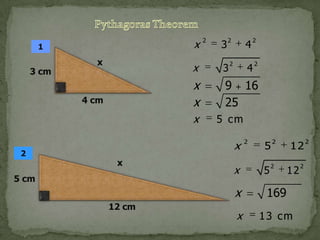
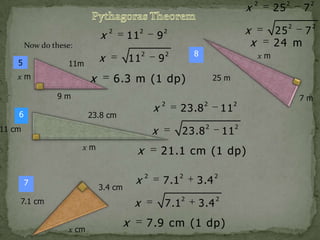
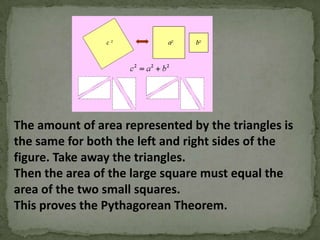
Pythagoras was an ancient Greek philosopher and mathematician born on the island of Samos in around 570 BC. He is best known for the Pythagorean theorem, which states that for any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. While Pythagoras likely did not discover this theorem himself, he is credited as being the first to prove why it is true. The Pythagorean theorem is one of the earliest and most important theorems in mathematics.




![Pythagoras of Samos (Ancient Greek: Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος
[Πυθαγόρης in Ionian Greek] Pythagóras ho Sámios "Pythagoras
the Samian", or simply Πυθαγόρας; b. about 570 – d. about 495
BC)[1][2] was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and
founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of
the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after
he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him. He
was born on the island of Samos, and might have travelled widely in
his youth, visiting Egypt and other places seeking knowledge.
Around 530 BC, he moved to Croton, a Greek colony in southern
Italy, and there set up a religious sect. His followers pursued the
religious rites and practices developed by Pythagoras, and studied his
philosophical theories. The society took an active role in the politics
of Croton, but this eventually led to their downfall. The Pythagorean
meeting-places were burned, and Pythagoras was forced to flee the
city. He is said to have ended his days in Metapontum.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythagorastheorem-140104033945-phpapp01/85/Pythagoras-theorem-5-320.jpg)
![Pythagoras made influential contributions to philosophy and
religious teaching in the late 6th century BC. He is often revered
as a great mathematician, mystic and scientist, but he is best
known for the Pythagorean theorem which bears his name.
However, because legend and obfuscation cloud his work even
more than that of the other pre-Socratic philosophers, one can
give only a tentative account of his teachings, and some have
questioned whether he contributed much
to mathematics and natural philosophy. Many of the
accomplishments credited to Pythagoras may actually have been
accomplishments of his colleagues and successors. Whether or
not his disciples believed that everything was related to
mathematics and that numbers were the ultimate reality is
unknown. It was said that he was the first man to call himself a
philosopher, or lover of wisdom,[3] and Pythagorean ideas
exercised a marked influence on Plato, and through him, all
of Western philosophy.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythagorastheorem-140104033945-phpapp01/85/Pythagoras-theorem-6-320.jpg)