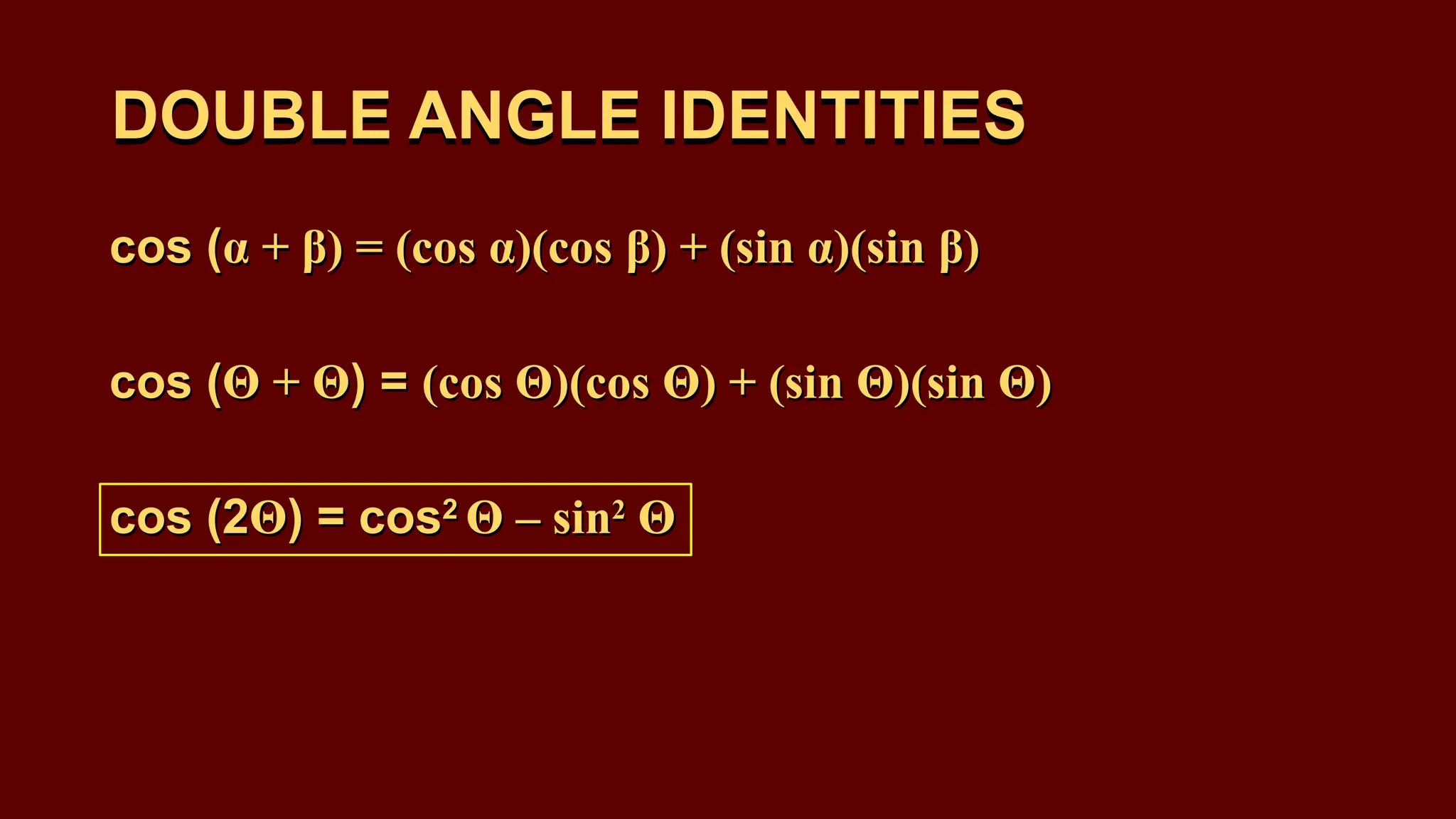
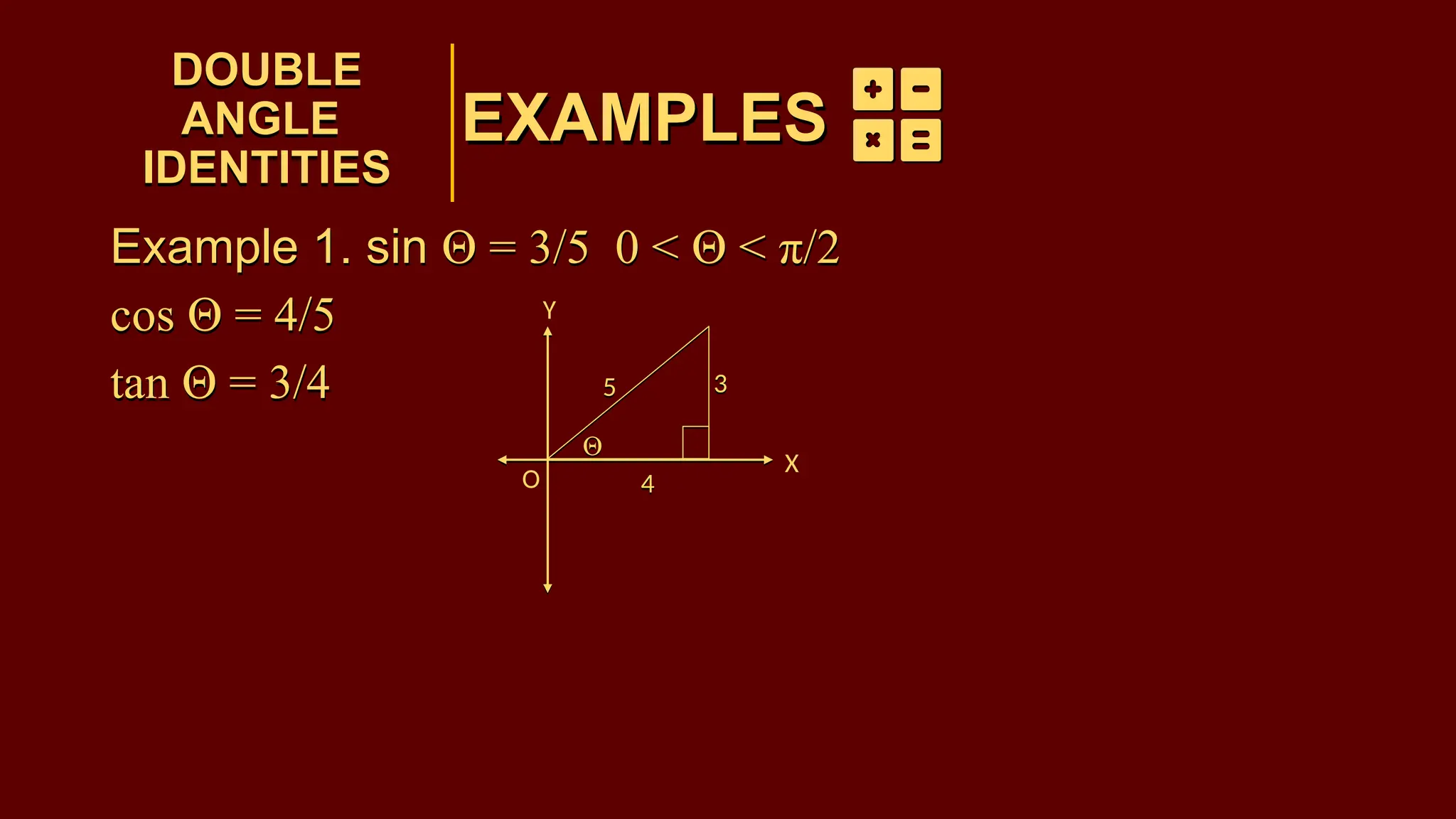
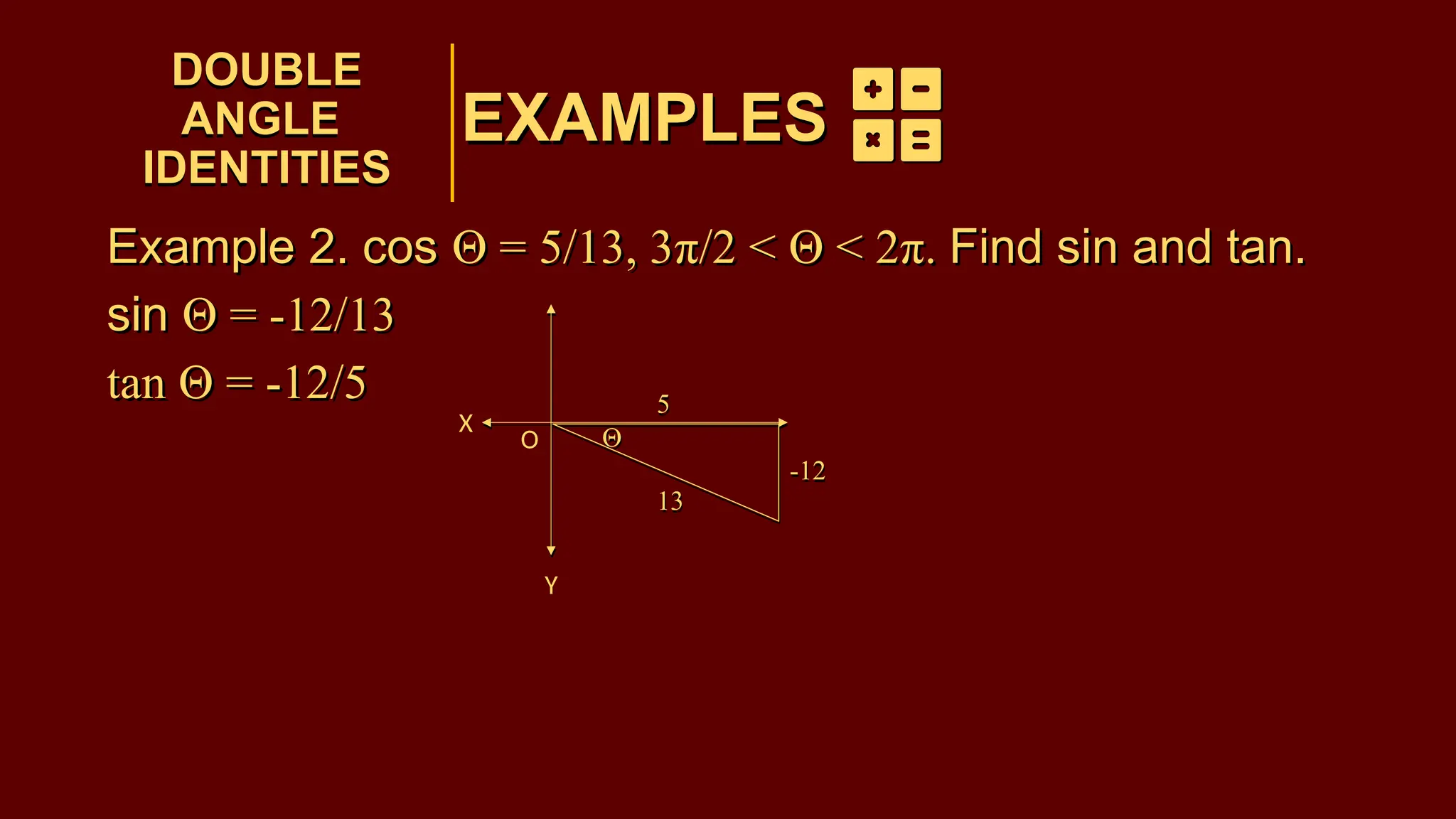
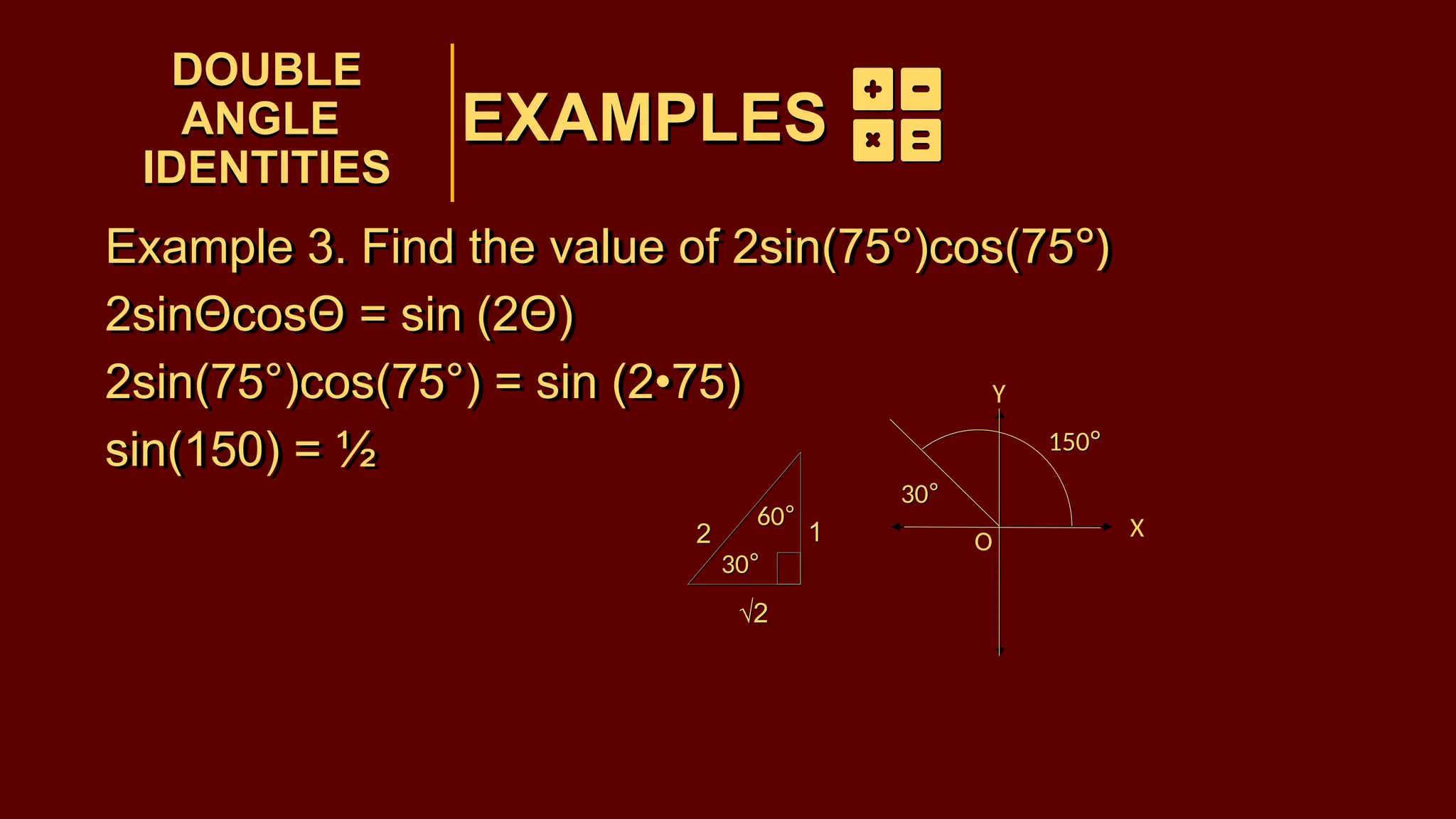
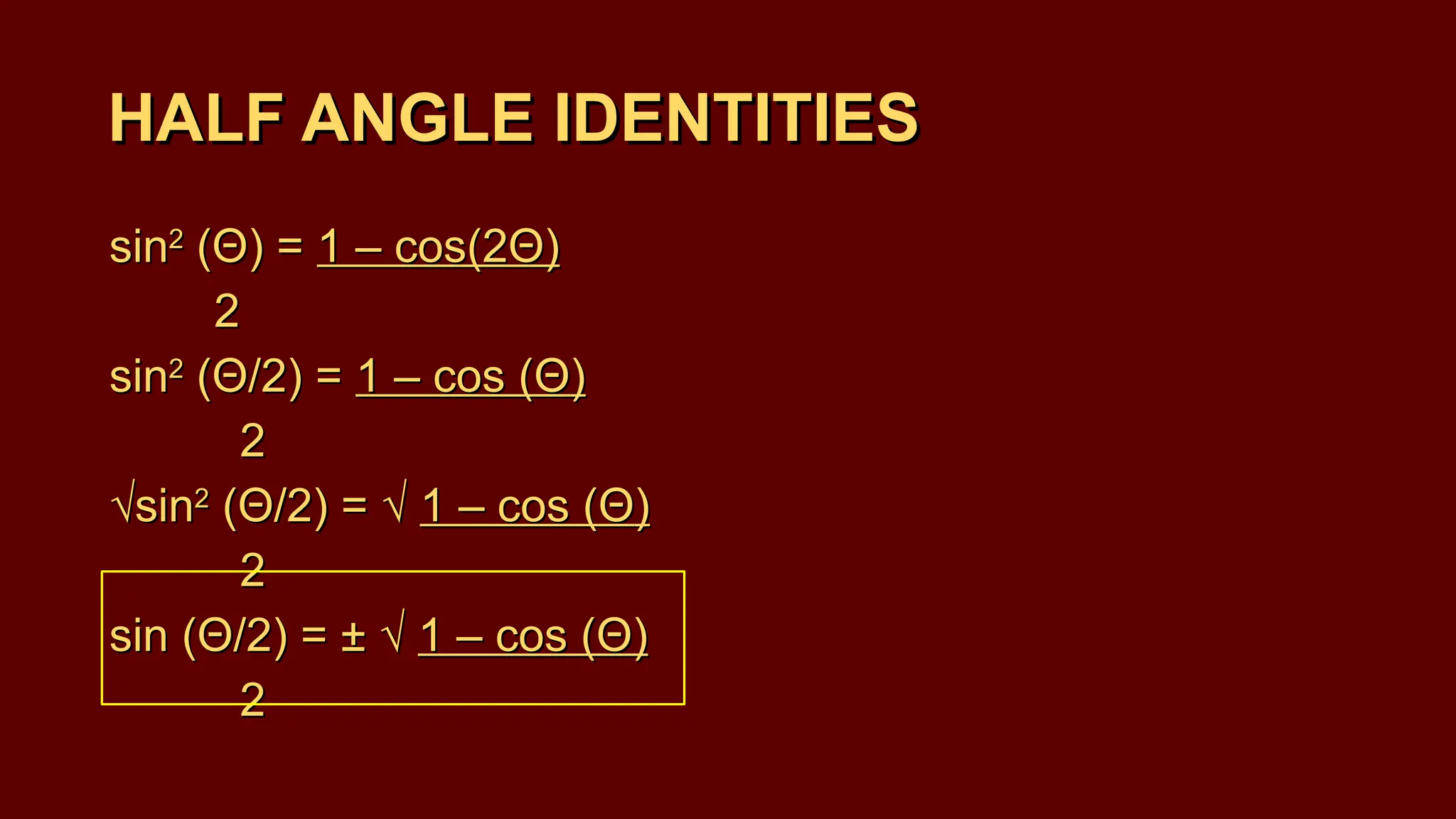
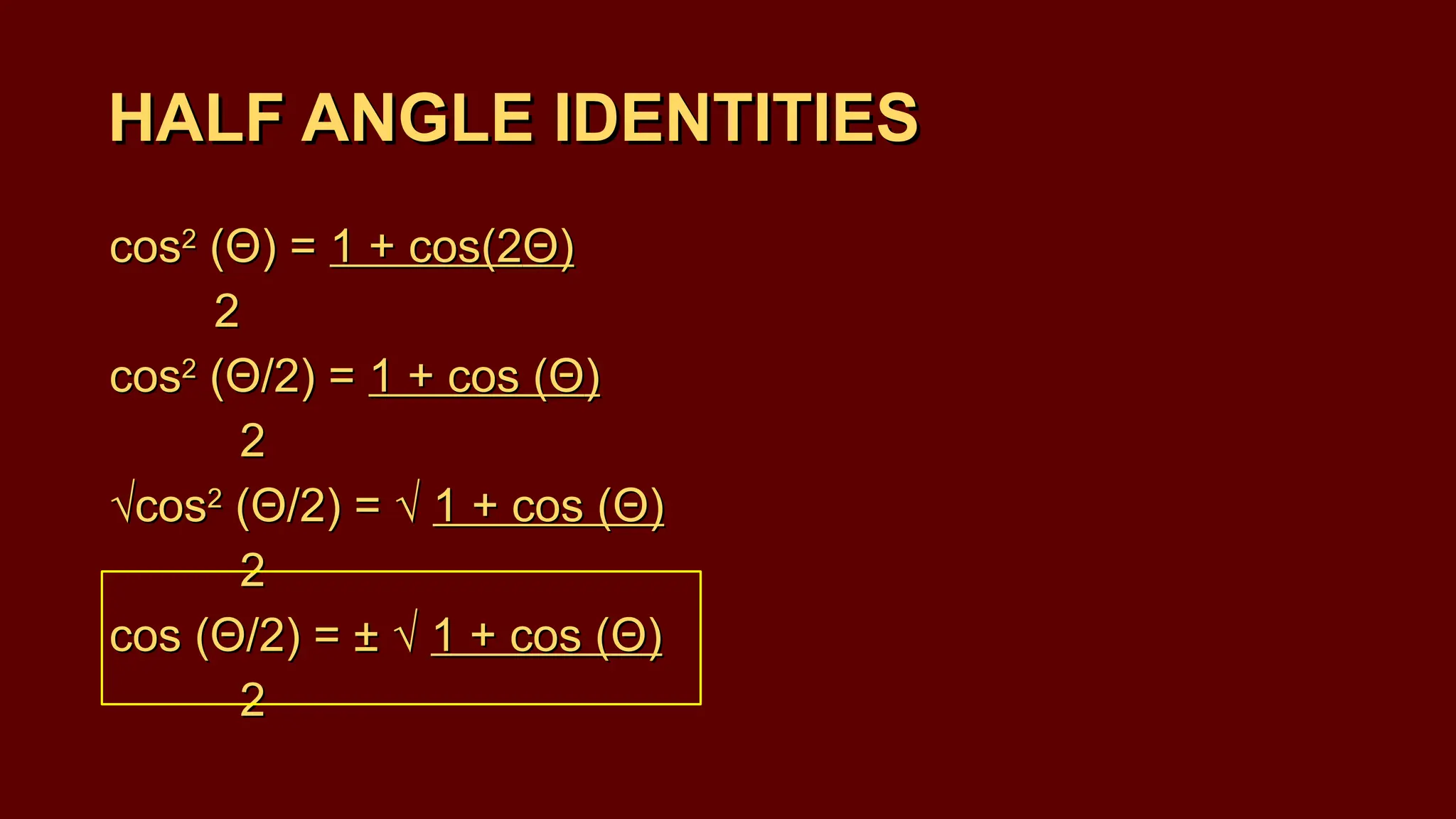
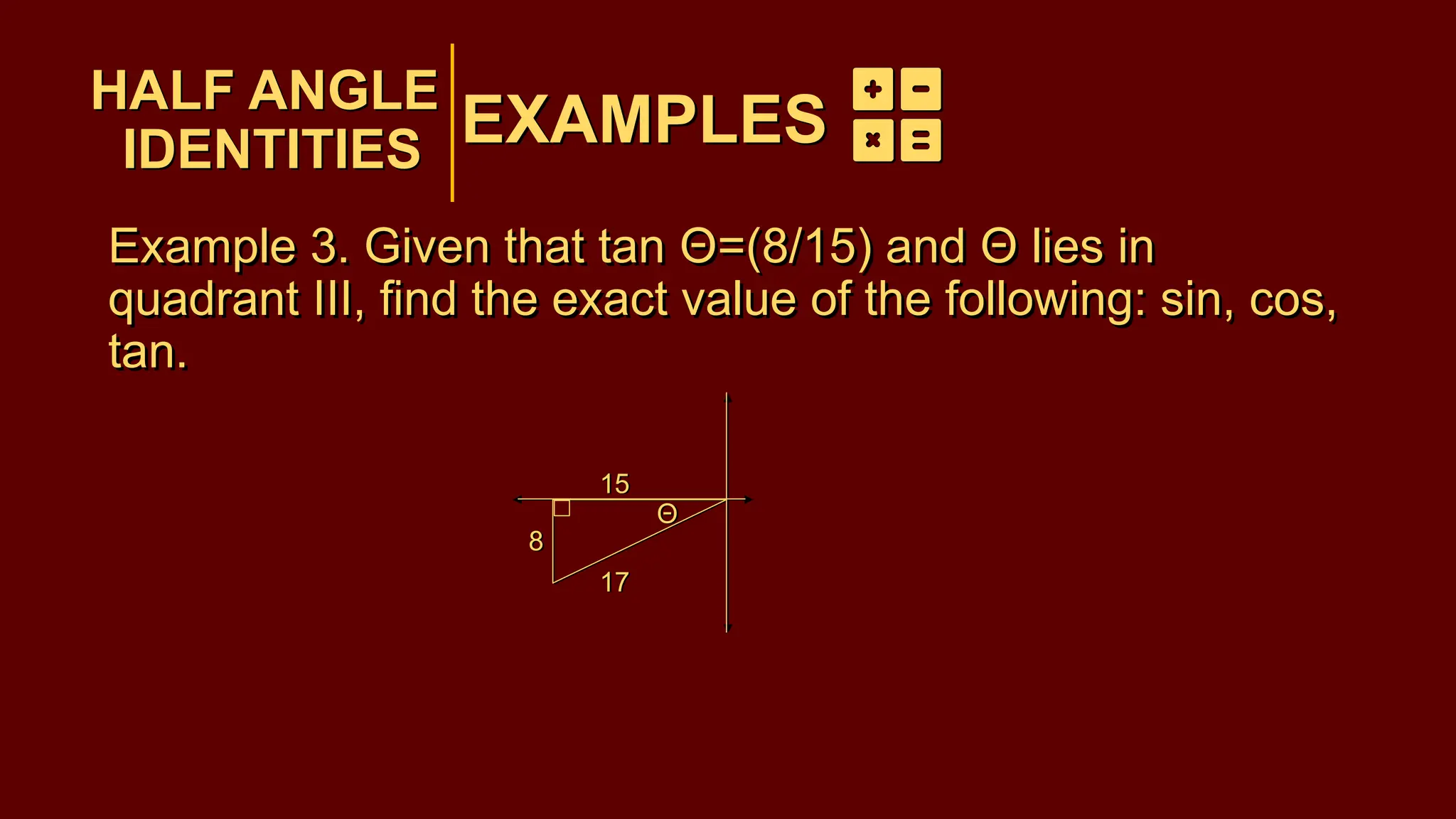
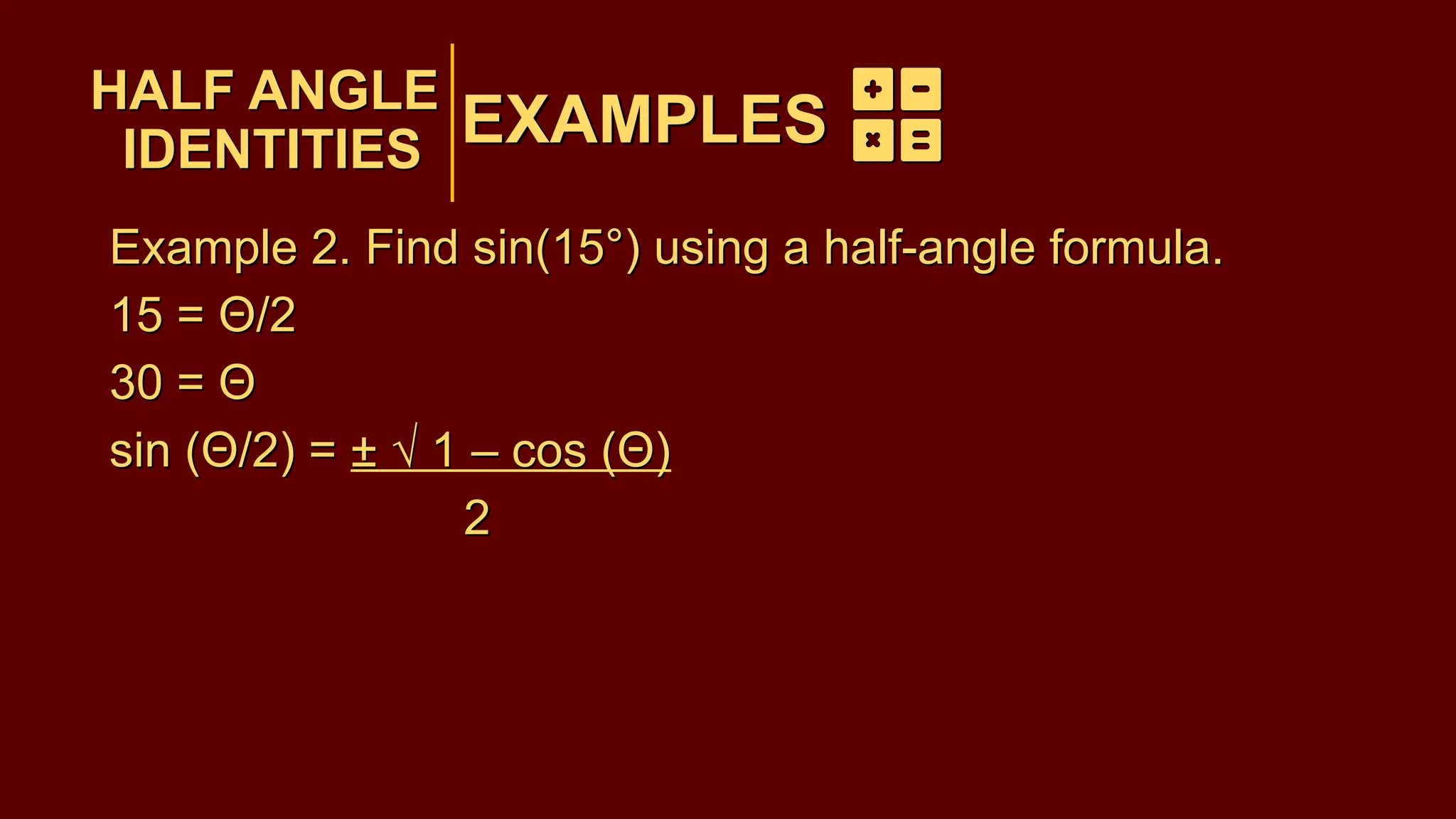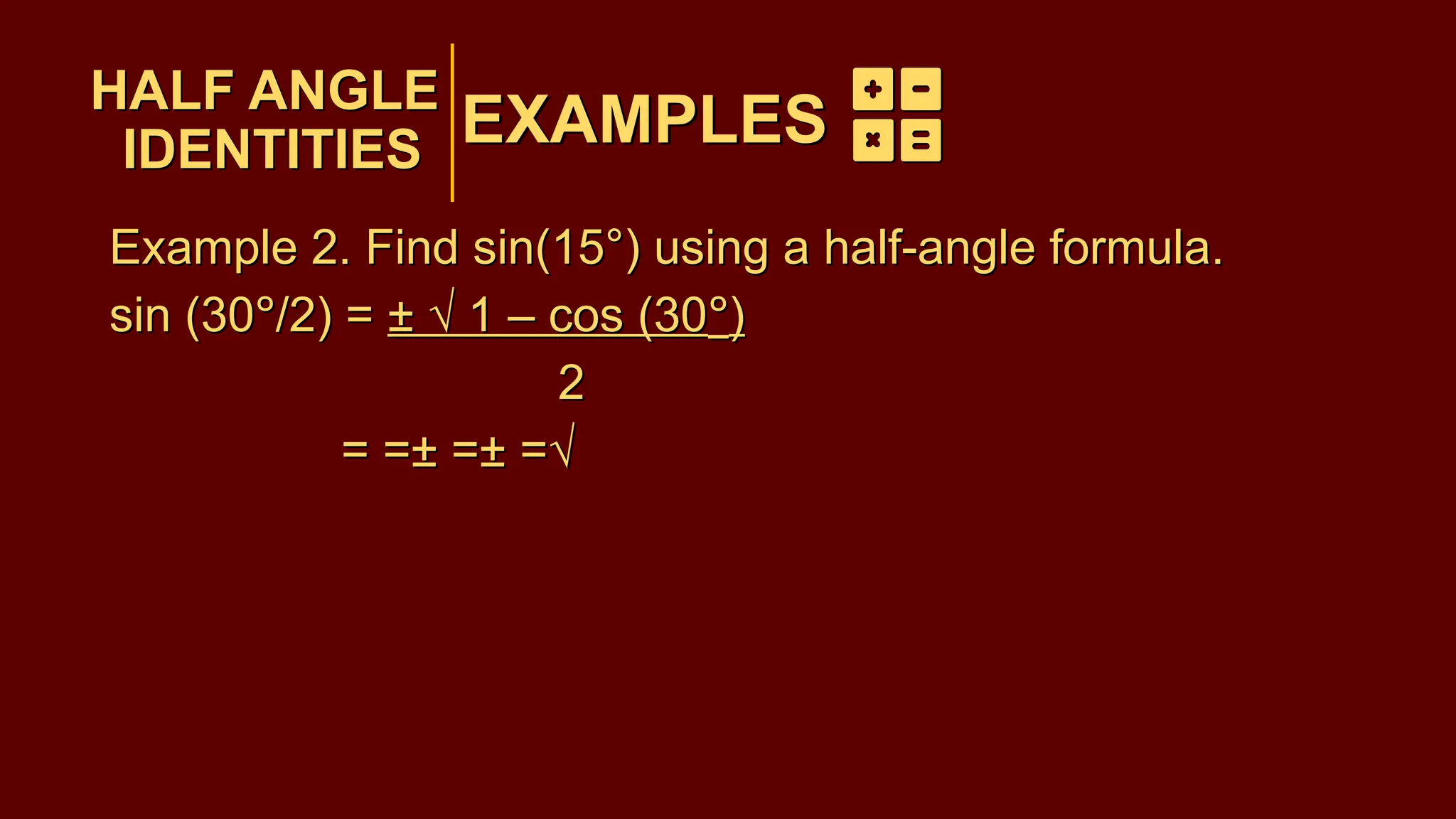The document covers half-angle and double-angle identities in trigonometry, detailing their definitions, formulas, and applications. It provides multiple examples illustrating how to use these identities to calculate sine, cosine, and tangent for various angles. Additionally, the document includes practice problems to reinforce understanding of these concepts.