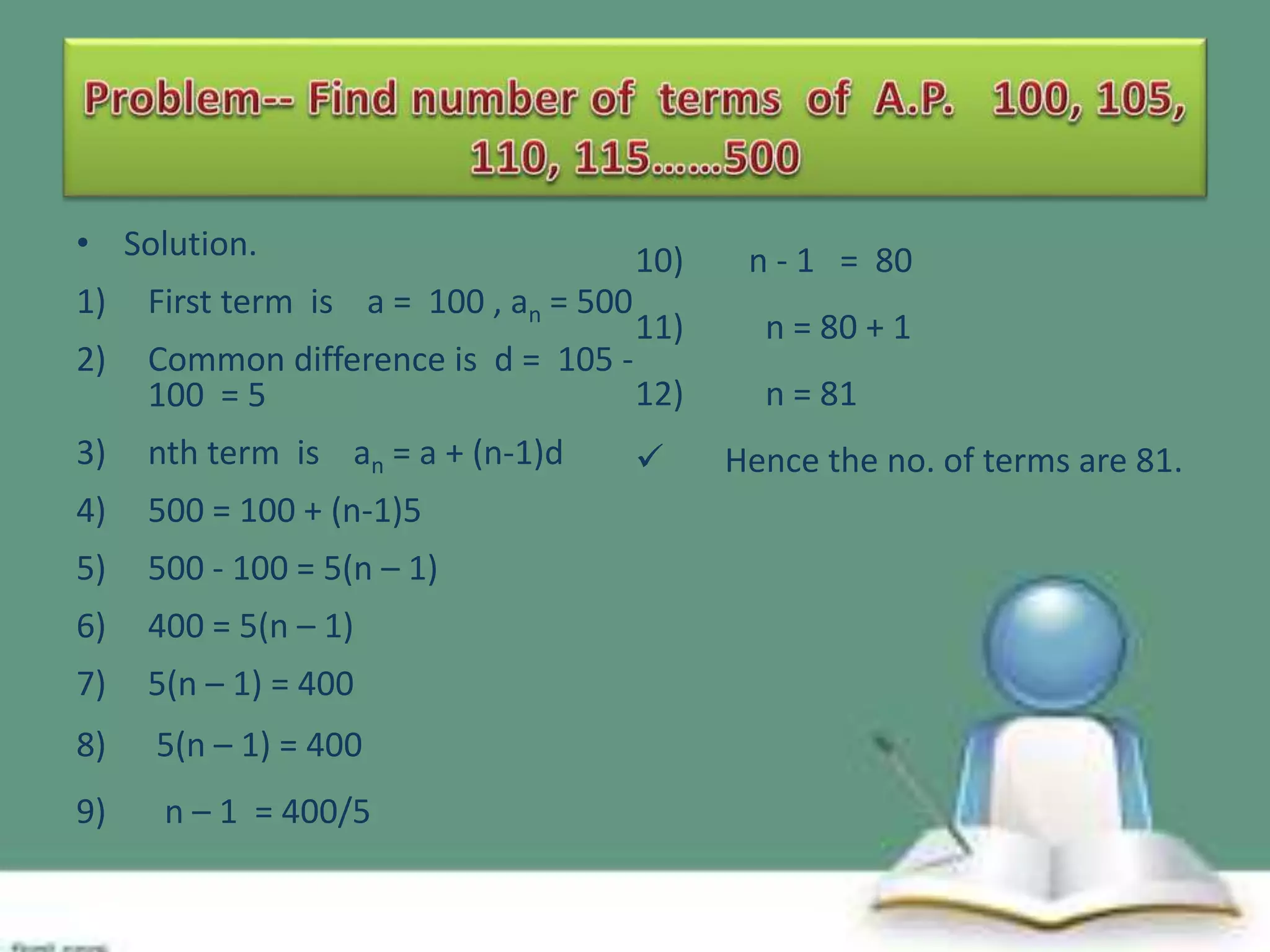
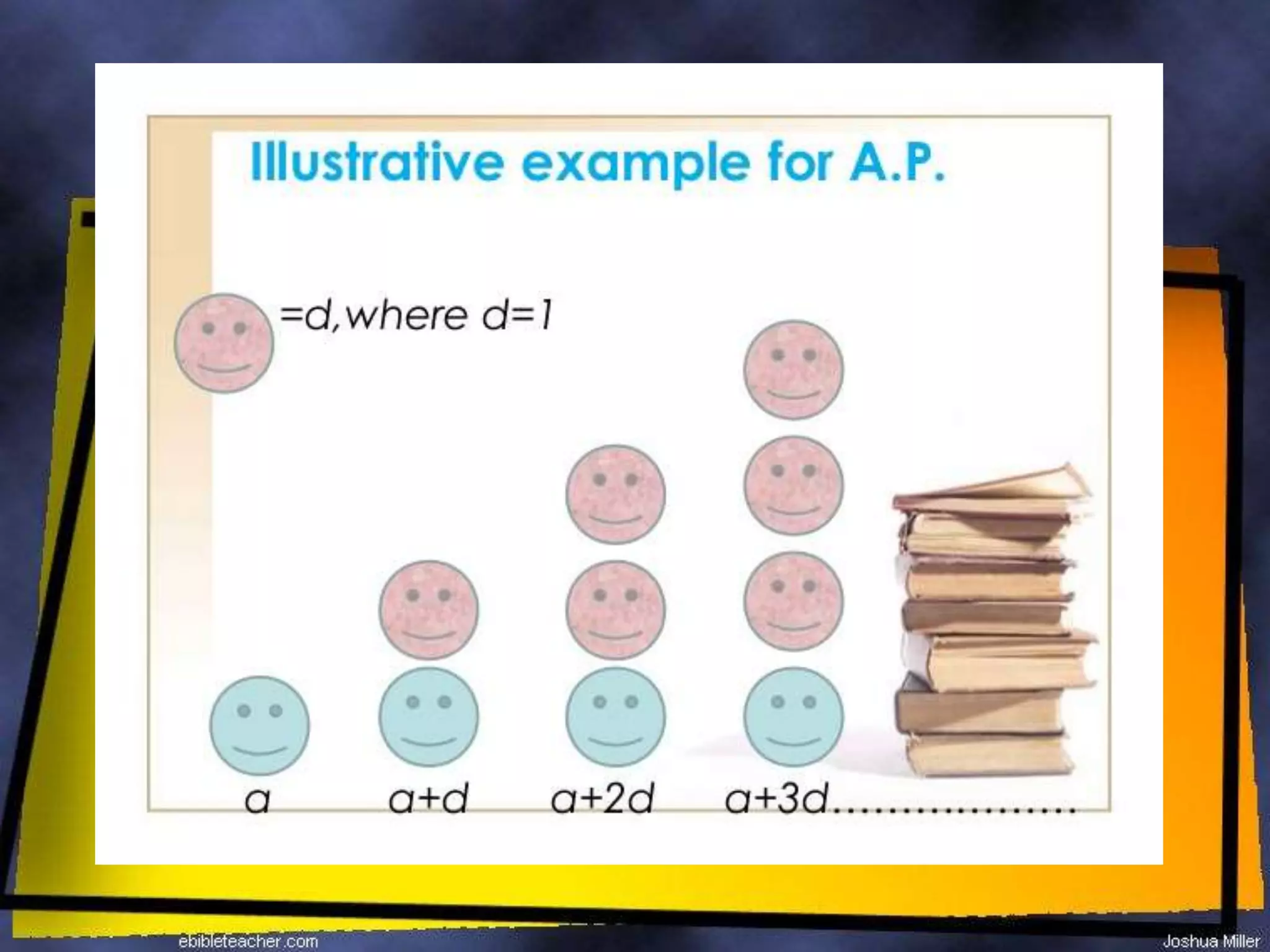
An arithmetic progression (AP) is a sequence where the difference between consecutive terms is constant, exemplified by sequences like 2, 4, 6, 8 and 5, 10, 15, 20. The nth term of an AP can be calculated using the formula an = a + (n-1)d, where 'a' is the first term and 'd' is the common difference. The sum of the first n terms of an AP is given by the formula Sn = n/2(2a + (n-1)d).








![The sum of n terms, we find as,
Sum = n X [(first term + last term) / 2]
Now last term will be = a + (n-1) d
Therefore,
Sum(Sn) =n X [{a + a + (n-1) d } /2 ]
= n/2 [ 2a + (n+1)d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmeticprogression-131016051857-phpapp01/75/Arithmetic-progression-11-2048.jpg)