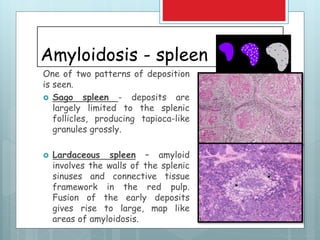
This document provides an overview of amyloidosis, including:
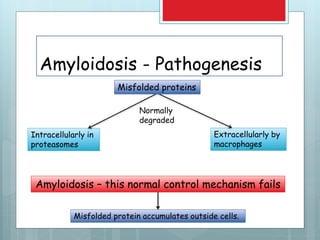
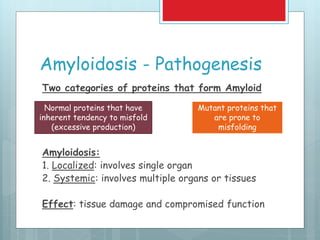
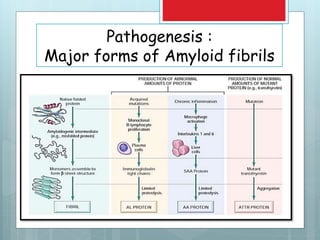
- Amyloidosis is characterized by extracellular deposition of misfolded proteins that form insoluble fibrils, damaging tissues.
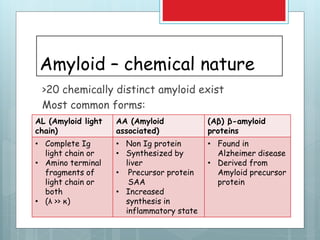
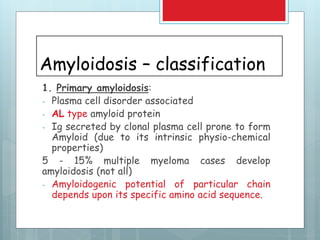
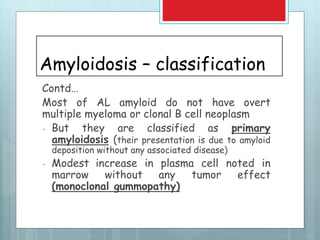
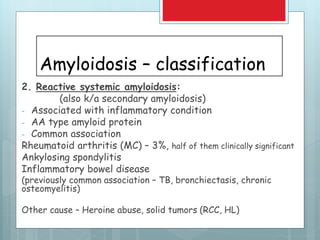
- There are different types classified by the misfolded protein involved, including AL, AA, and rare forms.
- Organs commonly affected include the kidney, heart, GI tract, and nerves.
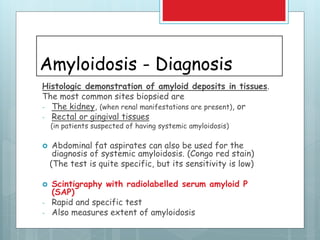
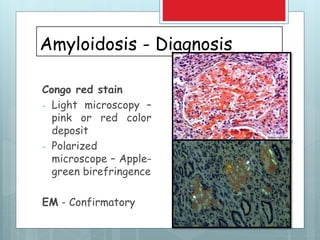
- Diagnosis involves biopsy of affected tissues and staining with Congo red to identify amyloid deposits.
- Prognosis depends on type and organ involvement, with generalized amyloidosis having a poor prognosis of around 2 years.







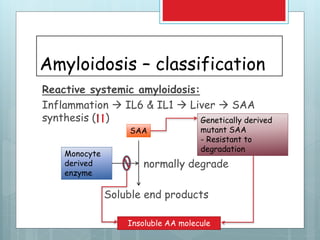
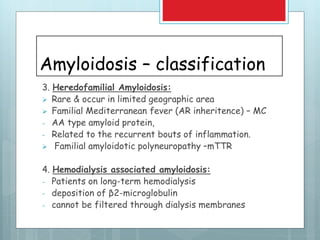


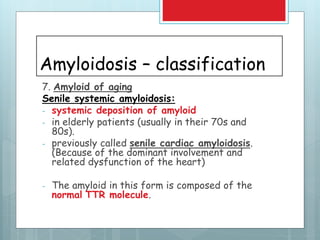
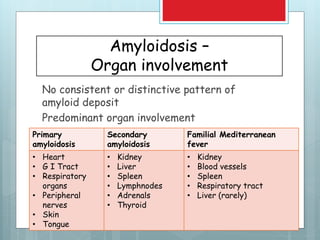
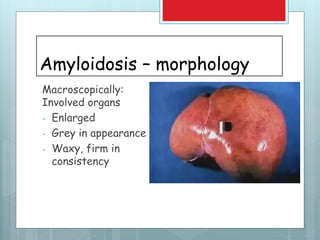
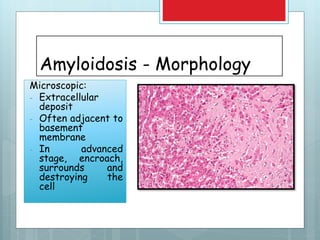
![Amyloidosis - kidney
Most common and
potentially most serious
form of organ
involvement
Gross – normal or
shrunken [due to ischemia
(vascular narrowing) in
advanced stage]
Microscopy – glomerular
deposit, interstitial,
peritubular, arterial wall
deposit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/amyloidosis-191122174858/85/AMYLOIDOSIS-23-320.jpg)