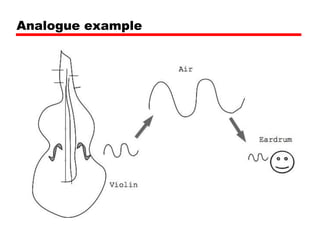
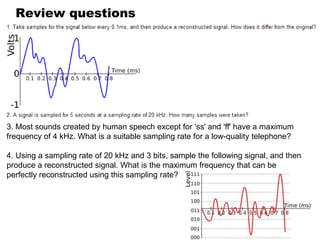
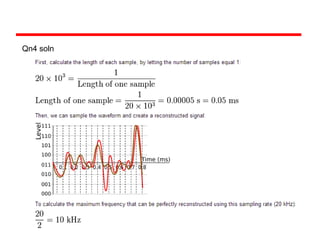
Digital and analogue systems process different types of signals. An analogue signal is continuous over time while a digital signal takes discrete values. Analogue signals are susceptible to noise but can convey any information, while digital signals are more tolerant of noise using error detection. Common examples of analogue systems are audio amplifiers and early telephone networks, while digital systems include computers using logic gates. The process of converting an analogue signal to digital involves sampling at a rate that captures the original signal, then reconstruction for playback.