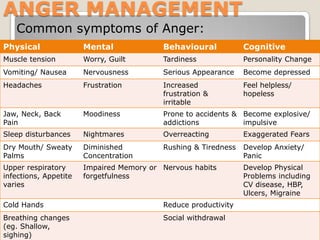
Anger is a normal human emotion, but it needs to be managed in a healthy way. The presentation discusses the causes and effects of anger, both positive and negative. It identifies external stressors like life events and everyday pressures, and internal stressors like values and expectations that can trigger anger. When angry, the body releases hormones that increase heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing. Strategies taught for managing anger include identifying feelings and triggers, understanding consequences, challenging angry thoughts, and using skills like calming down, problem solving, and forgiveness.