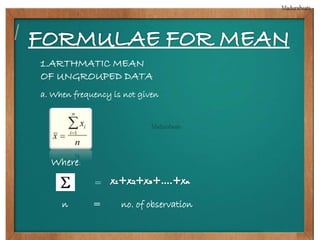
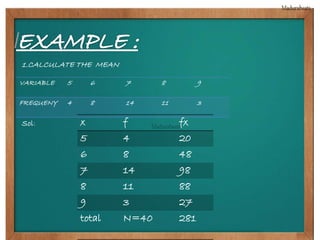
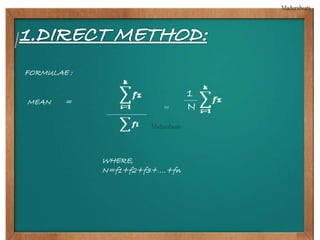
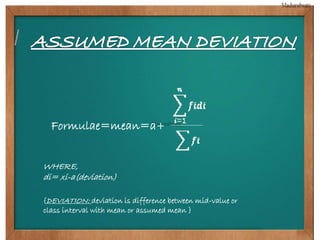
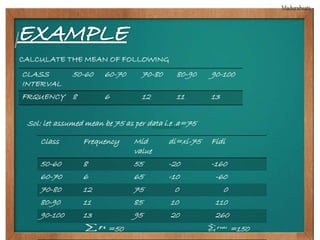
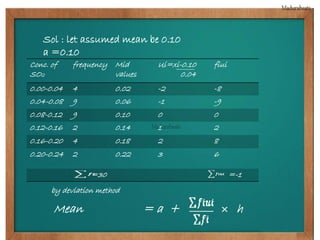
This document provides biographical information about the statistician Ronald Fisher:
- Fisher was born in 1890 in London, England and had a happy childhood until his father lost his business when Fisher was 14.
- He made significant contributions to statistics and developed concepts like maximum likelihood estimation and the analysis of variance.
- Fisher spent time in England and Australia in his career and made groundbreaking advances in the field of statistics.