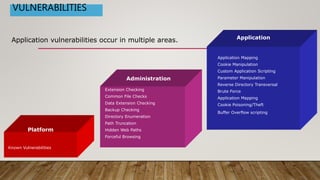
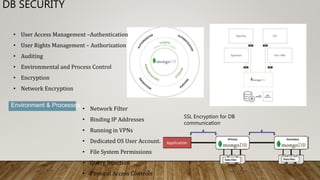
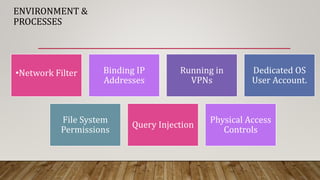
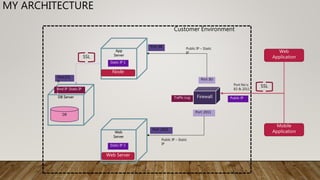
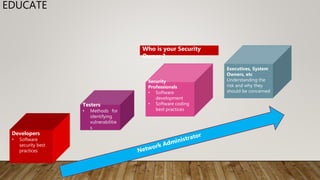
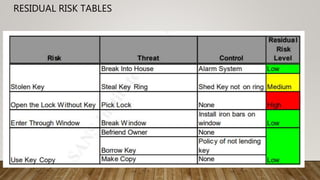
The document outlines essential security guidelines for safeguarding customer environments, emphasizing the security gaps that arise from a lack of collaboration between security professionals and application developers. It discusses various application vulnerabilities and outlines best practices for incorporating security into the software development lifecycle, including threat modeling and the use of security assessments. Additionally, it highlights the importance of educating developers, managing user access, and maintaining updated security protocols to protect against known vulnerabilities.