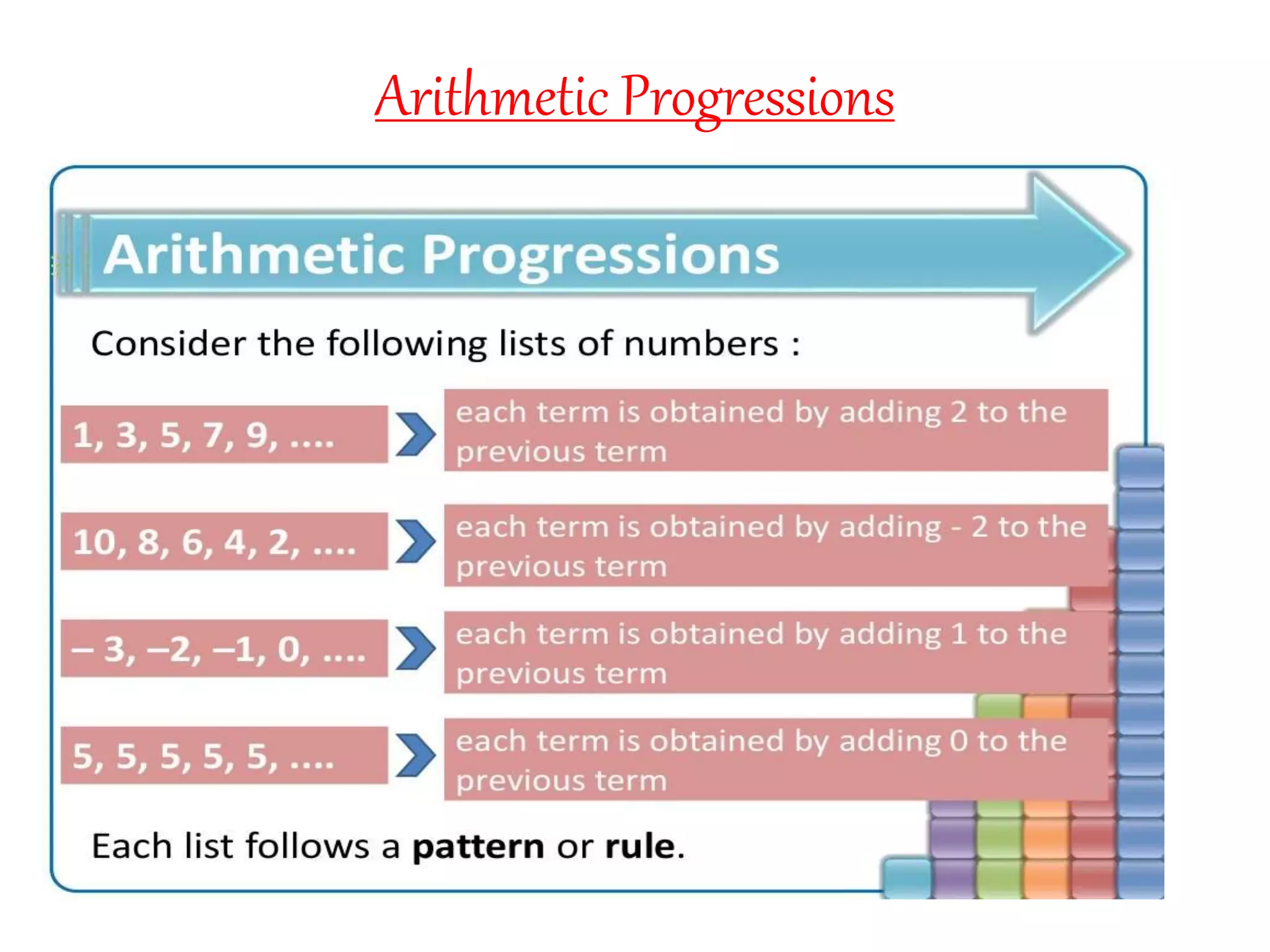
The document defines arithmetic progressions and provides examples. Some key points:
- An arithmetic progression is a list of numbers where each term is obtained by adding a fixed number (called the common difference) to the preceding term.
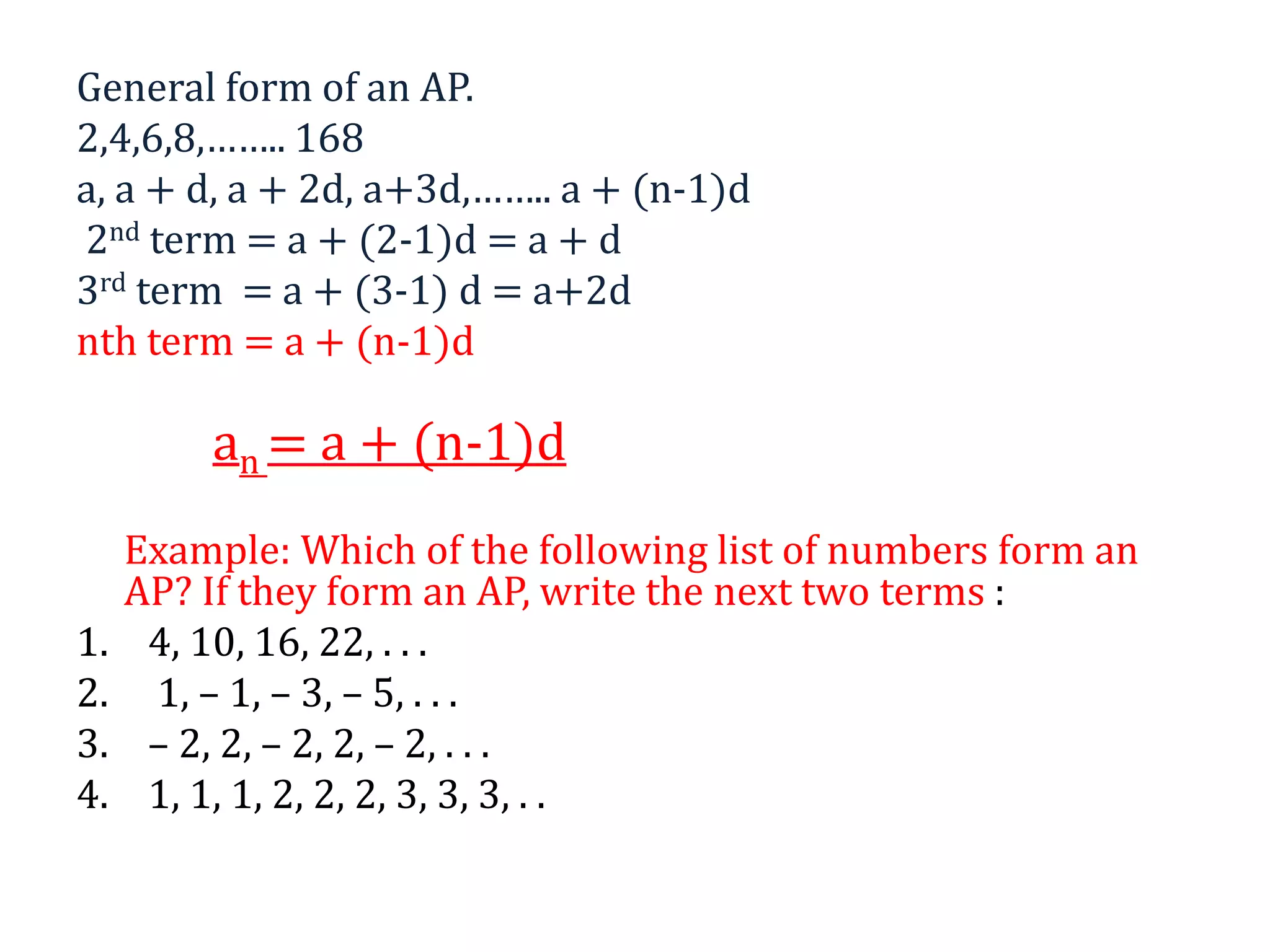
- The general formula for the nth term of an AP is an = a + (n-1)d, where a is the first term and d is the common difference.
- Examples show how to determine if a list of numbers forms an AP, write the next terms, and find a specific term by using the general formula.
- There are finite APs, which have a last term, and infinite APs, which go on forever without a last term.



![Types of AP
• There are two types of AP, they are
a) Finite AP:
the series of the numbers are having finite
terms.[ these are having last term i.e. an]
Exa: 3,6,9,…….., 42
b) Infinite AP:
the series of the numbers are having infinite
terms/ no last term
Exa: 3,6,9,……………., am
an is also called the general term of the AP. If there
are m terms in the AP, then
am represents the last term which is sometimes also
denoted by l.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-6-2048.jpg)

![4. Which term of the AP : 21, 18, 15, . . . is – 81? Also, is any
term 0? Give reason for your answer.
Ans. Here, a = 21, d = 18 – 21 = -3 and an = - 81.
We have an = a + (n – 1) d
- 81 = 21 + (n-1)-3
- 81= 21 - 3n + 3
- 81 = 24 - 3n
- 81 – 24 = - 3n
- 3n = - 105
n = 35
Therefore, the 35th term of the given AP is – 81.
Next, we want to know if there is any n for which an = 0. If
such an n is there, then
21 + (n – 1) (–3) = 0,
i.e., 3(n – 1) = 21 [ 3n – 3 = 21]
i.e., n = 8
So, the 8th term of AP is 0.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-8-2048.jpg)
![4. Determine the AP whose 3rd term is 5 and the 7th term is 9.
Solution : We have
a3 = a + (3 – 1) d = 5
a + 2d = 5 (1)
And a7 = a + (7 – 1) d =
a + 6d = 9 (2)
By subtracting equation number 2 from 1, we get
a + 6d = 9
- [a + 2d = 5]
--------------
4d = 4 => d = 1
By equation 1, we get a + 2d = 5
a + 2 x 1 = 5 => a = 5 – 2 => a = 3
Therefor AP : 3, 4,5,6,......
5. Find the 31st term of an AP whose 11th term is 38
and the 16th term is 73.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-9-2048.jpg)
![Exa. 6. Check whether 301 is a term of the list of numbers 5, 11, 17, 23,…..,
Exa. 7. How many two-digit numbers are divisible by 3?
Exa. 8. Find the 11th term from the last term (towards the first term)
of the AP : 10, 7, 4, . . ., – 62.
Ans. Here, a = 10, d = 7 – 10 = – 3, l = – 62,
Since we need to find last 11th term
-62, -59, -56, …….. 10 [ reverse form of AP]
a = - 62, d = 3 and n = 11
11th term of AP
a11 = a + (n – 1 ) d
a11 = -62 + (11-1)3
= - 62 + 10 x 3
= - 62 + 30
= - 32
Therefore the 11th term of AP is - 32 .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-10-2048.jpg)

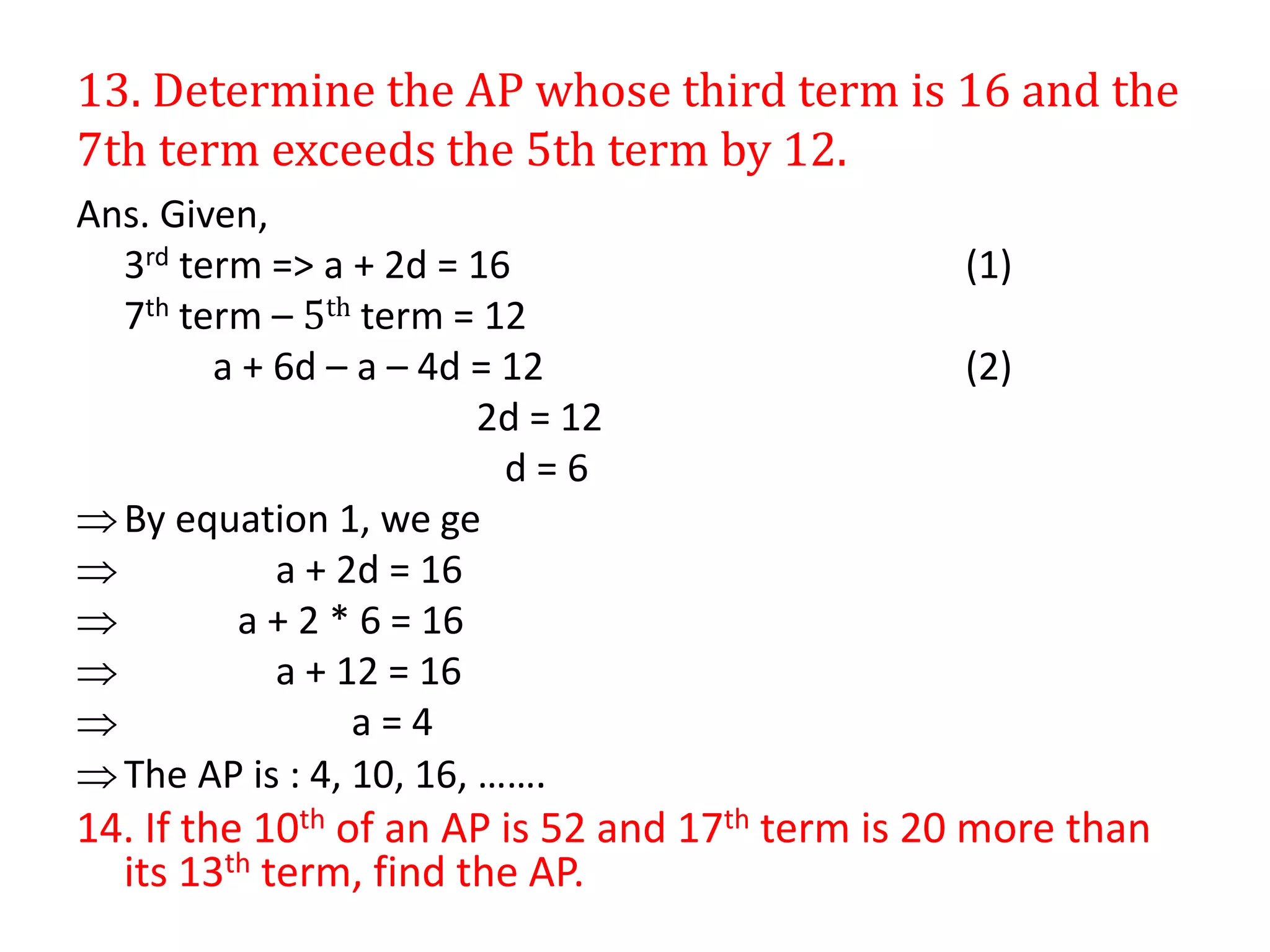


![27. Find four terms of AP whose sum is 28 and the sum of whose
square is 216.
Ans. Given,
Sum of four terms: (a-3d) + (a-d) + (a+d) + (a+3d) = 28
a-3d + a-d+ a+d + a - 3d = 28
4a= 28
a = 7
The sum of whose squares are = 216
(a-3d)2 + (a-d)2 + (a+d)2 + (a+3d)2 = 216
[a2 + 9d2 – 6ad] + [a2 +d2 – 2ad] + [a2 + 9d2 +6ad] + [a2 +d2 + 2ad] = 216
4a2+ 20d2 = 216
4 *49 + 20 d2 = 216
196 + 20 d2 = 216
20 d2 = 20
d2 = 1 => d = 1
Therefore the 4 terms of AP is : 4, 6, 8, 10, ……..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-18-2048.jpg)

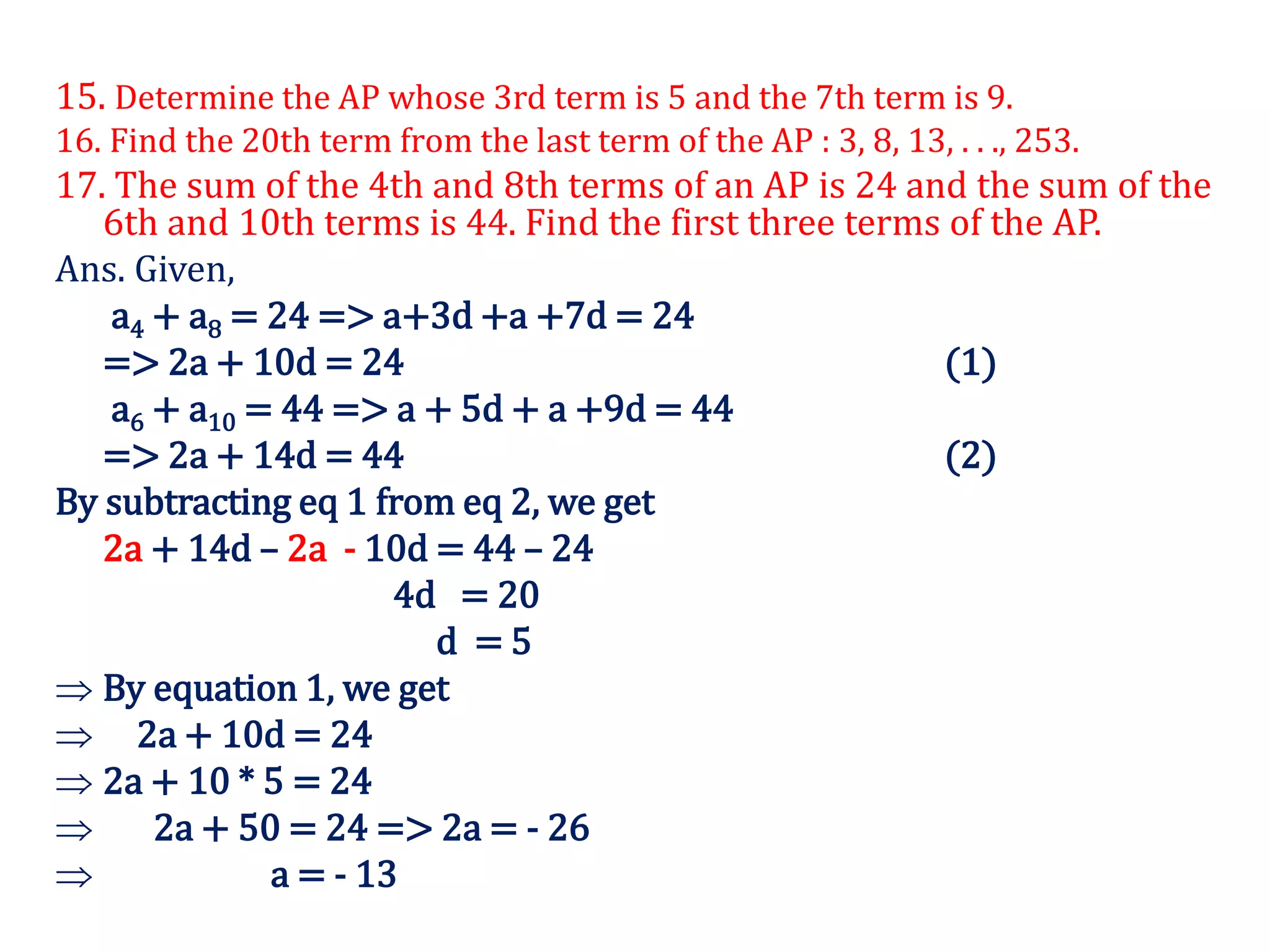
![32. The sum first three terms of an AP is 48. if the product of
first and second terms exceeds 4 times the third term by 12.
Find the AP.
Ans. Given
First three terms of AP = a-d, a, a+d
=> a-d+a+a+d = 48
=> 3a = 48
=> a = 16
[a-d]a – 4 [a+d] = 12
=> a^2 – ad – 4a – 4d = 12
=> 256 – 16d – 64– 4d = 12
=> 192 – 20d = 12
=> - 20 d = 12 - 192
=> - 20 d = - 180
=> d= 9
Therefore the three term are = 7, 16, 25.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-20-2048.jpg)

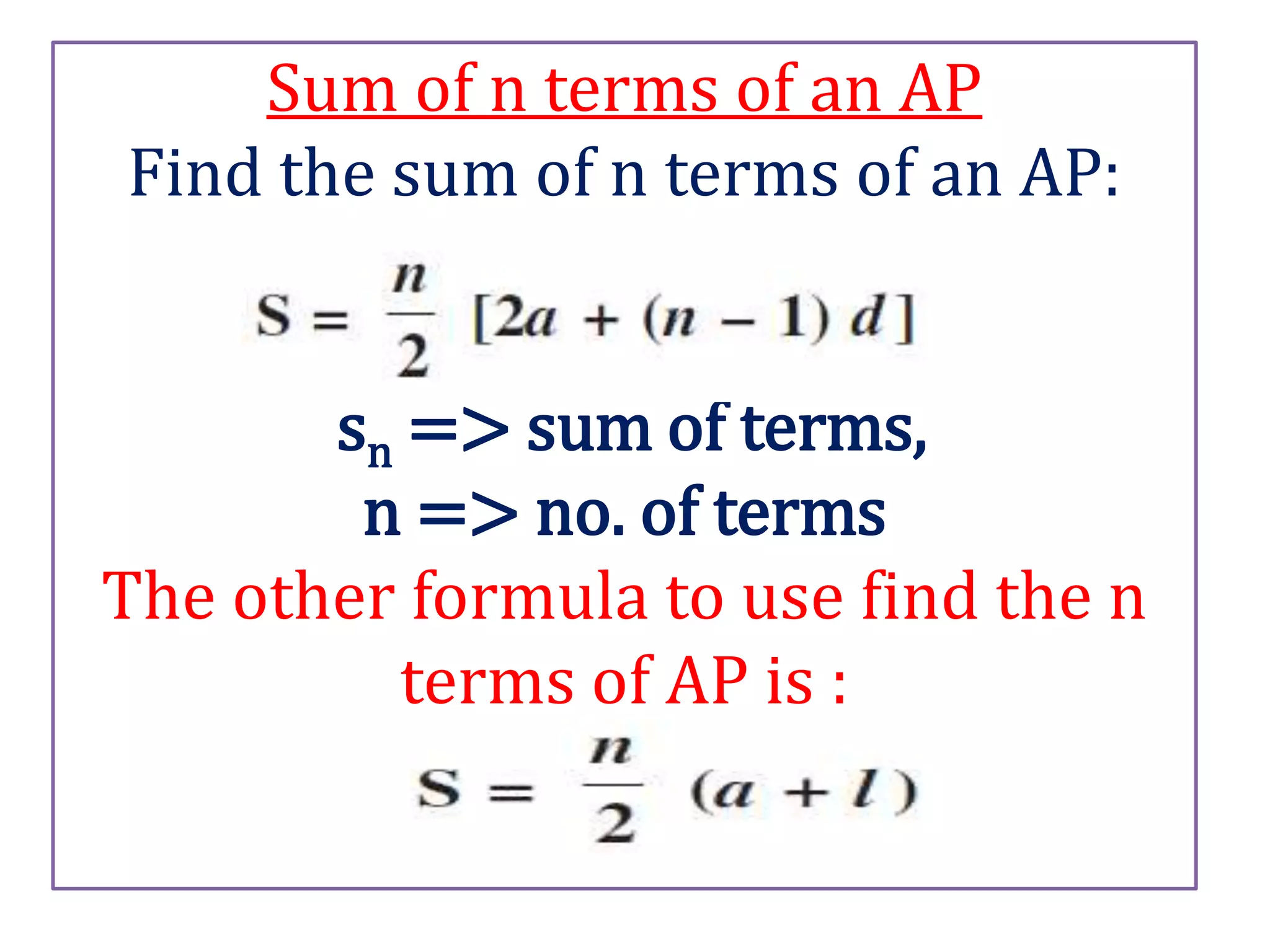
![3. Find the sum of first 24 terms of the list of
numbers whose nth term is given by an = 3 + 2n.
Ans. Given
an = 3 + 2n
a1 = 3 + 2 => a1 = 5
a2 = 3 + 2*2 => a1 = 7
a3 = 3 + 2*3 => a1 = 9
The AP : 5,7,9, ………… s24
a = 5, n = 24, d= 2
=> Sn = n/2 [2a + (n-1) d]
=> s24= 12 [ 2*5 + 23 *2]
=> = 12 [ 10 + 46]
= 12 * 56
= 672
Therefore the sum of 24 terms of AP is 672](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-23-2048.jpg)

![9. If the sum of the first 14 terms of an AP is 1050 and its first
term is 10,find the 20th term.
Ans. Given,
s14= 1050, a = 10 a20 = ?
=> s14= n/2 [ 2a + (n-1)d]
=> 1050 = 7 [ 2*10 + 13 *d]
=> 1050 / 7 = 20 + 13d
=> 150 = 20 + 13d
=> 13d = 150 – 20
=> d = 130/13
=> d =10
Therefore a20 = 10 + 19 * 10
= 10 +190
= 200
Therefore the 20th term of AP is 200](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-25-2048.jpg)




![ii. If m times mth of AP is equals n times the nth term and m ≠
n, show that its ( m+ n )th term is 0.
Ans. Let a be the first term and d be the common difference
of the given AP.
Given m*am = n* an
=> m [a + ( m – 1 )d] = n [a + (n – 1)d]
=> m [a + ( m – 1 )d] - n [a + (n – 1)d] = 0
=> am + (m2 – m)d – an – ( n2 – n ) d = 0
=> a ( m – n) + [m2 - n2 – m + n] d = 0
=> a ( m – n) + [(m2 - n2) – (m – n)] d = 0
=> [m – n ] *{a + [( m + n ) – 1]d} = 0
=> [ m – n ] * a m+n = 0
=> a m+n = 0
Therefore a m+n term of AP is 0
iii. If the mth term of AP is 1/n and its nth term is 1/m, then
show that its (mn)th term is 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogressions-200918032407/75/Arithmetic-progressions-30-2048.jpg)