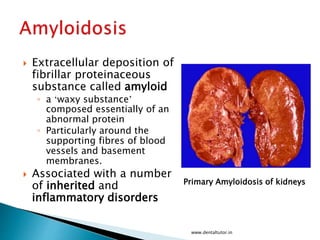
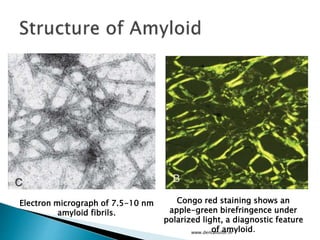
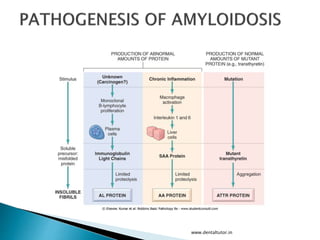
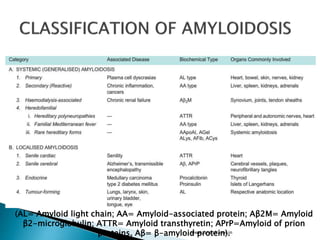
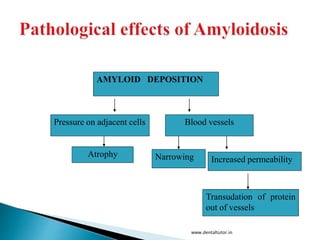
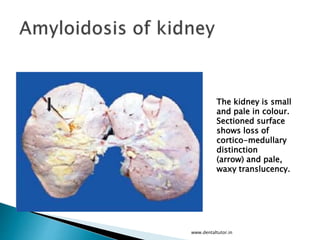
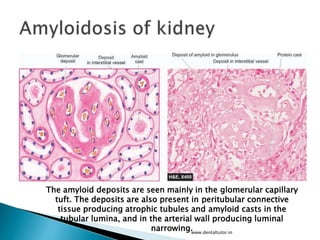
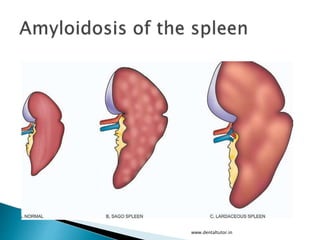
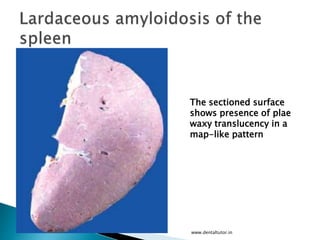
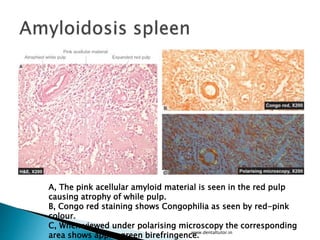
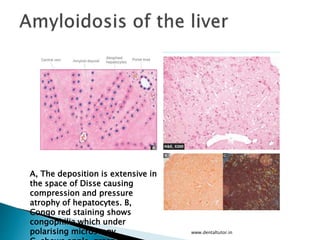
This document discusses amyloidosis, which is the extracellular deposition of abnormal protein fibrils called amyloid in tissues and organs. Amyloidosis can be primary, meaning the deposition is in the disease itself, or secondary, as a complication of another underlying disease. Diagnosis involves biopsy and staining of tissues with Congo red dye to detect amyloid deposits. The kidney is a commonly affected organ where amyloid deposits are seen in the glomerular capillary tuft and surrounding tissues, which can lead to atrophy and impaired function.