The document defines and provides examples of arithmetic progressions (AP). It states that an AP is a sequence where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. The key characteristics of an AP include:
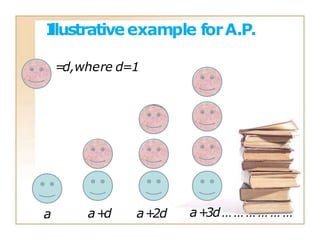
- The first term is denoted as a
- The common difference is denoted as d
- The nth term is calculated as an = a + (n-1)d
Several examples are provided to illustrate how to determine if a sequence is an AP and how to calculate individual terms and the sum of terms in an AP using the above formulae.









![The sumofn term
s, we find as,
Sum =n X [(first term +last term) / 2]
Now last term will be =a +(n-1) d
Therefore,
Sum(Sn
) =n X [{
a +a +(n-1) d }/2 ]
=n/2 [2a +(n+1)d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmaticprogression-230815174956-18c29967/85/arithmatic-progression-pptx-12-320.jpg)
![DERIVATION
T
he sum to n termsisgiven by:
Sn =a +(a +d) +(a +2d) +… +(a +(n –1)d) (1)
Ifwe write this out backwards, we get:
Sn =(a +(n –1)d) +(a +(n –2)d) +… +a (2)
Now let’sadd (1) and (2):
2Sn =[2a +(n –1)d] +[2a +(n –1)d] +…
… … … +[2a +(n –1)d]
So, Sn = n/2[2
a +(n –1)d]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmaticprogression-230815174956-18c29967/85/arithmatic-progression-pptx-13-320.jpg)


![Problem . Find the sum of 30 terms of given
A.P. ,12 , 20 , 28 , 36………
Solution :Given A.P. is12 , 20, 28 , 36
Its first term is a =12
Common difference isd =20 –12 =8
The sum to n termsof an arithmetic progression
Sn =n/2 [ 2a +(n - 1)d ]
=½x 30 [ 2x 12 +(30-1)x 8]
=15 [ 24 +29 x8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmaticprogression-230815174956-18c29967/85/arithmatic-progression-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![=15[24 +232]
=15 x 246
=3690
THE SUM OF TERMS IS 3690](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmaticprogression-230815174956-18c29967/85/arithmatic-progression-pptx-17-320.jpg)

![The sum to n terms of an arithmetic
progression Sn =n/2[ 2a +(n - 1)d ]
S100 =100/2 [ 2x 2 +(100-1)x 2]
=50 [ 4 +198]
=50[202]
=10100](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/arithmaticprogression-230815174956-18c29967/85/arithmatic-progression-pptx-19-320.jpg)

