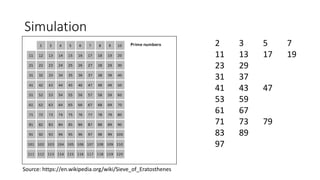
This document discusses prime numbers and the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm for finding prime numbers. It defines a prime number as a whole number greater than 1 that is only divisible by 1 and itself. It then presents an approach to determine if a number is prime or composite by checking if it has any smaller factors. Finally, it provides pseudocode and a C++ implementation of the Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithm, which involves iteratively marking as composite the multiples of each prime, producing the primes sequentially.





![C++ Code
#include<stdio.h>
int p = 999;
bool prime[1000];
int main(){
int i,c=0;
generatePrime();
for(i=2;i<=100;i++){
if(prime[i]){
printf("%d ",i);
c++;
}
}
printf("nPrime: %d",c);
return 0;
}
void generatePrime(){
int i,j;
prime[0]=prime[1]=false;
for(i=2;i<=p;i++)
prime[i]=true;
for(i=2;i*i<=p;i++){
if(prime[i]){
for(j=i*i;j<=p;j+=i)
prime[j]=false;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/primenumber-180407061339/85/Prime-Number-Sieve-7-320.jpg)


