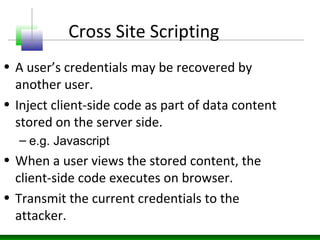
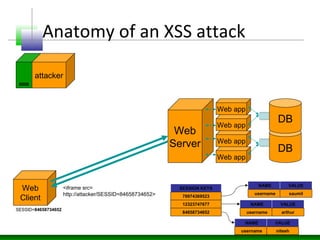
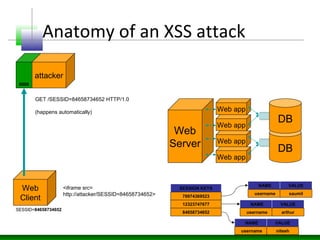
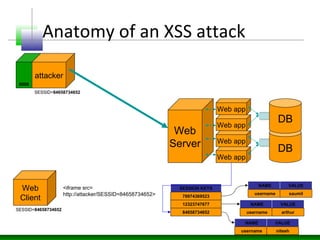
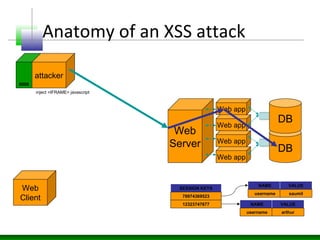
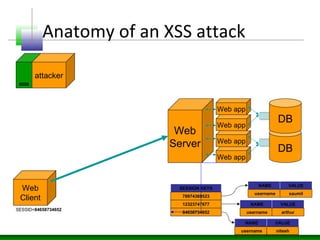
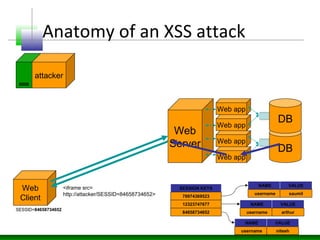
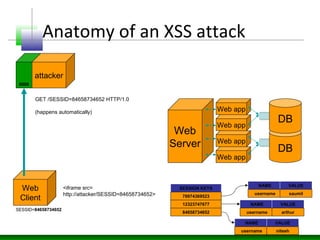
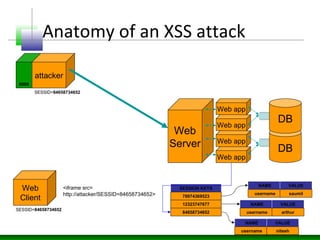
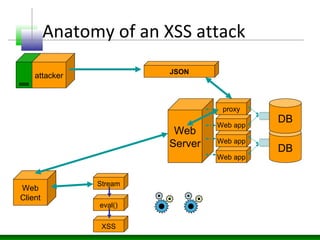
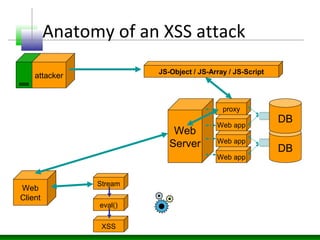
This document discusses cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and defenses. It describes different types of XSS (persistent, non-persistent, DOM-based), how XSS attacks work, and examples of XSS injection vectors. It also provides recommendations for preventing XSS, including encoding output, sanitizing input, and using features like HttpOnly cookies.












![DOM based XSS
if (http.readyState == 4) {
var response = http.responseText;
var p = eval("(" + response + ")");
document.open();
document.write(p.firstName+"<br>");
document.write(p.lastName+"<br>");
document.write(p.phoneNumbers[0]);
document.close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-32-320.jpg)
![DOM based XSS
document.write(…)
document.writeln(…)
document.body.innerHtml=…
document.forms[0].action=…
document.attachEvent(…)
document.create…(…)
document.execCommand(…)
document.body. …
window.attachEvent(…)
document.location=…
document.location.hostname=…
document.location.replace(…)
document.location.assign(…)
document.URL=…
window.navigate(…)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-36-320.jpg)



![Prevent XSS
• Encode output using HtmlEncode /
URLEncode methods.
• Do this even for user input, a database, or
a local file.
The HtmlEncode method replaces characters that have special meaning in
HTML to HTML variables that represent those characters. For example, <
is replaced with < and " is replaced with ". Encoded data does
not cause the browser to execute code. Instead, the data is rendered as
harmless HTML.
Response.Write(HttpUtility.HtmlEncode(Request.Form["name"]));](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-41-320.jpg)



![Prevent XSS
• Validating Unicode Characters,
using System.Text.RegularExpressions;
private void Page_Load(object sender, System.EventArgs e)
{
// Name must contain between 1 and 40 alphanumeric characters
// together with (optionally) special characters '`' for names such
// as D'Angelo
if (!Regex.IsMatch(Request.Form["name"], @"^[p{L}p{Zs}p{Lu}p{Ll}']{1,40}$"))
throw new ArgumentException("Invalid name parameter");
}
•{<name>} specifies a named Unicode character class.
•p{<name>} matches any character in the named character class specified by
{<name>}.
•{L} performs a left-to-right match.
•{Lu} performs a match of uppercase.
•{Ll} performs a match of lowercase.
•{Zs} matches separator and space.
•{1,40} means no less that 1 and no more than 40 characters.
•{Mn} matches mark and non-spacing characters.
•{Zs} matches separator and space.
•* specifies zero or more matches.
•$ means stop looking at this position.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-45-320.jpg)

![Prevent XSS
• Use the HttpOnly Cookie Option.
• prevents client-side script from
accessing the cookie from the
document.cookie property
protected void Application_EndRequest(Object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string authCookie = FormsAuthentication.FormsCookieName;
foreach (string sCookie in Response.Cookies)
{
if (sCookie.Equals(authCookie))
{
// Force HttpOnly to be added to the cookie header
Response.Cookies[sCookie].Path += ";HttpOnly";
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-47-320.jpg)

![Prevent XSS
• Use AntiXSS library,
//bad code
String Name = Request.QueryString["Name"];
//code with antixss library
String Name = AntiXss.HtmlEncode(Request.QueryString["Name"]);
namespace Microsoft.Application.Security
{
public class AntiXss
{
public static string HtmlEncode(string s);
public static string HtmlAttributeEncode(string s);
public static string JavaScriptEncode(string s);
public static string UrlEncode(string s);
public static string VisualBasicScriptEncode(string
s);
public static string XmlEncode(string s);
public static string XmlAttributeEncode(string s);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/xssinjections-151026085036-lva1-app6892/85/XSS-Attacks-Defense-49-320.jpg)
