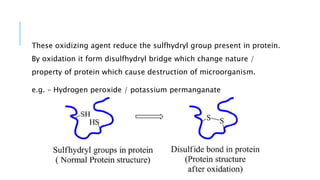
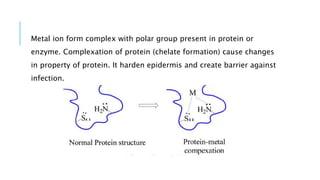
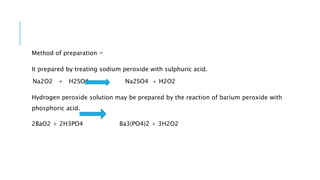
The document discusses various antimicrobial agents including antiseptics, disinfectants, and germicides. It provides examples like potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, and chlorinated lime. It describes their preparation, properties, uses, and mechanisms of action like oxidation, halogenation, and protein precipitation. The agents discussed are commonly used for sterilization, sanitization, and preventing infection by destroying microorganisms.