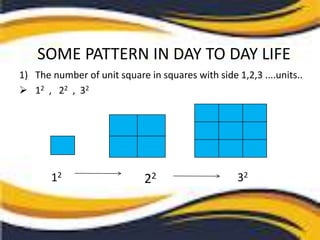
The document defines and provides examples of arithmetic progressions (AP). An AP is a sequence of numbers where each term is calculated by adding a fixed number (the common difference) to the preceding term. Examples given include the heights of students in line increasing by 1 each time, and daily temperatures decreasing by 0.1 degrees each day. Finite APs have a last term, while infinite APs do not. The general form of an AP is shown as a, a+d, a+2d, a+3d, etc., where a is the first term and d is the common difference.