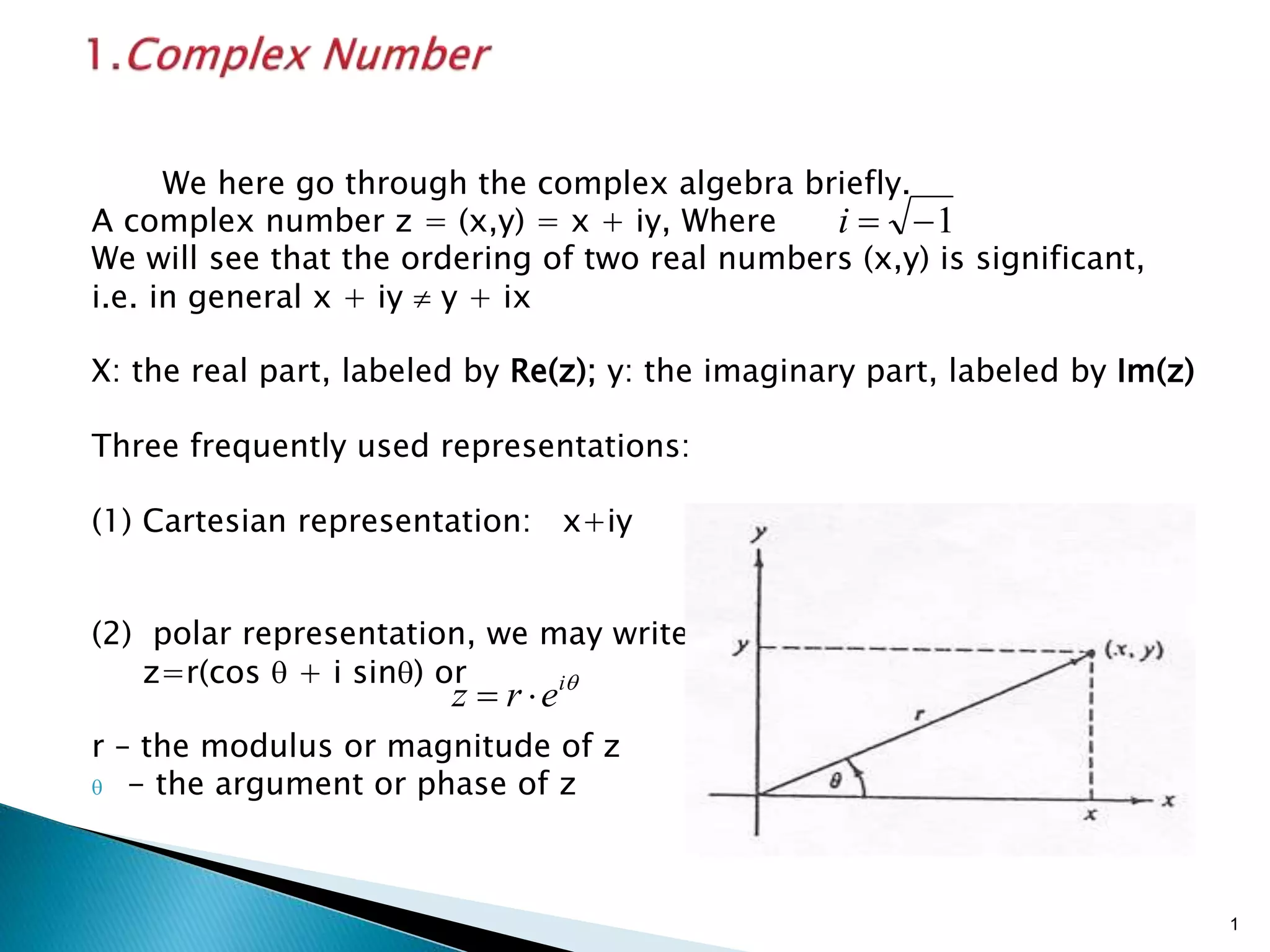
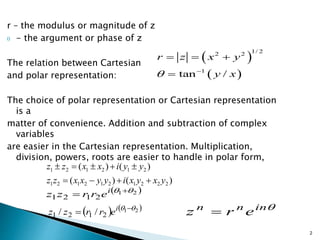
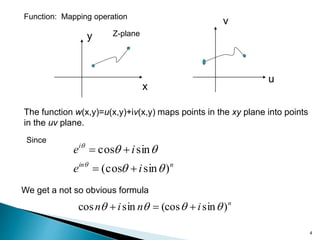
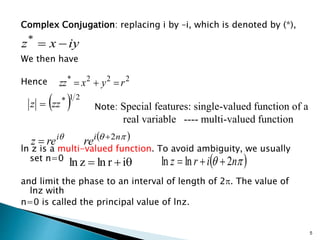
1) Complex numbers can be represented in Cartesian (x + iy) or polar (r(cosθ + i sinθ)) form, with conversions between the two.
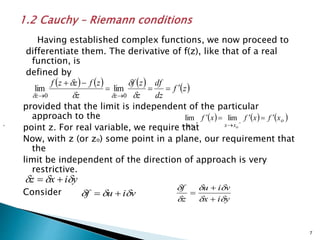
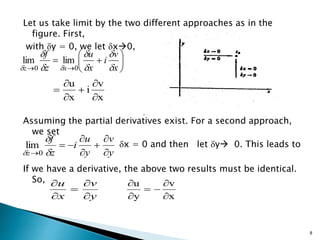
2) The derivative of a complex function f(z) is defined if the Cauchy-Riemann equations are satisfied.
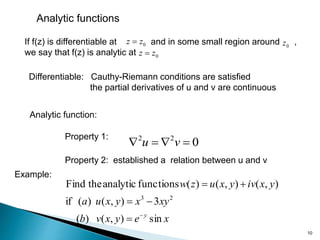
3) A function is analytic if it is differentiable and its partial derivatives are continuous, implying the Cauchy-Riemann equations always hold. Analytic functions have properties like equality of second partial derivatives.