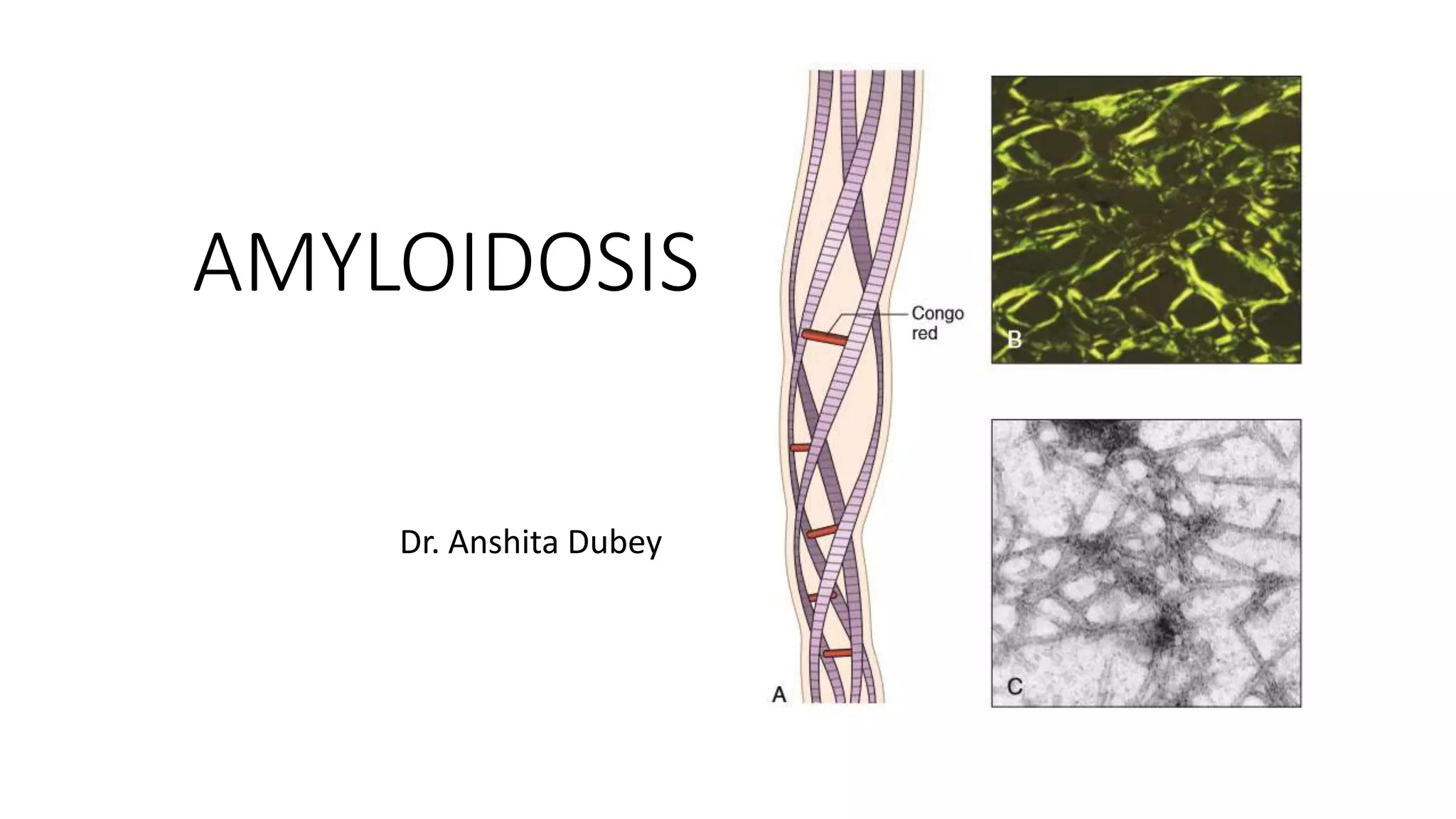
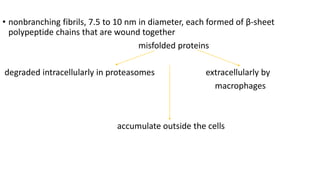
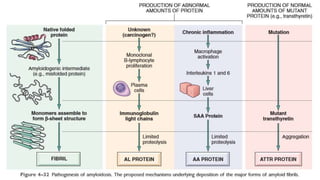
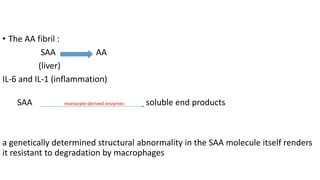
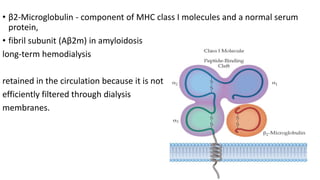
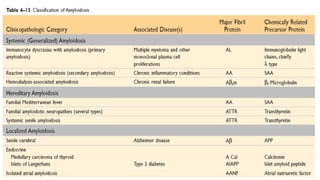
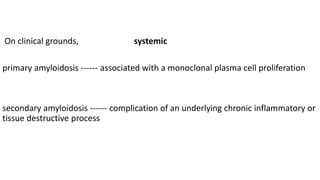
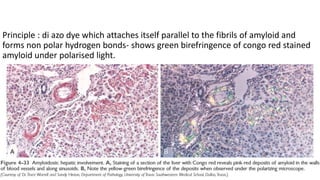
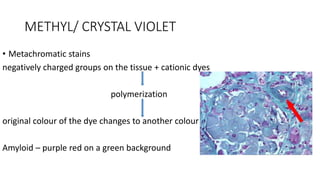
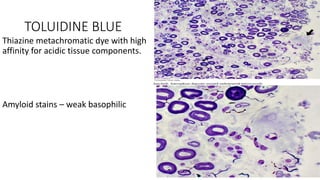
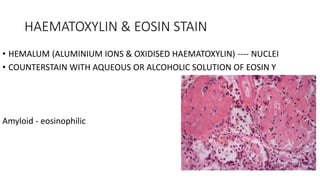
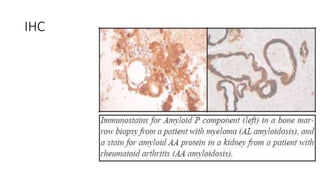
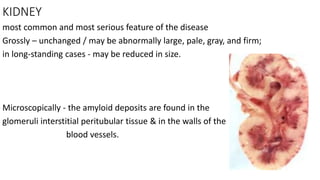
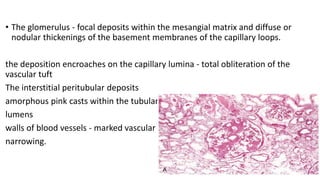
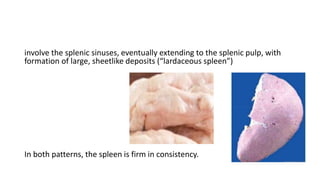
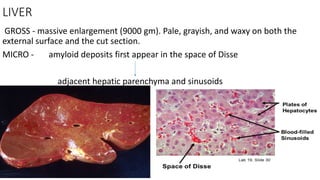
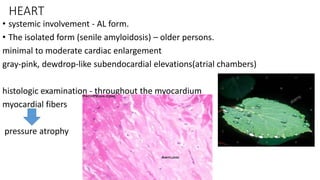
This document discusses amyloidosis, a condition caused by extracellular deposition of fibrillar proteins that can damage tissues. There are two main types - AL amyloidosis associated with plasma cell disorders and AA amyloidosis linked to inflammation. Common sites of deposition include kidneys, liver, spleen, and heart. Amyloid is identified on histology as an extracellular eosinophilic deposit that stains red with Congo red dye under polarized light. The deposits can obstruct organs over time and cause nonspecific symptoms. Biopsy with Congo red staining is important for diagnosis.