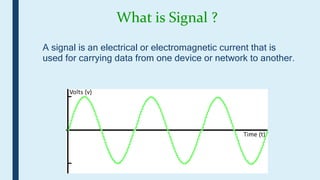
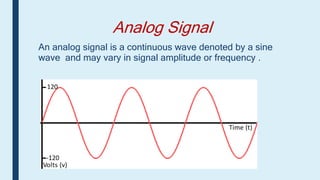
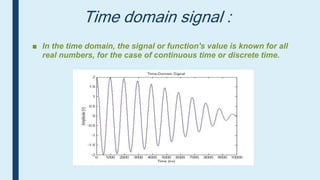
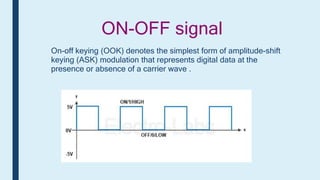
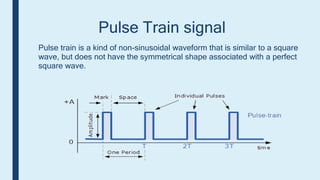
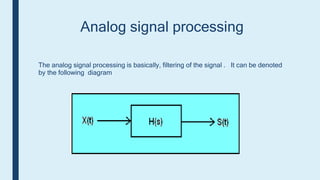
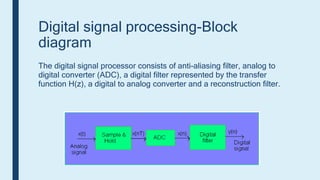
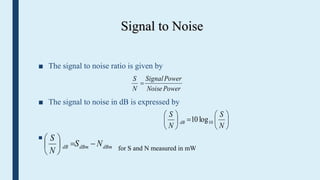
This document provides an introduction to signals for a presentation. It begins with welcoming the audience and introducing the presenters. It then defines what a signal is and describes the main types as analog and digital. It provides examples and classifications of different analog and digital signals. It discusses continuous and discrete time signals. It also includes block diagrams of analog and digital signal processing and defines signal to noise ratio. It concludes by comparing the advantages of analog versus digital signals.