Embed presentation
Downloaded 183 times


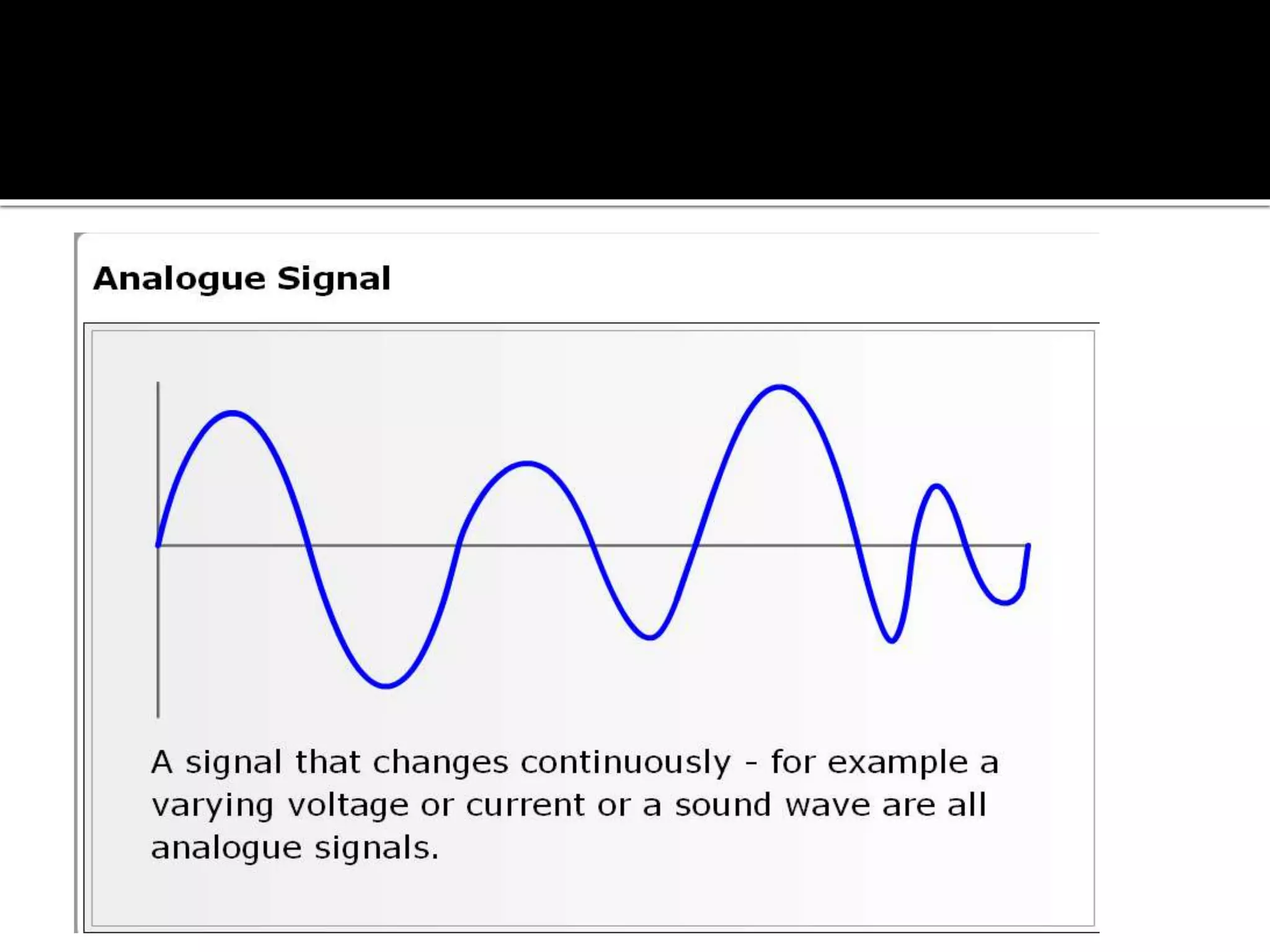
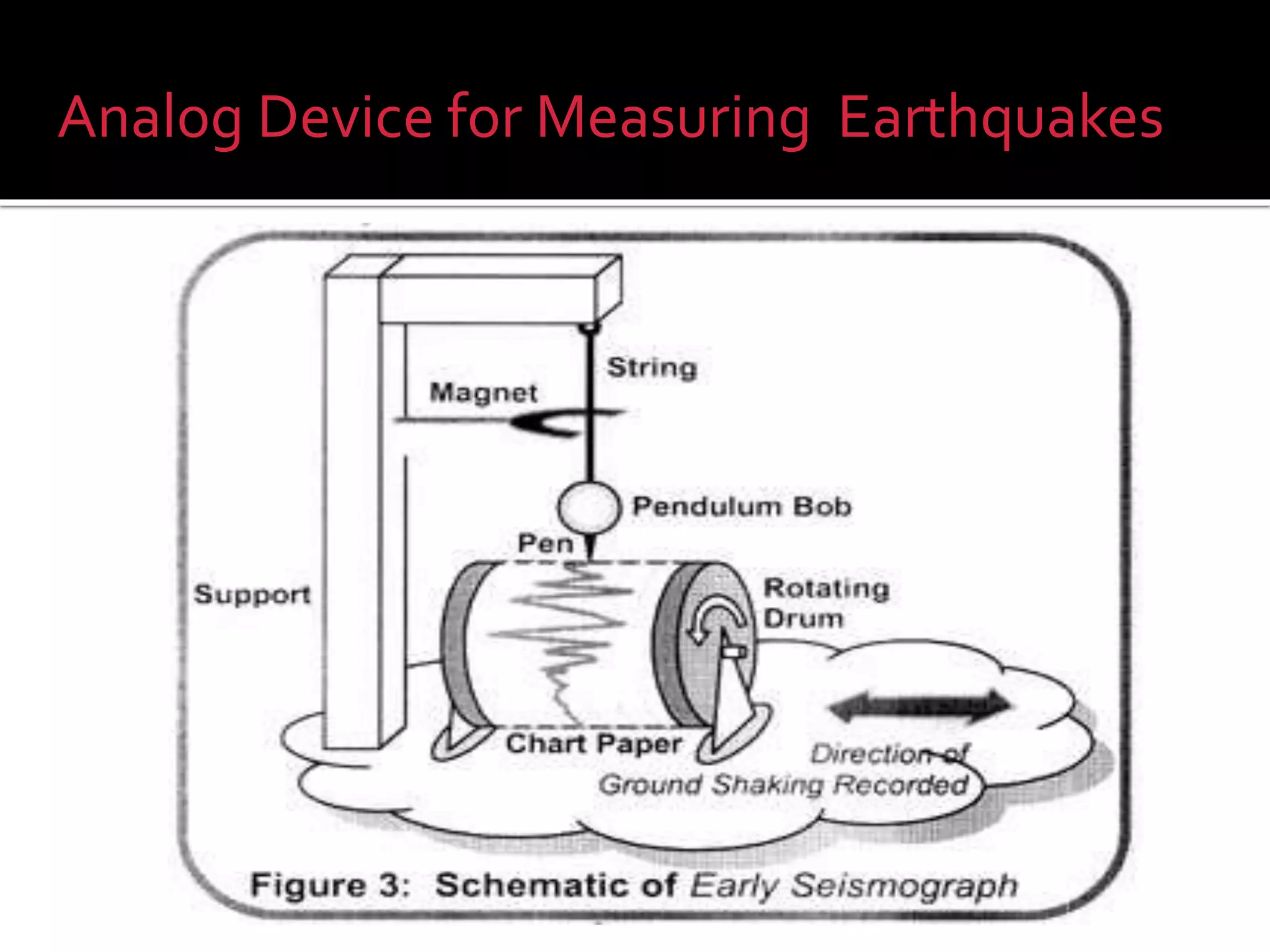

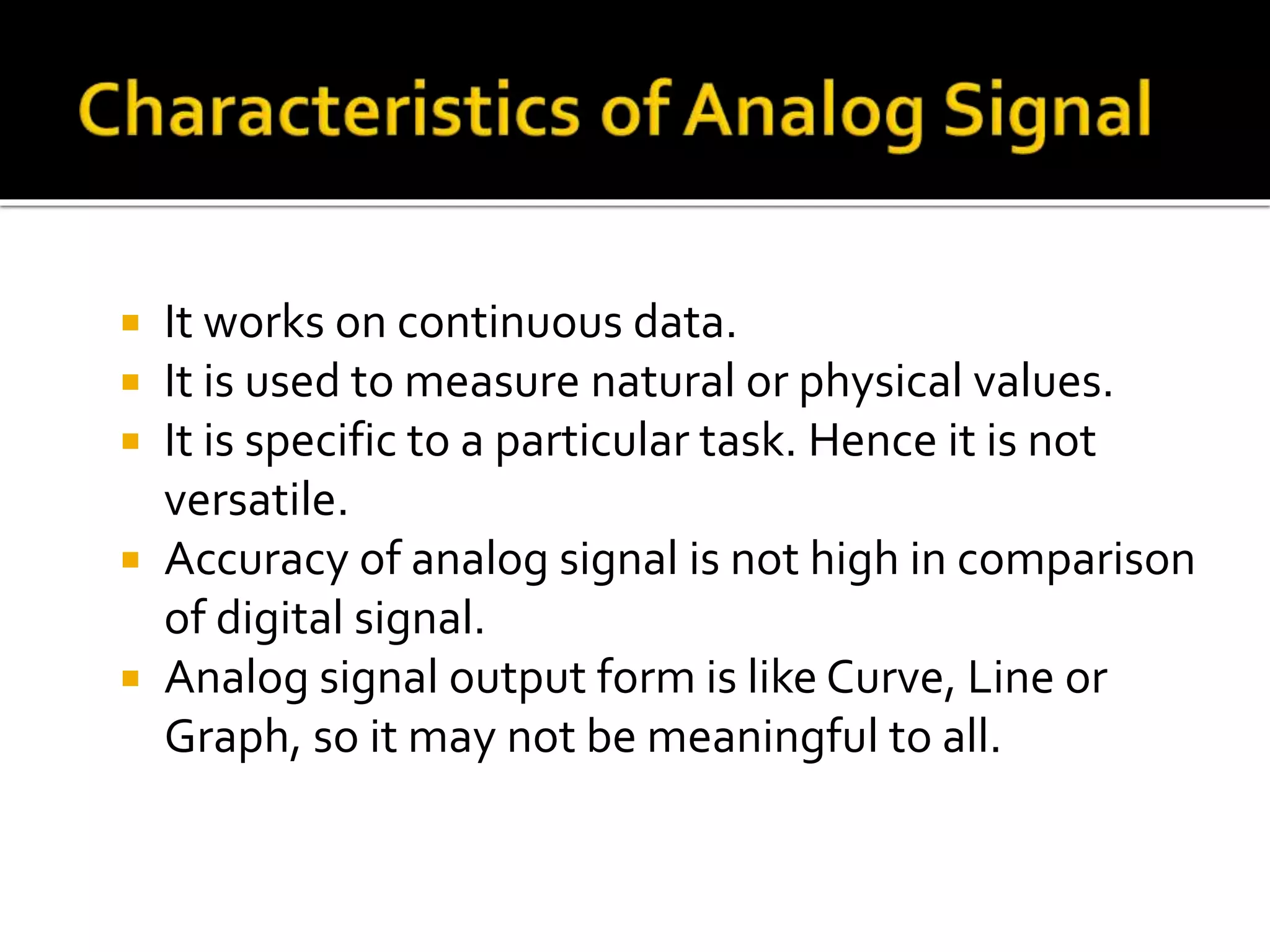
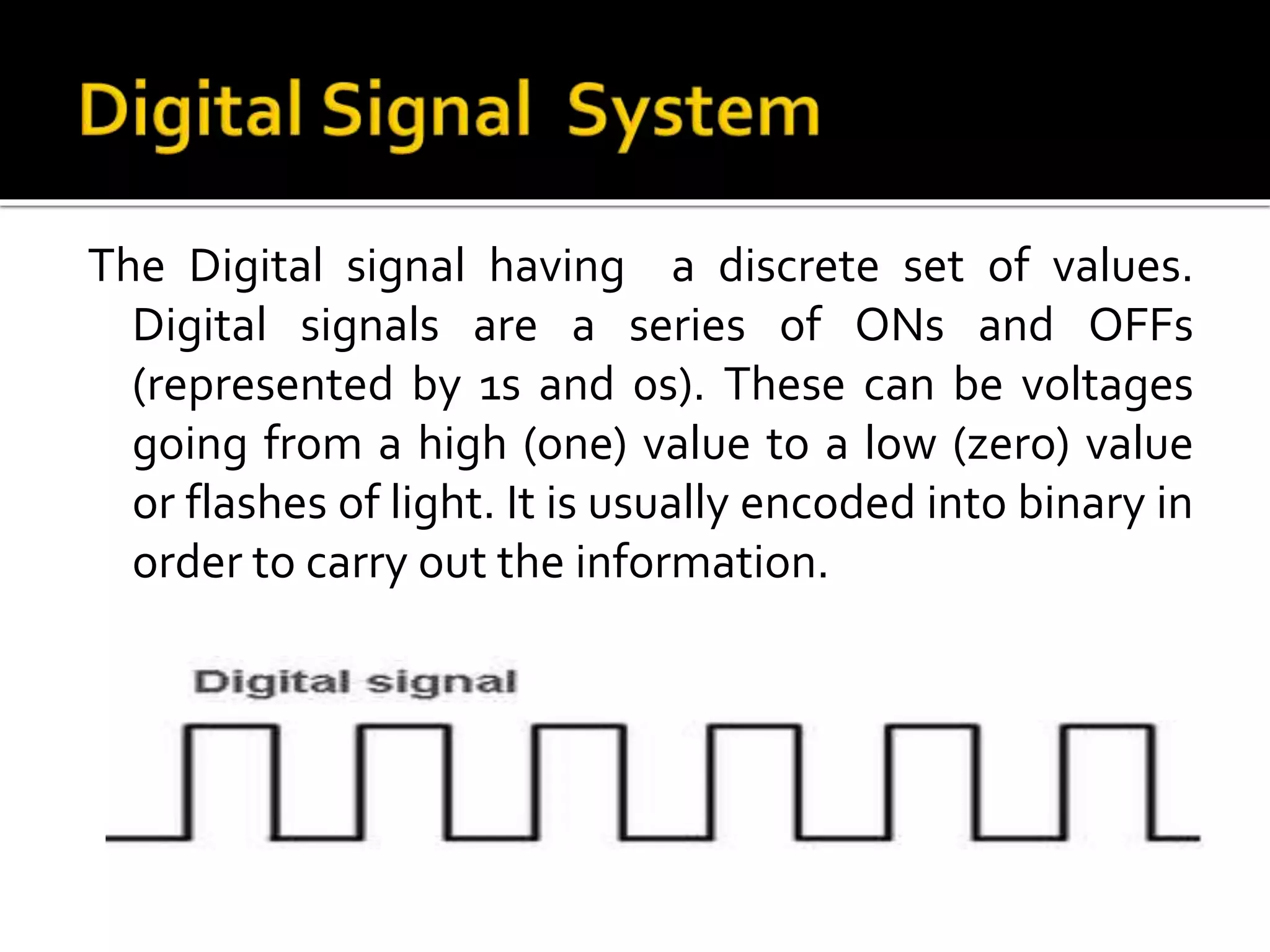
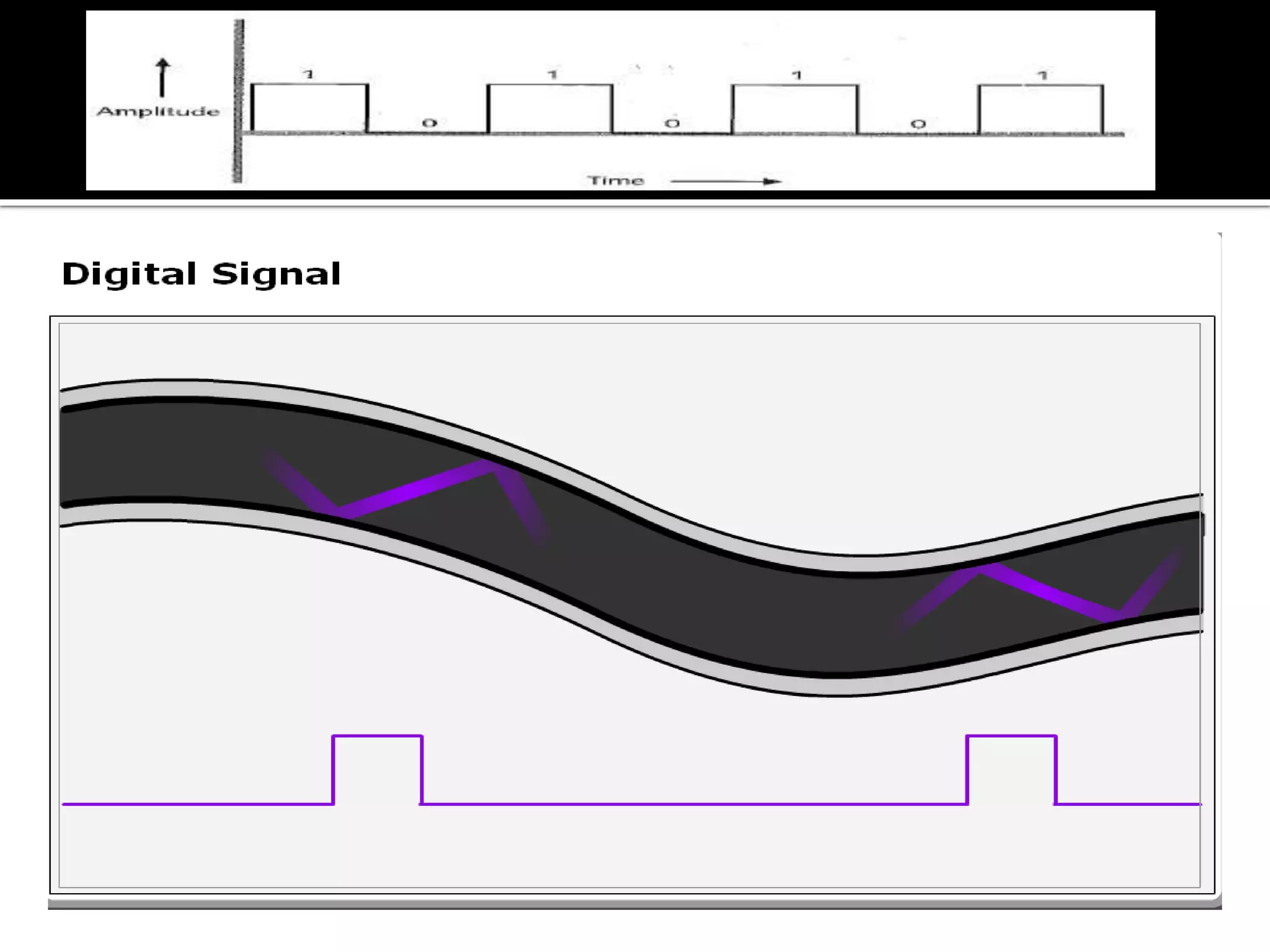


The document explains the differences between analog and digital signals, noting that analog signals represent continuous time-varying quantities and are specific, with lower accuracy compared to digital signals. Digital signals, on the other hand, are comprised of discrete values (0s and 1s), allowing for more efficient processing and greater versatility. Overall, digital signals outperform analog signals in accuracy and reliability.
Analog signals represent continuous natural phenomena. They measure values like frequency and earthquakes, but are task-specific and less accurate.
Analog signals represent continuous natural phenomena. They measure values like frequency and earthquakes, but are task-specific and less accurate.
Analog signals represent continuous natural phenomena. They measure values like frequency and earthquakes, but are task-specific and less accurate.
Digital signals consist of discrete values (1s and 0s), allowing efficient processing. They are versatile and more accurate than analog signals.
Digital signals consist of discrete values (1s and 0s), allowing efficient processing. They are versatile and more accurate than analog signals.









