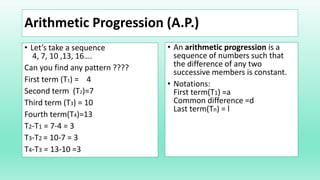
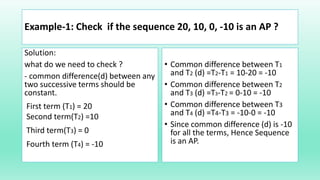
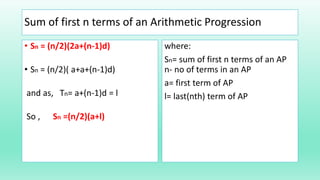
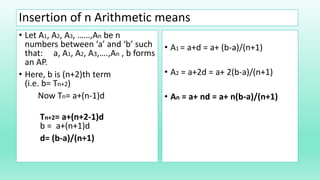
- An arithmetic progression is a sequence of numbers where the difference between consecutive terms is constant. It can be represented by the first term (a), common difference (d), and last term (l).
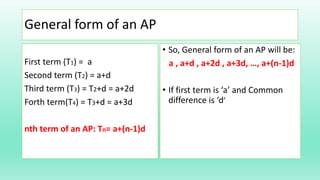
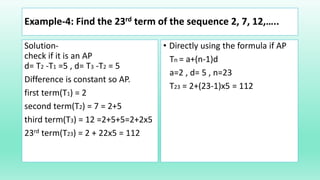
- The general formula for the nth term (Tn) of an AP is: Tn = a + (n-1)d
- The sum (Sn) of the first n terms of an AP can be calculated as: Sn = (n/2)(a + l)
- Inserting arithmetic means between two numbers a and b results in an AP where the common difference (d) is (b-a)/(n+1) and the inserted terms are: a + d, a + 2