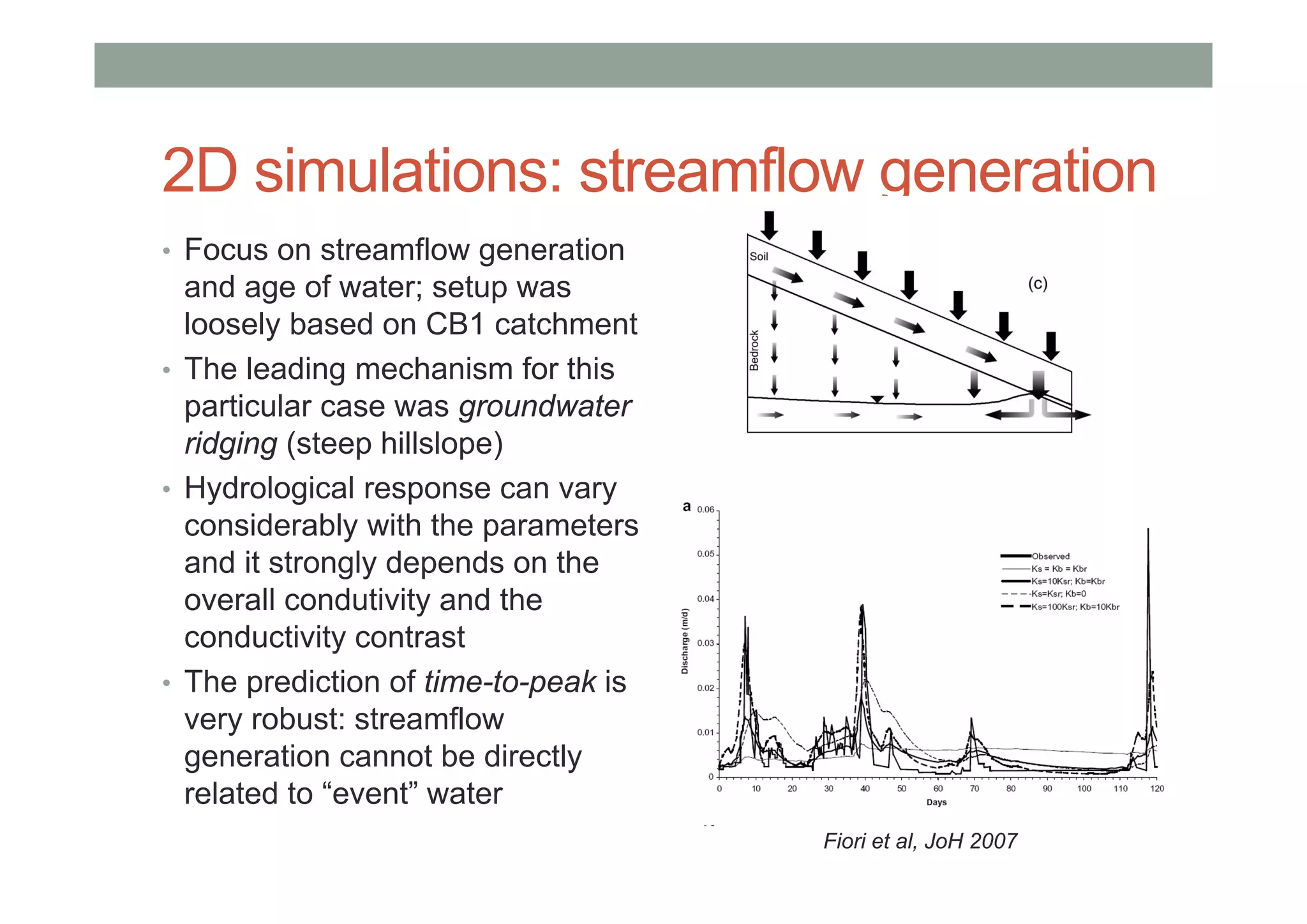
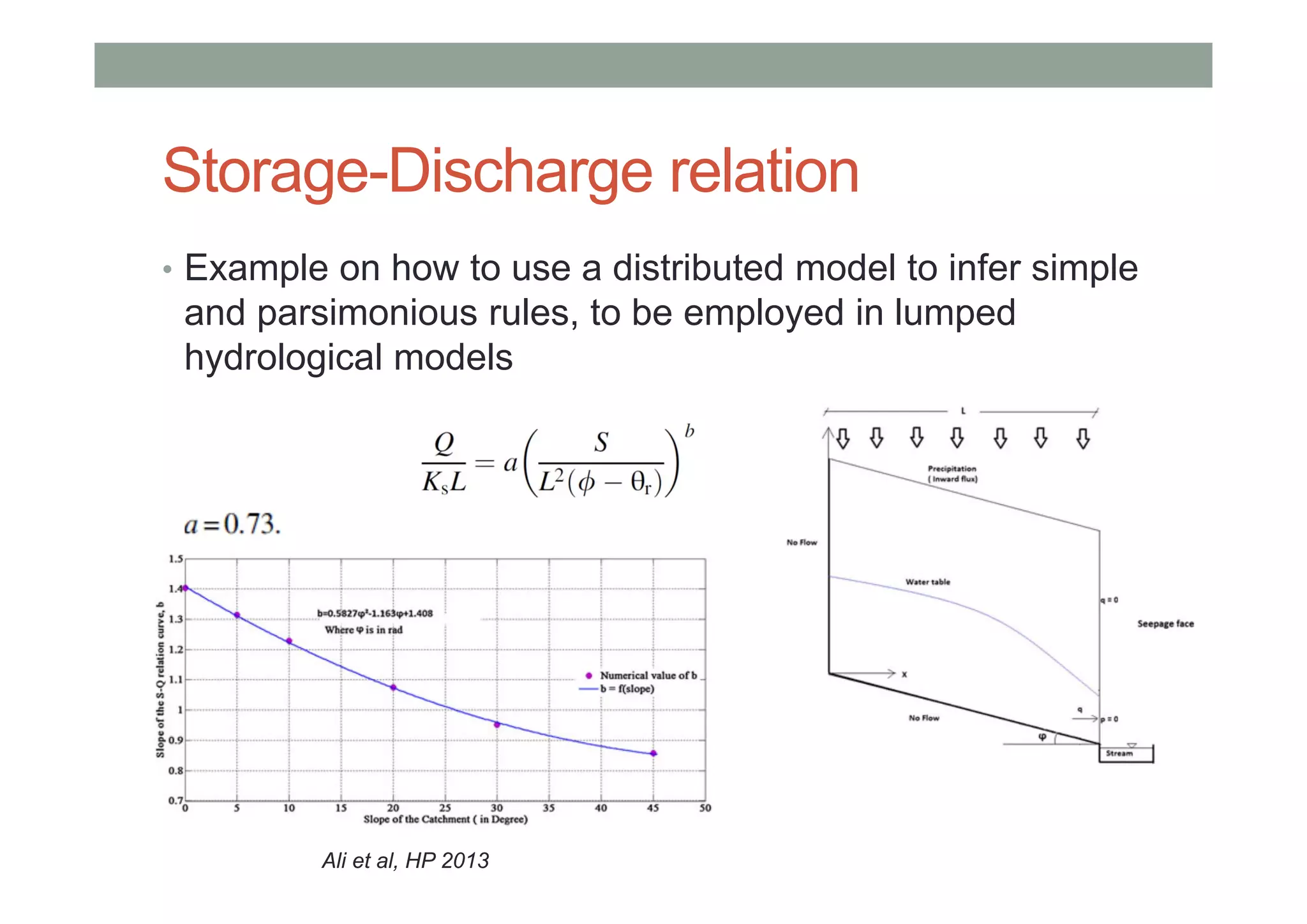
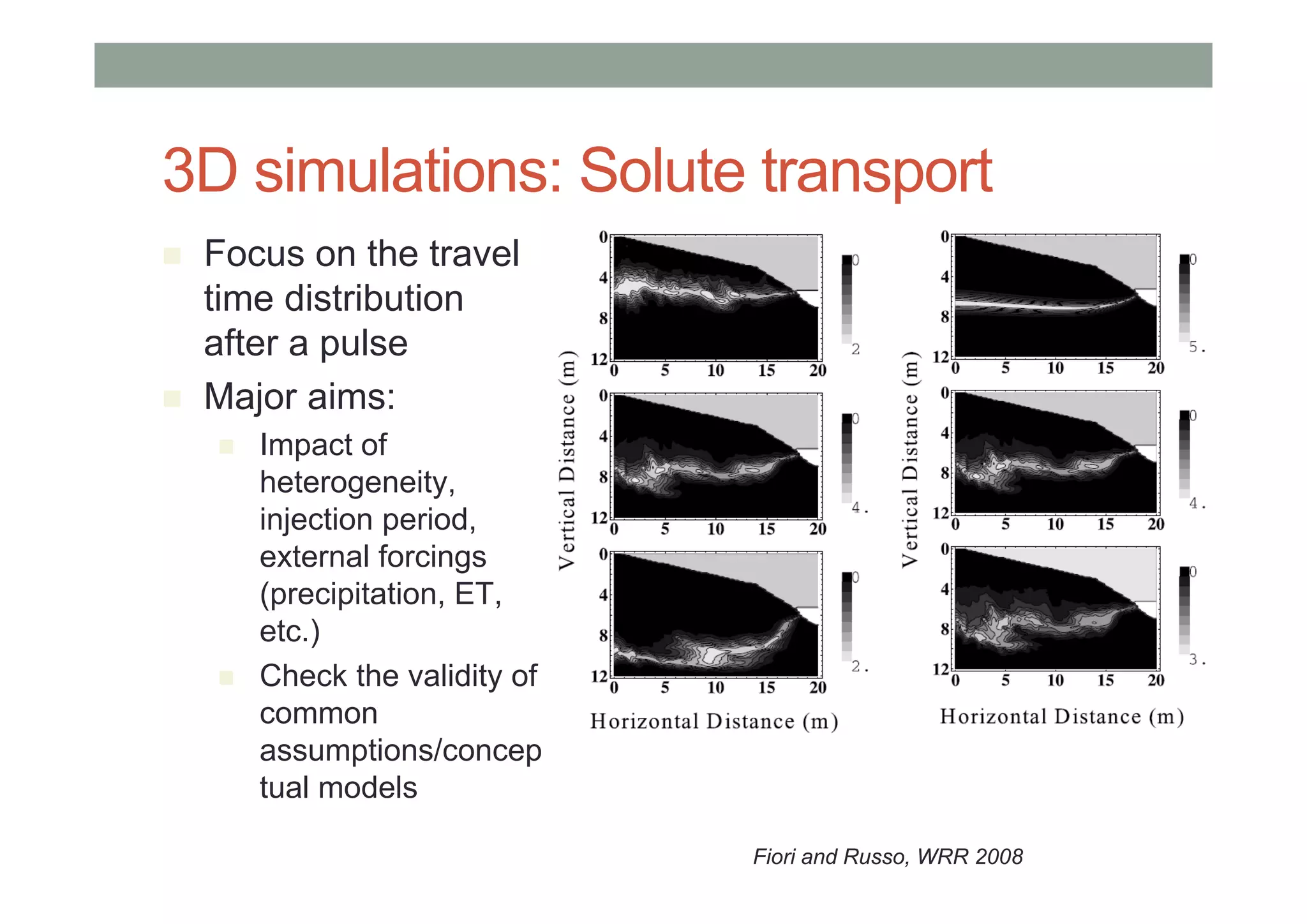
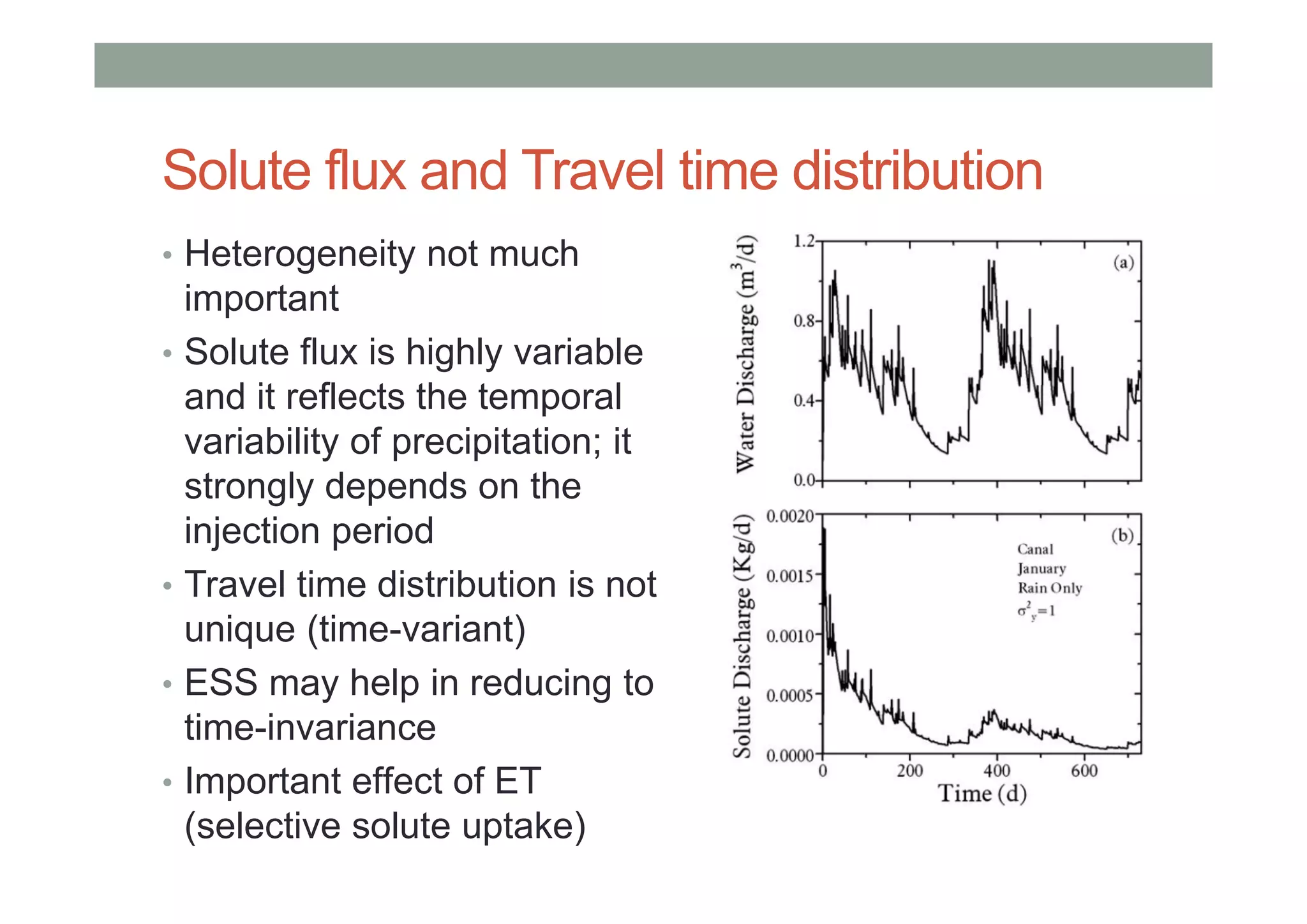
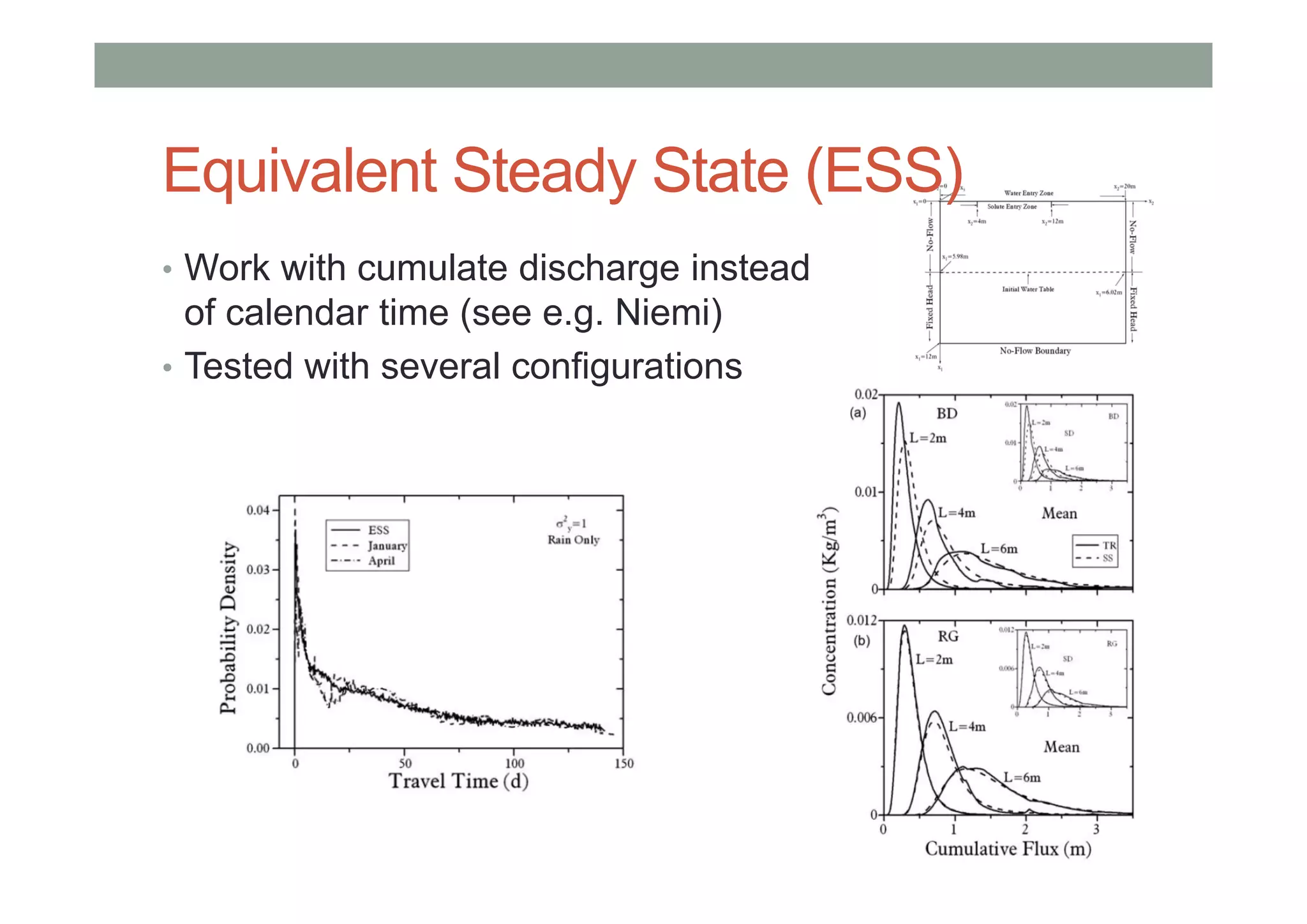
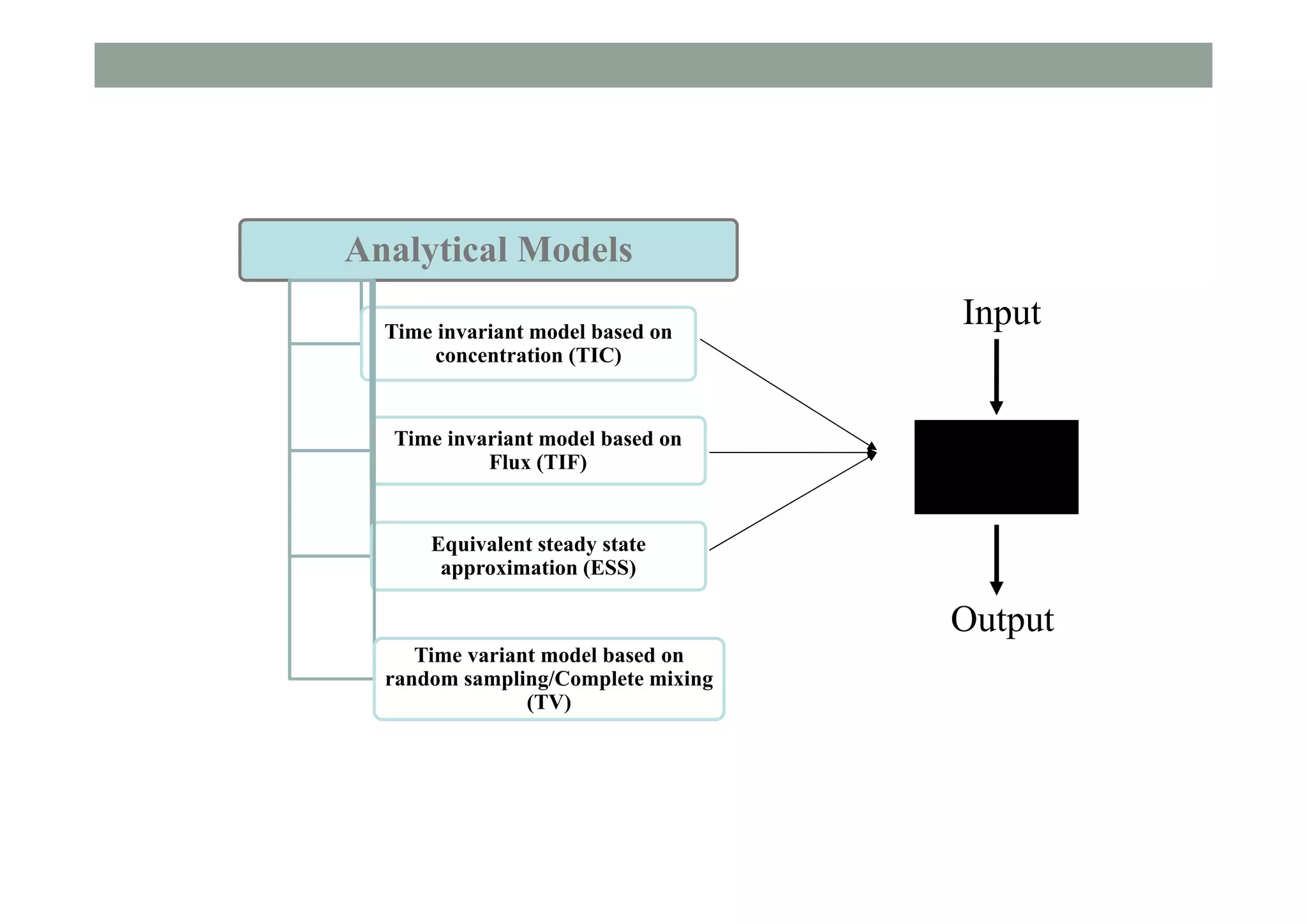
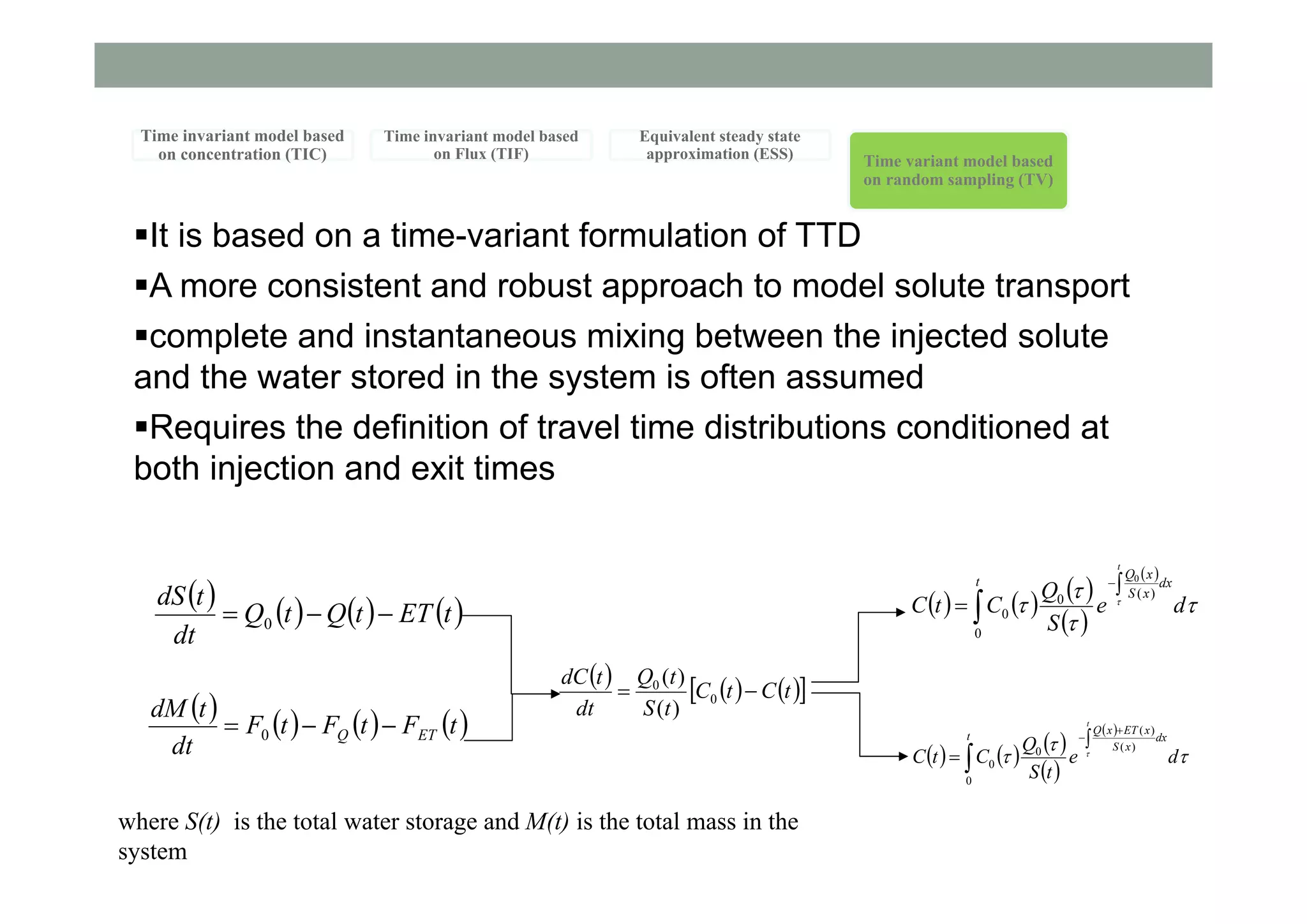
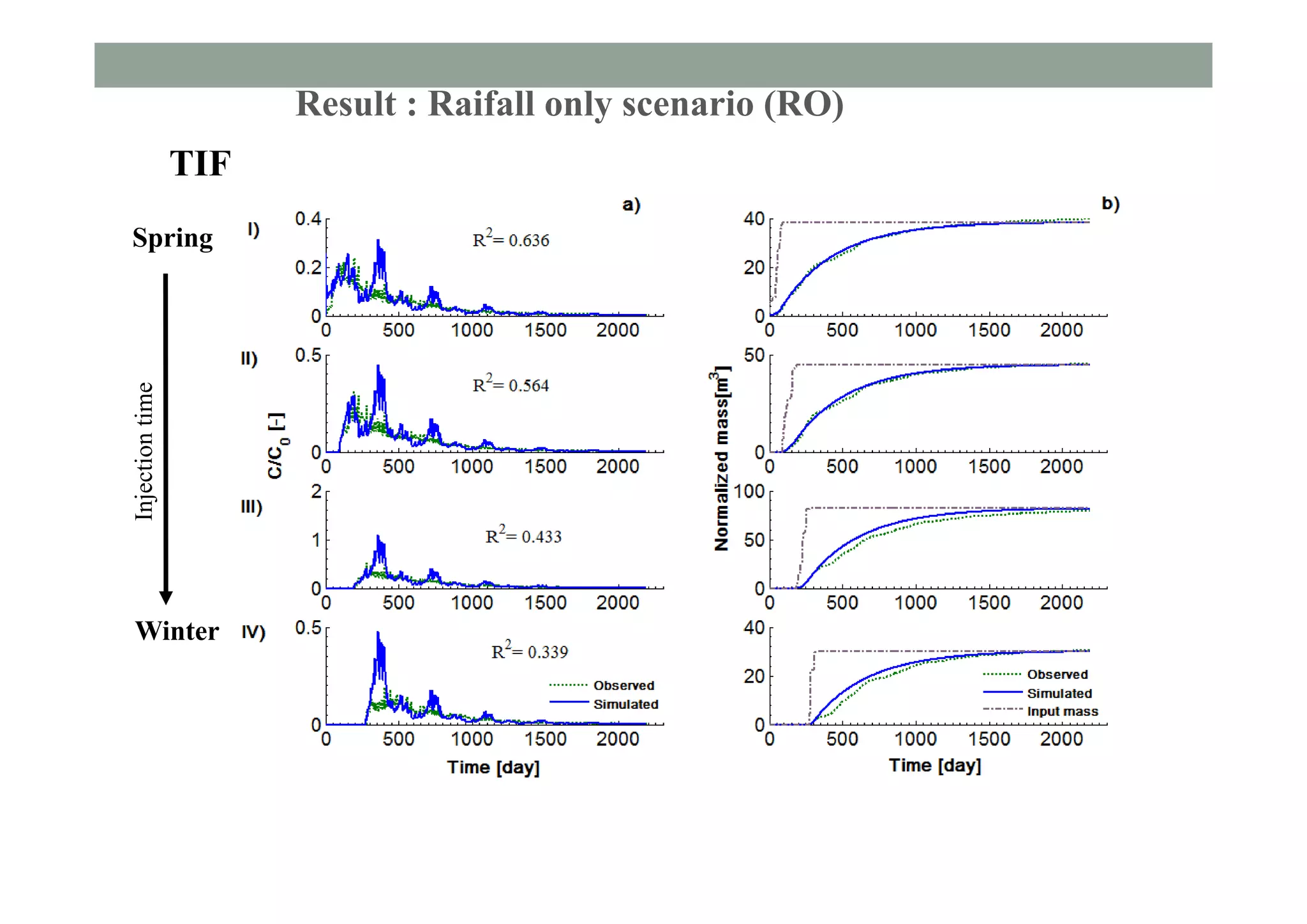
This document summarizes lessons learned from physically-based hydrological models. It discusses how distributed hydrological models can be useful tools for understanding processes like streamflow generation, solute transport, and groundwater-surface water interactions through detailed numerical simulations. While complex models may not be suited for predictions, they can serve as virtual laboratories for testing hypotheses. 2D and 3D simulations discussed provide insights into mechanisms of streamflow generation, the old water contribution to streams, and the impact of heterogeneity on solute transport. Simpler models that are less realistic but more generalizable, like the Boussinesq model, can also provide useful understanding when calibrated against more complex simulations. The document evaluates the performance of lumped transport models representing