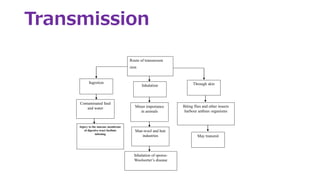
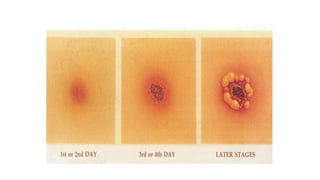
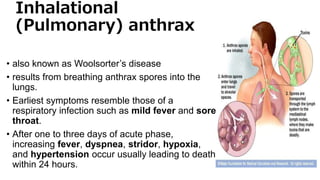
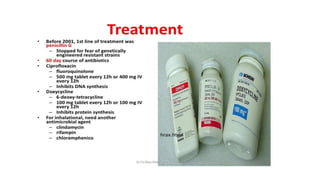
Bacillus anthracis is a gram-positive, spore-forming bacterium that causes the zoonotic disease anthrax. It forms spores that allow it to survive in the environment for many years. Anthrax infection can occur in three forms - cutaneous, inhalational, and gastrointestinal - depending on the route of exposure. The bacterium produces lethal and edema toxins that are major virulence factors. While livestock are usually affected, humans can contract anthrax through contact with infected animals or contaminated animal products. Proper handling and cooking of meat and vaccination of high-risk individuals are important for prevention. Antibiotics like ciprofloxacin are the primary treatment for anthrax infection.