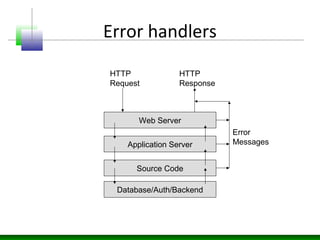
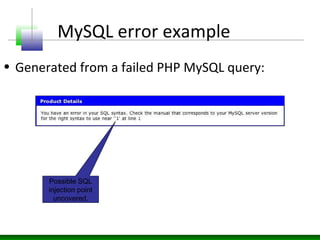
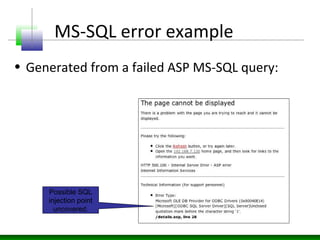
This document discusses application layer fuzzing and the potential information leaks that can occur. It describes how an attacker can inject faults through HTTP requests to trigger exceptions and scan responses for signatures. Errors can reveal details like the technology stack, network architecture, intranet applications, database connection information, file system layouts, and authentication mechanisms. Information leaks occur when deployment components like web servers and databases are misconfigured or have vulnerabilities, or when application source code does not properly handle errors. Various examples show how errors from web servers, application servers, databases, and source code can disclose internal paths, nature of errors, and potential injection points.