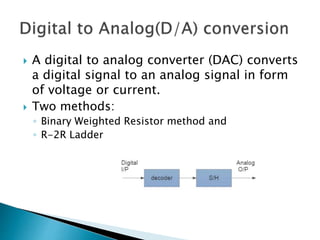
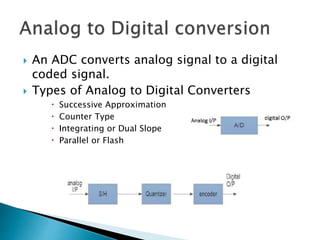
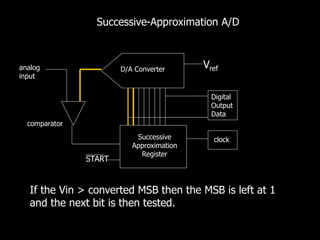
The document discusses Digital to Analog Converters (DAC) and Analog to Digital Converters (ADC), detailing methods such as binary weighted resistor and R-2R ladder for DACs and successive approximation for ADs. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each type, including construction simplicity and conversion speed for DACs, and accuracy and resolution for ADCs. Various ADC types are presented along with their sampling, quantizing, and encoding processes.