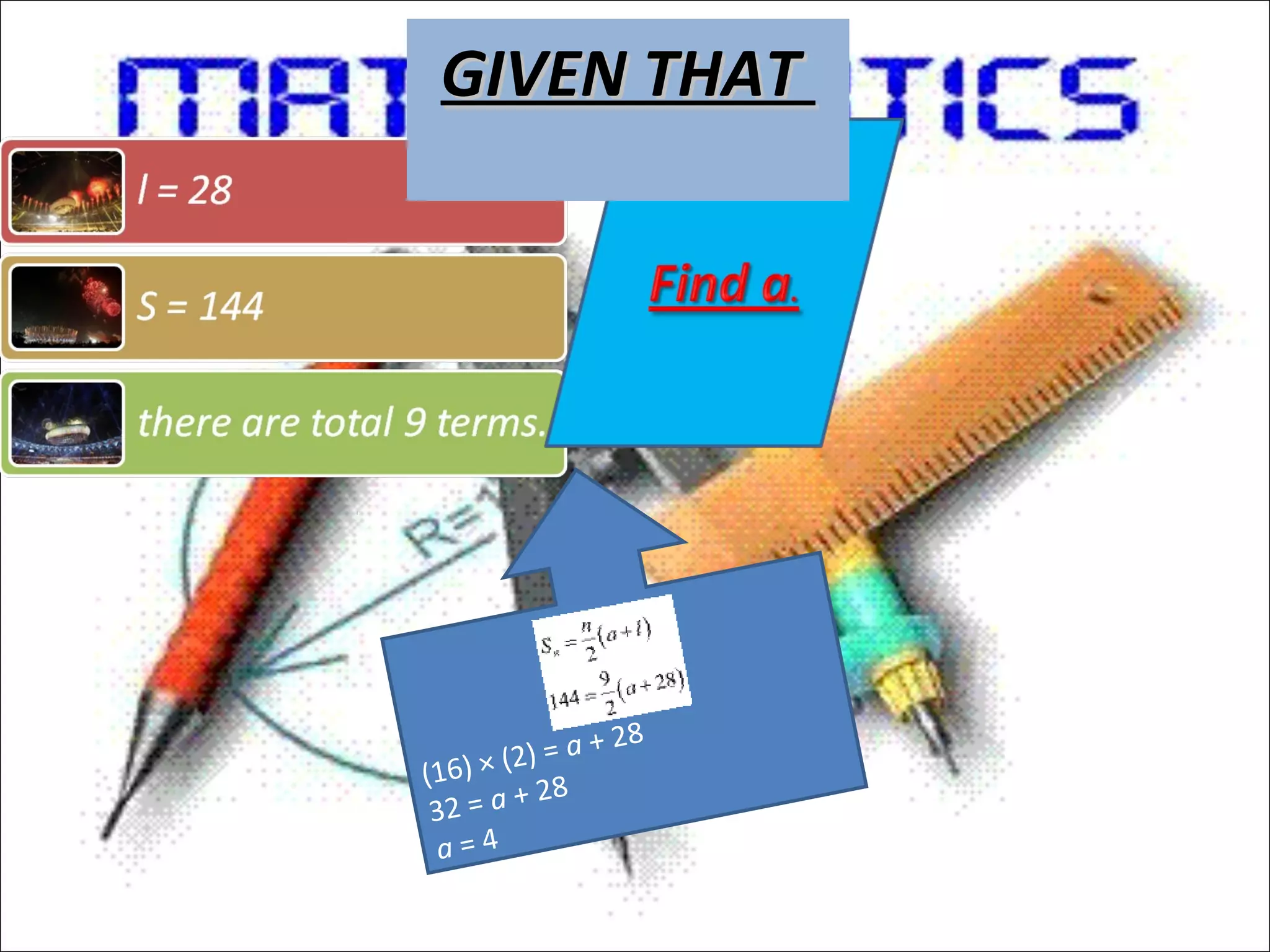
![GIVEN THATGIVEN THAT
find n and an.
90 = n [2 + (n − 1)4]
90 = n [2 + 4n − 4]
90 = n (4n − 2) = 4n2
− 2n
4n2
− 2n − 90 = 0
4n2
− 20n + 18n − 90 = 0
4n (n − 5) + 18 (n − 5) = 0
(n − 5) (4n + 18) = 0
Either n − 5 = 0 or 4n + 18 =
0
n = 5 or
However, n can neither be
negative nor fractional.
Therefore, n = 5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arthmeticprogression-130822000818-phpapp01/75/CBSE-Class-XI-Maths-Arthmetic-progression-12-2048.jpg)
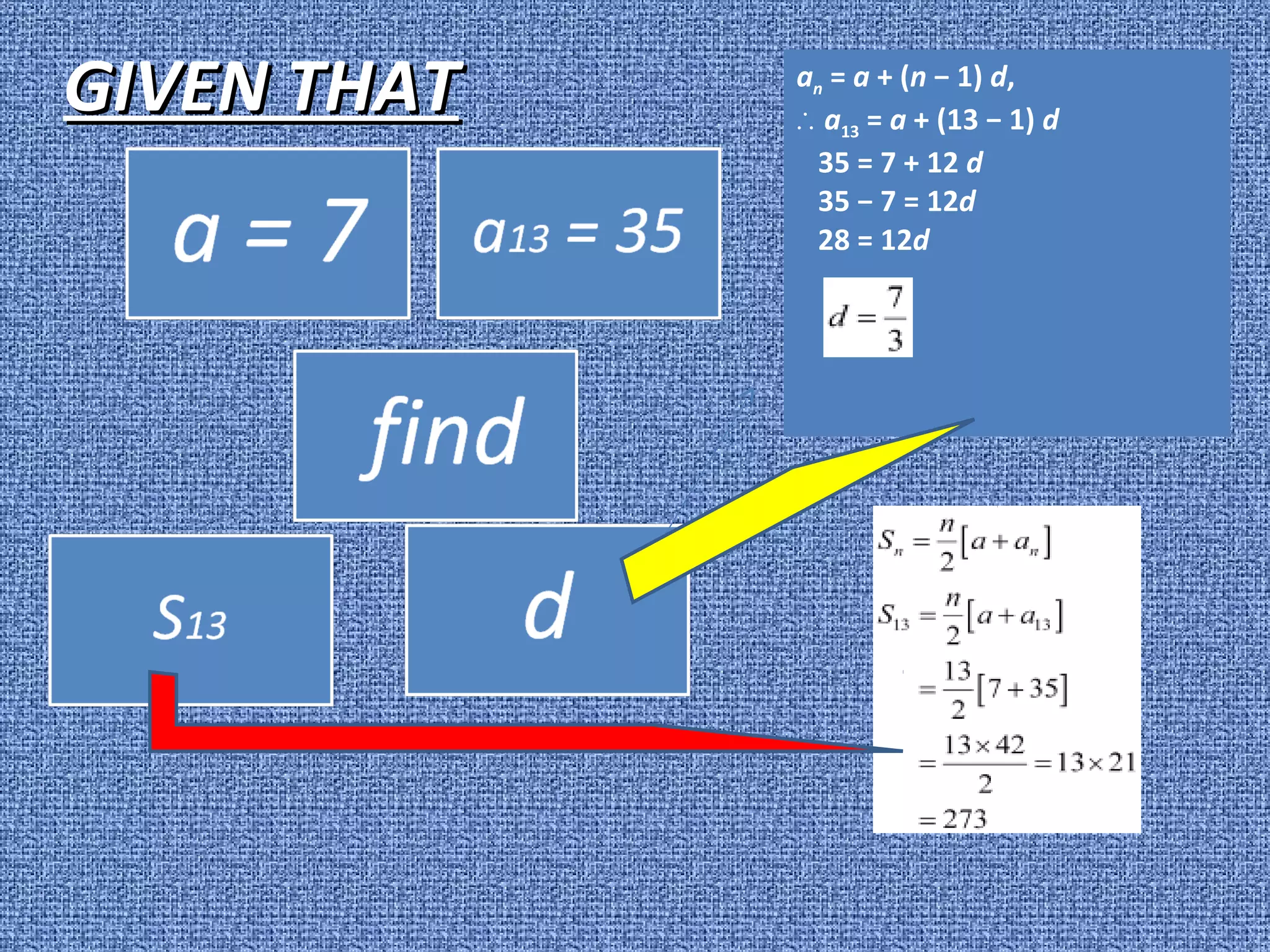
![a = 3
n = 8
S = 192
a = 3
n = 8
S = 192
as 192 = 4 [6 + 7d]
48 = 6 + 7d
42 = 7d
d = 6
Find
d
GIVEN THAT
GIVEN THAT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arthmeticprogression-130822000818-phpapp01/75/CBSE-Class-XI-Maths-Arthmetic-progression-13-2048.jpg)