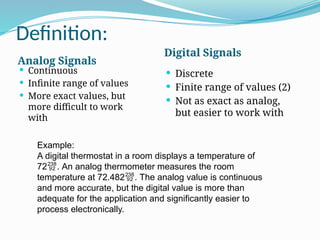
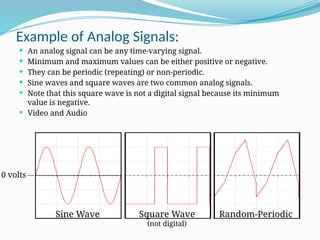
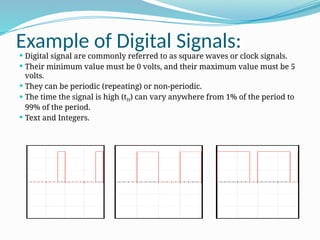
The document compares analog and digital signals, detailing their definitions, workings, examples, and pros and cons. Analog signals are continuous and more precise, while digital signals are discrete and easier to process, with digital having advantages in speed and data transfer capabilities, but requiring more bandwidth. Applications of analog include traditional telephones and thermometers, whereas digital applications include PCs and mobile phones.