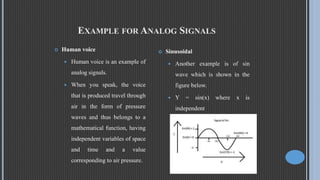
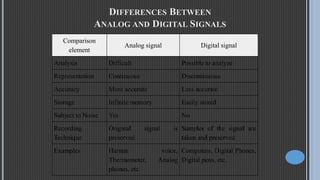
This document provides an overview of digital and analog signals and systems. It defines signals as functions that convey information over time or space. Analog signals are continuous while digital signals are discrete, represented by binary values. Digital signals are easier to analyze but less accurate than analog signals. Examples of analog signals include voices and sine waves, while digital signals include computer keyboards and digital phones. The document also defines systems as having signal inputs and outputs, with the input known as excitation and output as response.