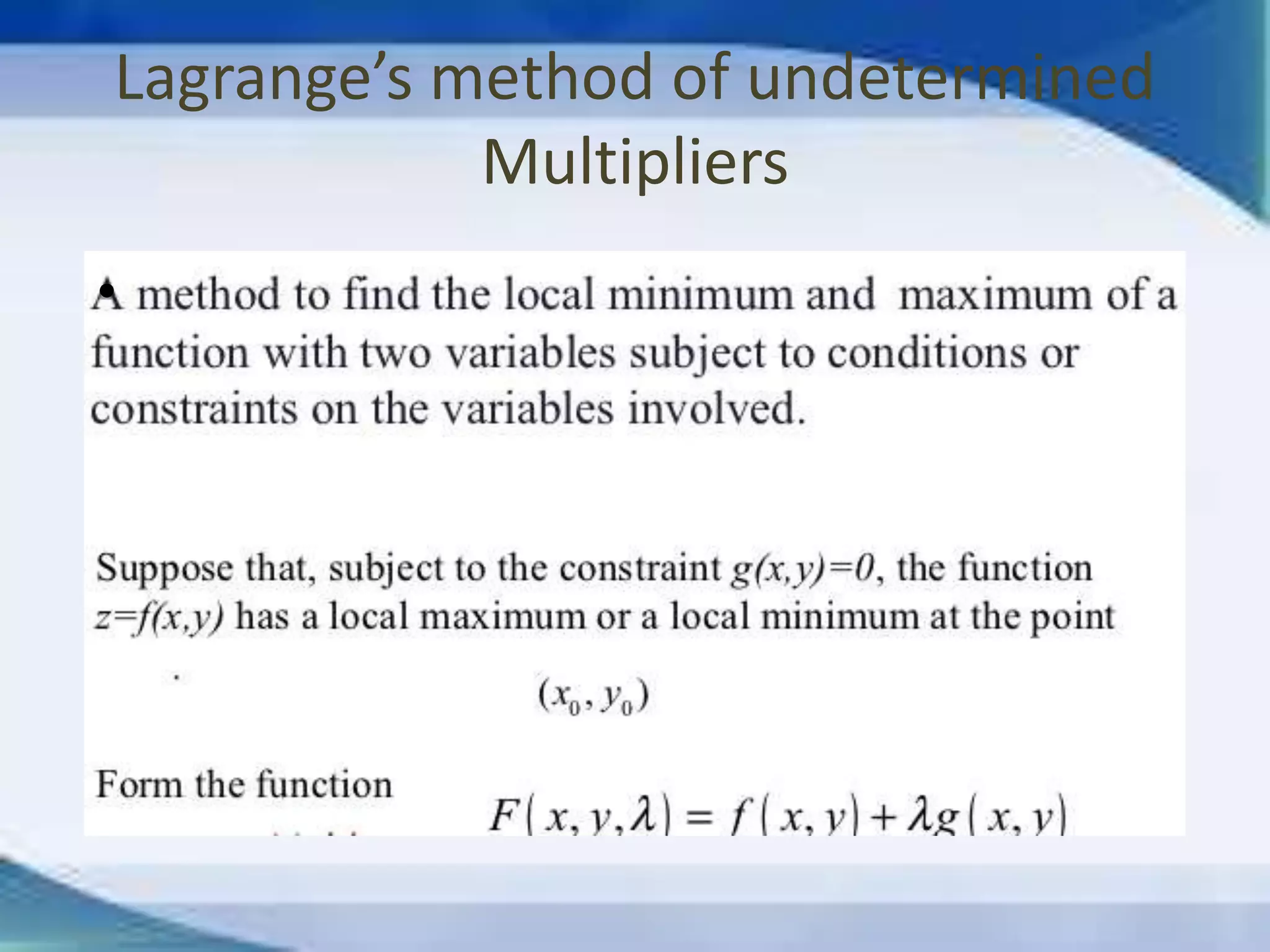
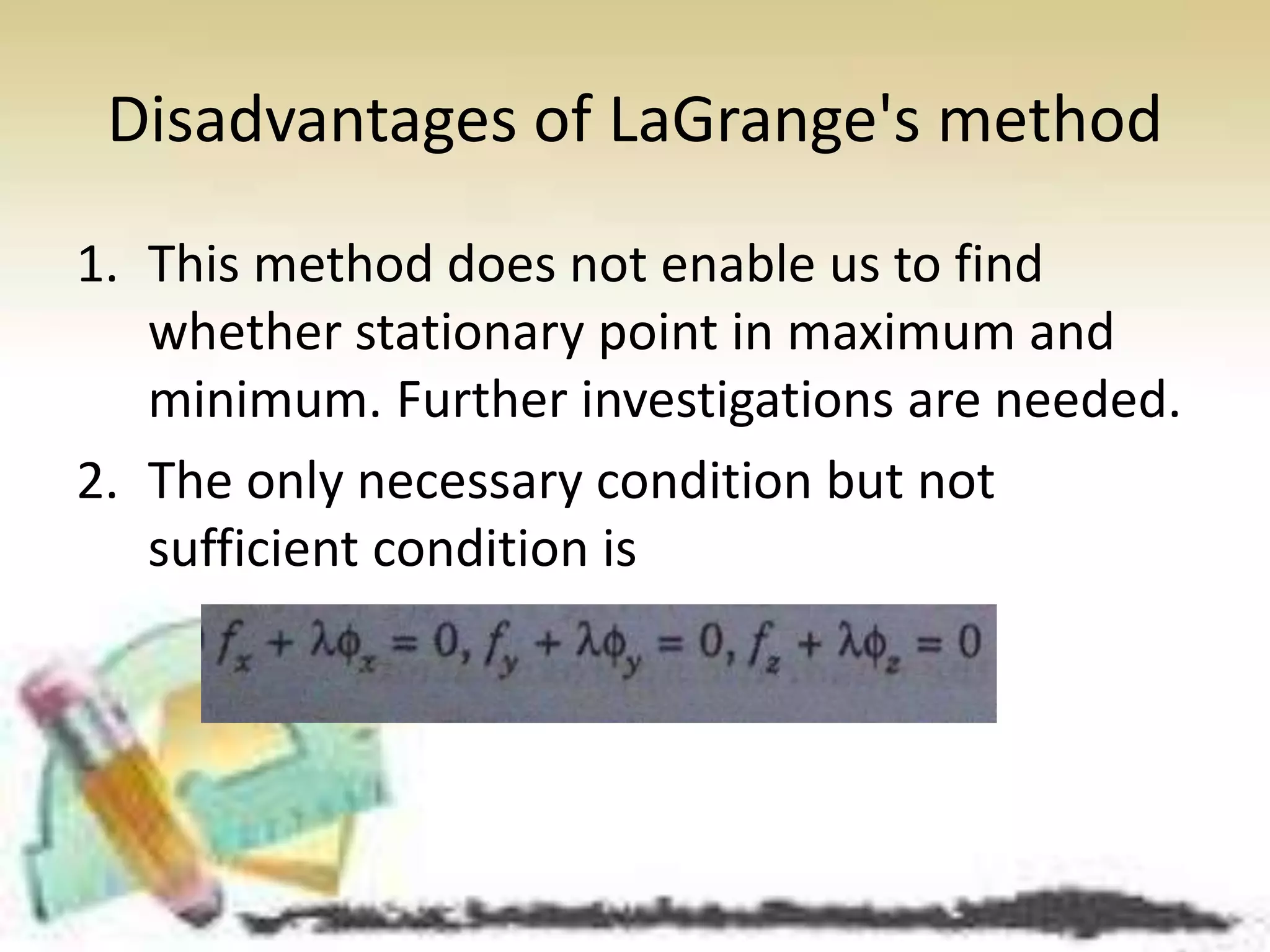
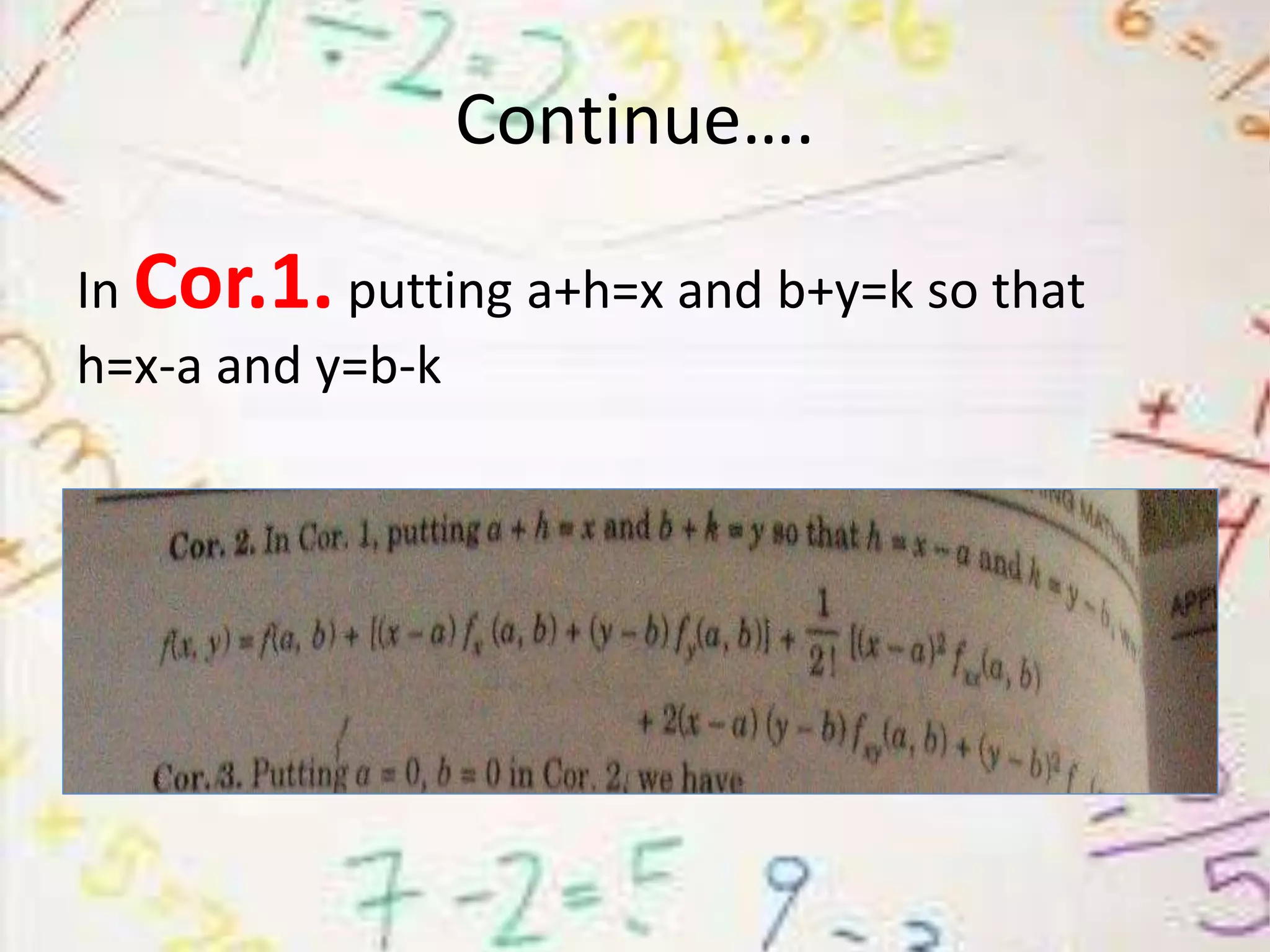This document discusses topics in partial differentiation including:
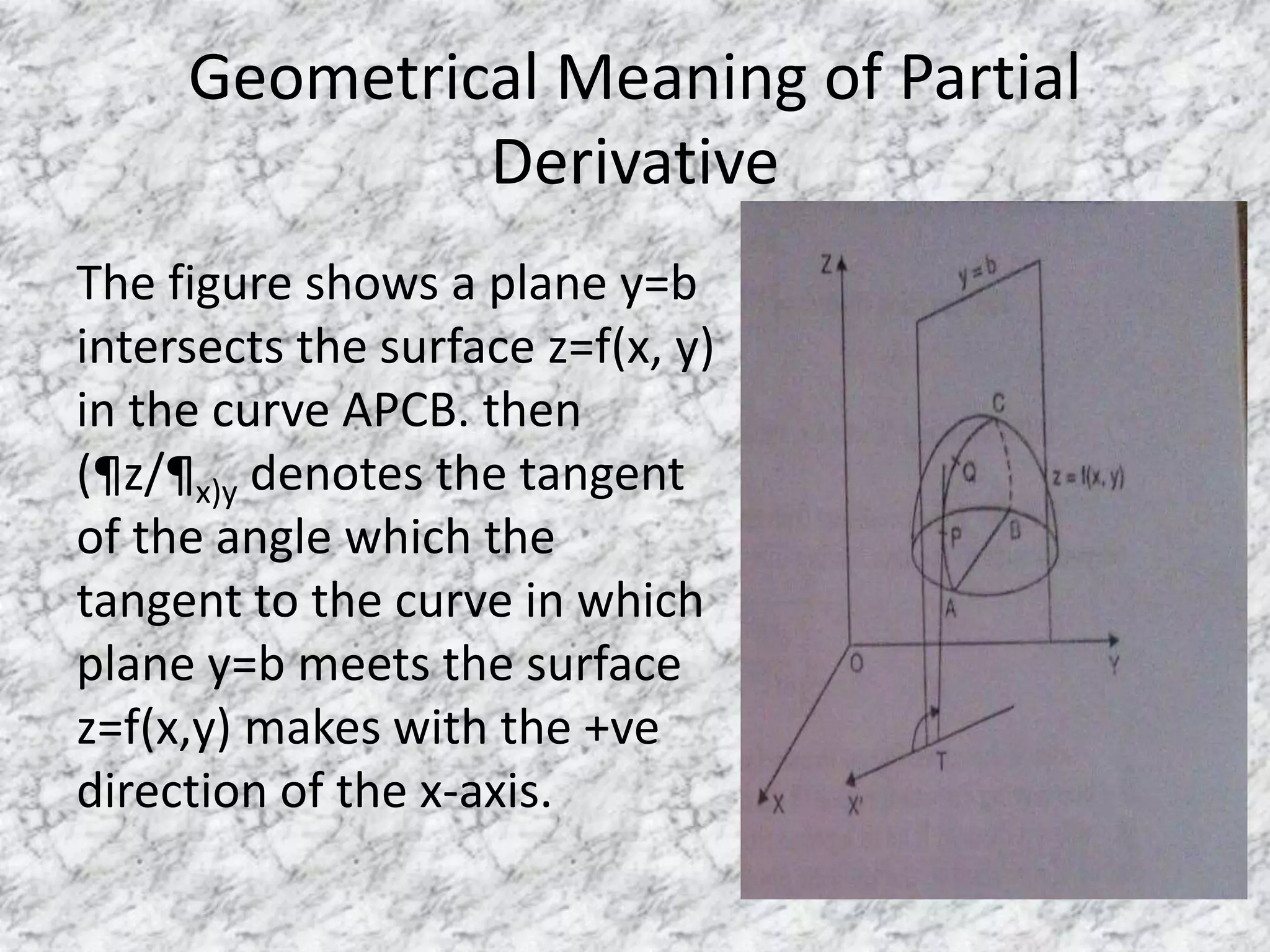
1) The geometrical meaning of partial derivatives as the slope of the tangent line to a surface.
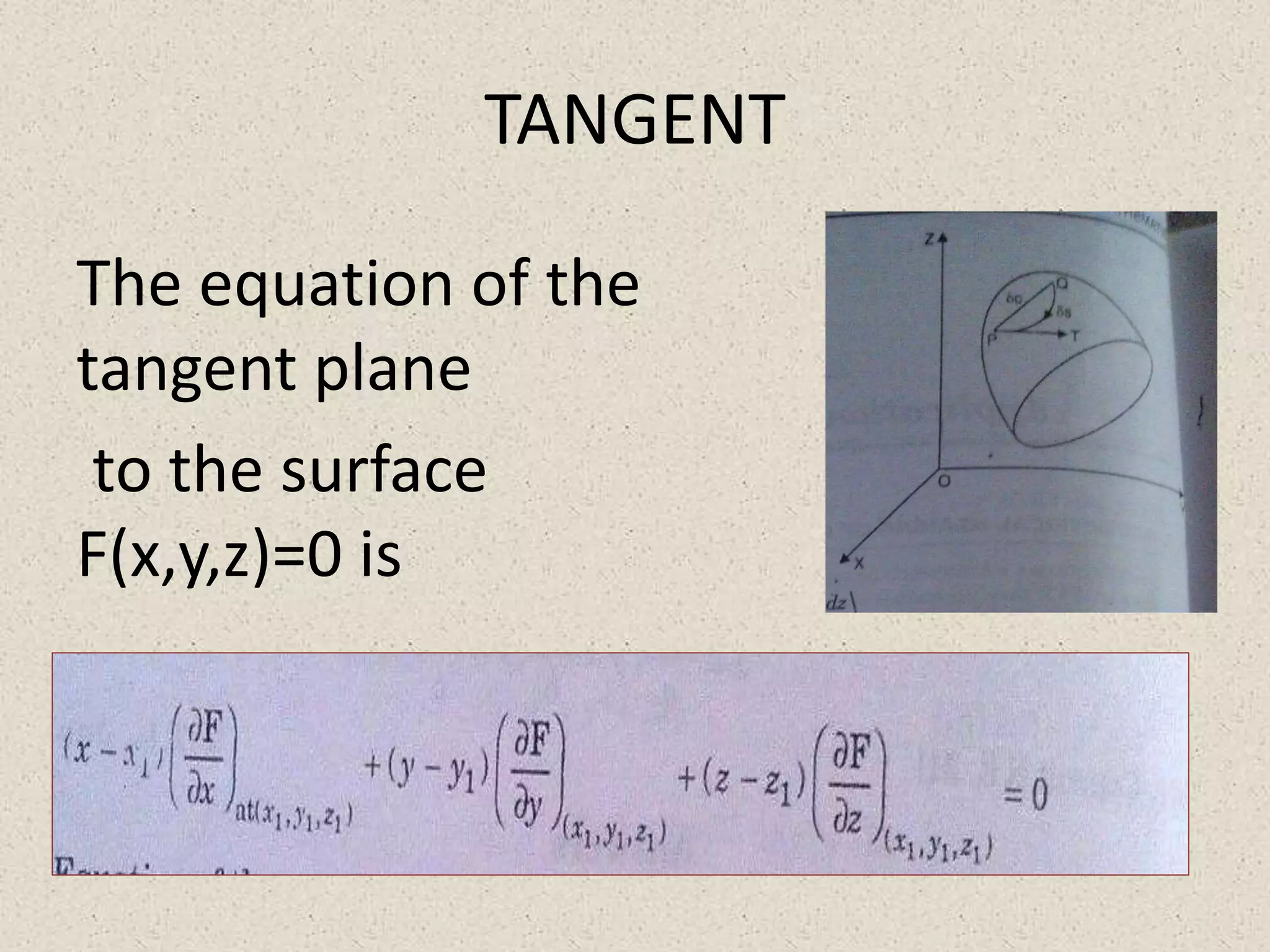
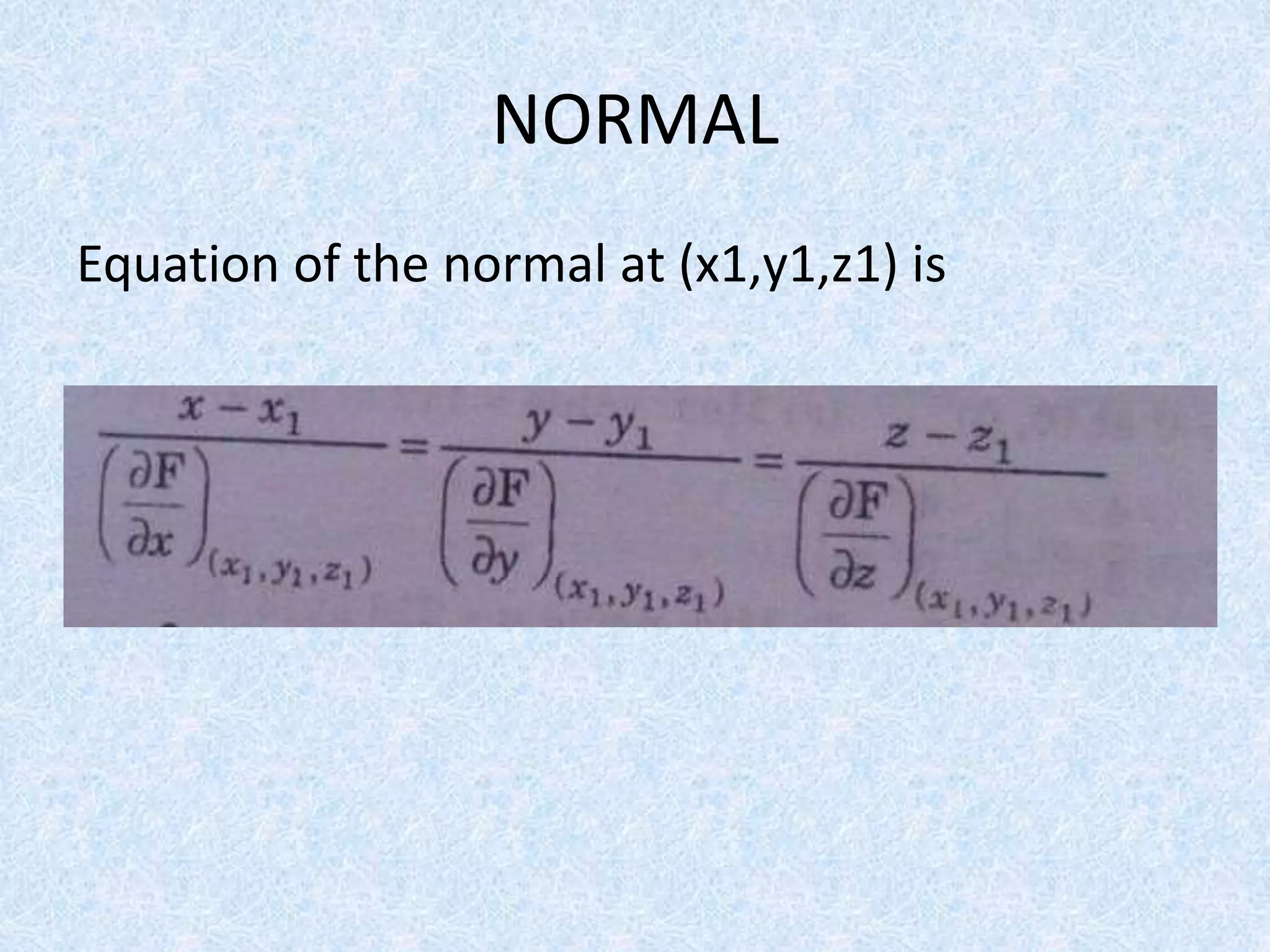
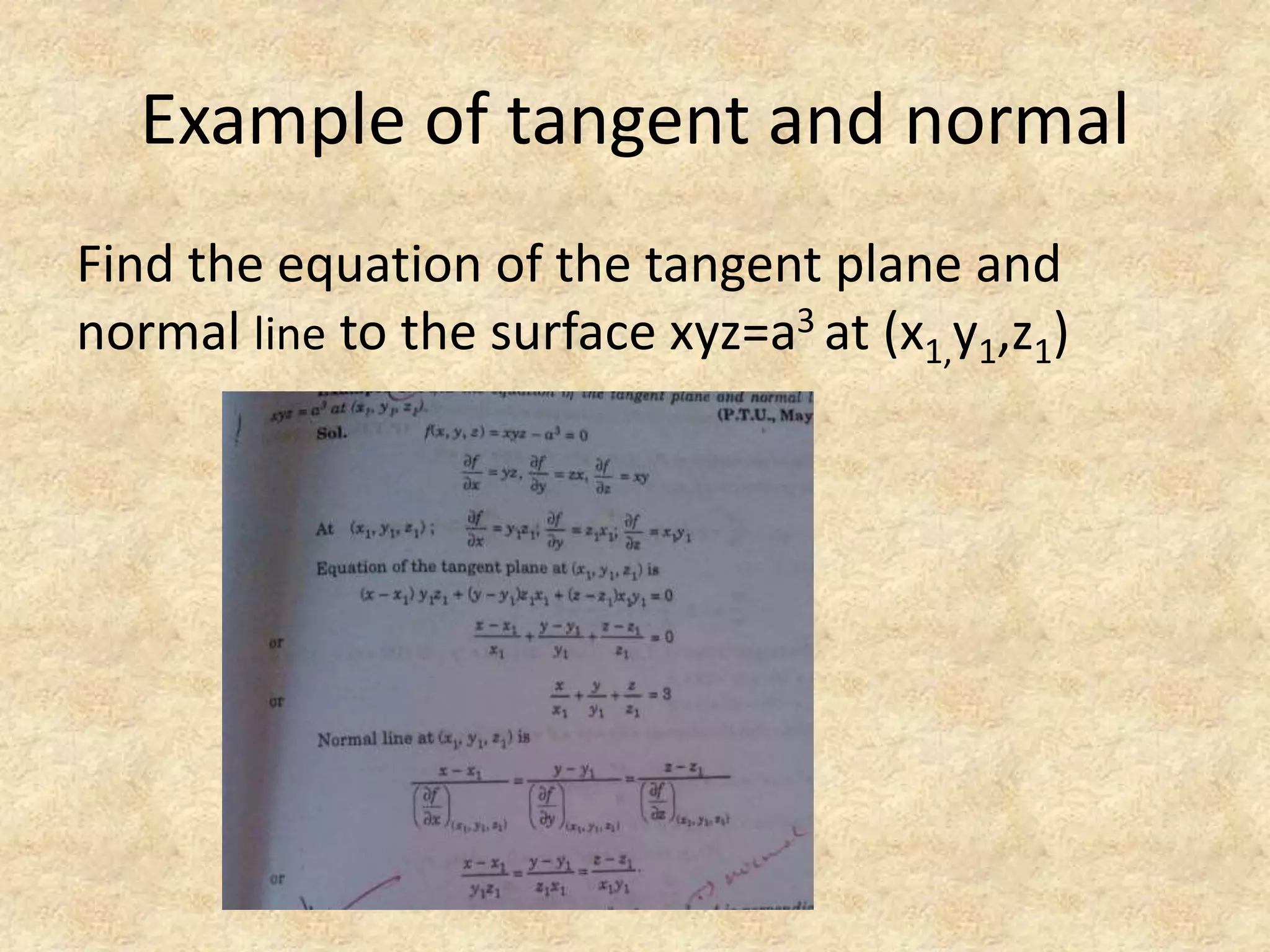
2) Finding the equation of the tangent plane and normal line to a surface.
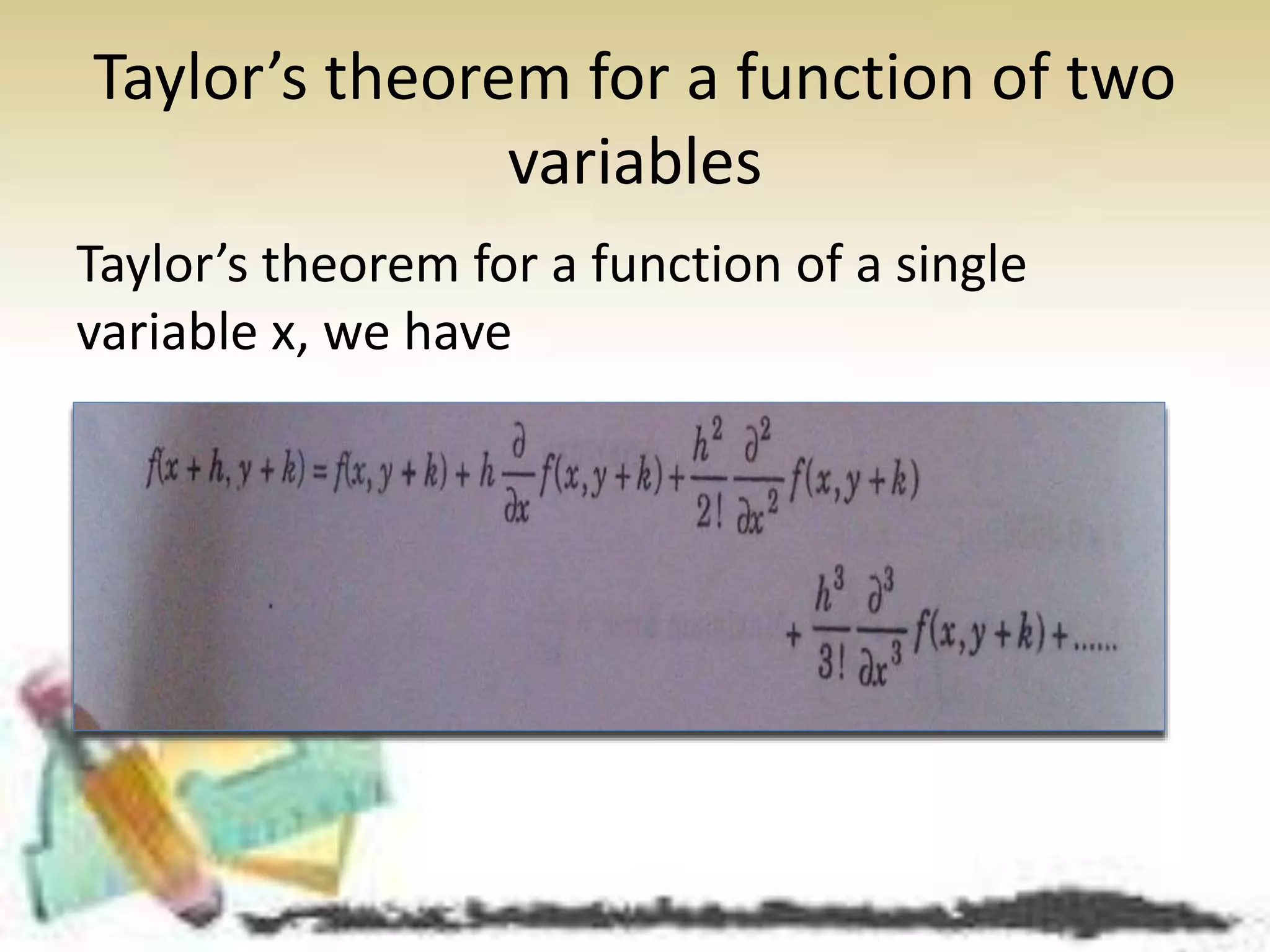
3) Taylor's theorem and Maclaurin's theorem for functions with two variables, which can be used to approximate functions and calculate errors.