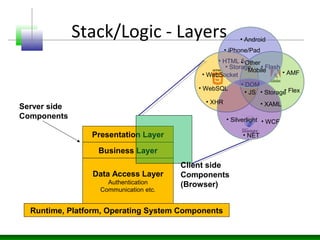
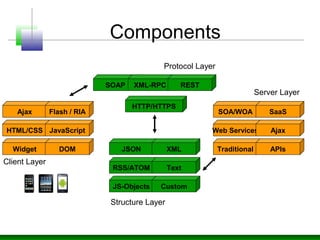
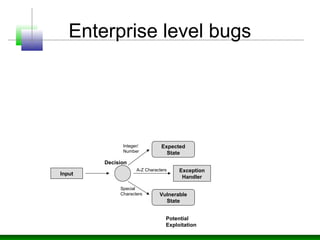
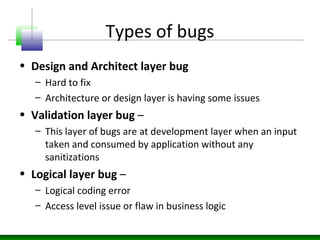
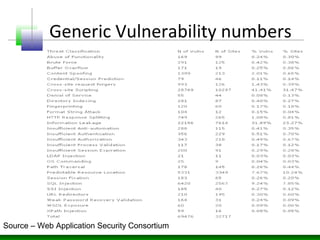
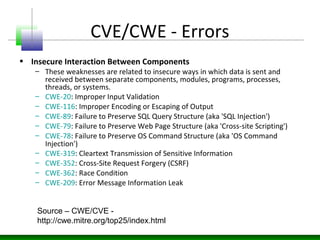
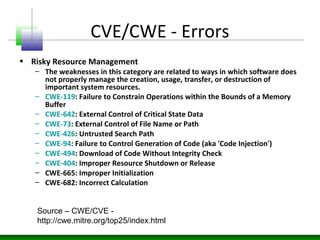
The document discusses various technology trends related to enterprise application architecture including the growth of web services, service-oriented architecture, and enterprise 2.0. It also covers trends in mobile/HTML5 and the flexible/cloud/API era. Diagrams show sample enterprise network infrastructure and the layers of a typical application stack including presentation, business, and data access layers. The document also summarizes common types of bugs like design/architecture bugs and validation bugs. Finally, it discusses the CWE/CVE framework for categorizing common vulnerabilities related to insecure interaction between components, risky resource management, and porous defenses.


![Enterprise Technology Trend
• 2007. Web services would rocket from $1.6
billion in 2004 to $34 billion. [IDC]
• 2008. Web Services or Service-Oriented
Architecture (SOA) would surge ahead.
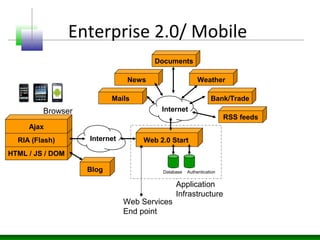
• 2009-10. Enterprise 2.0 in action and
penetrating deeper into the corporate
environment
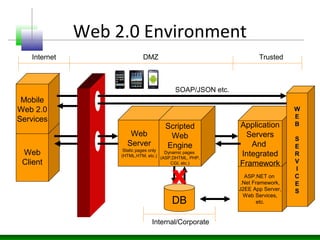
• 2011-13. Flex/Cloud/API era.
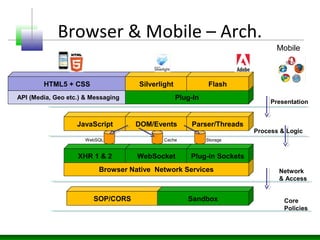
• 2015. Mobile/HTML5 era.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/advanced-applications-architecture-threats-151024093341-lva1-app6891/85/Advanced-applications-architecture-threats-3-320.jpg)