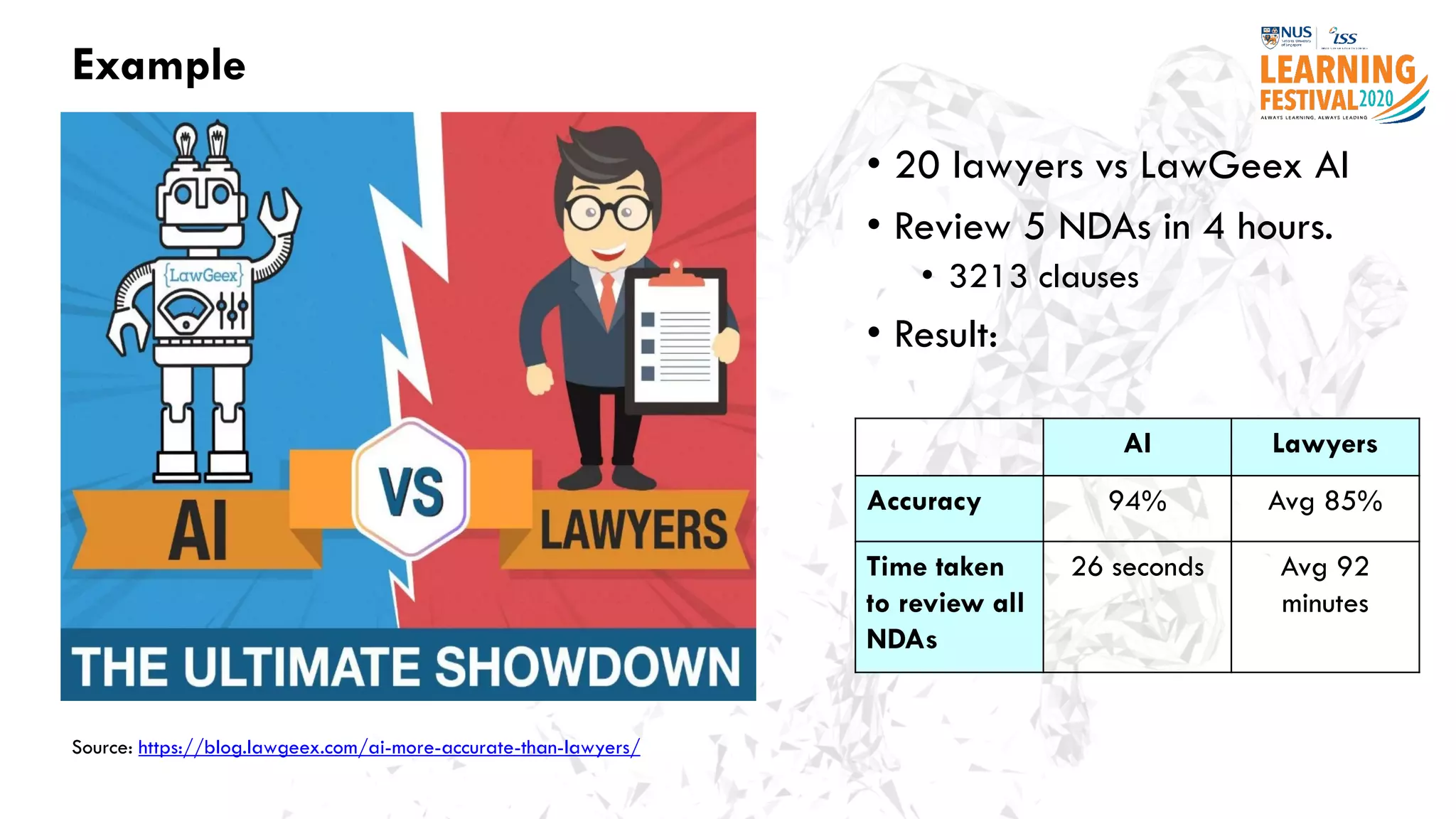
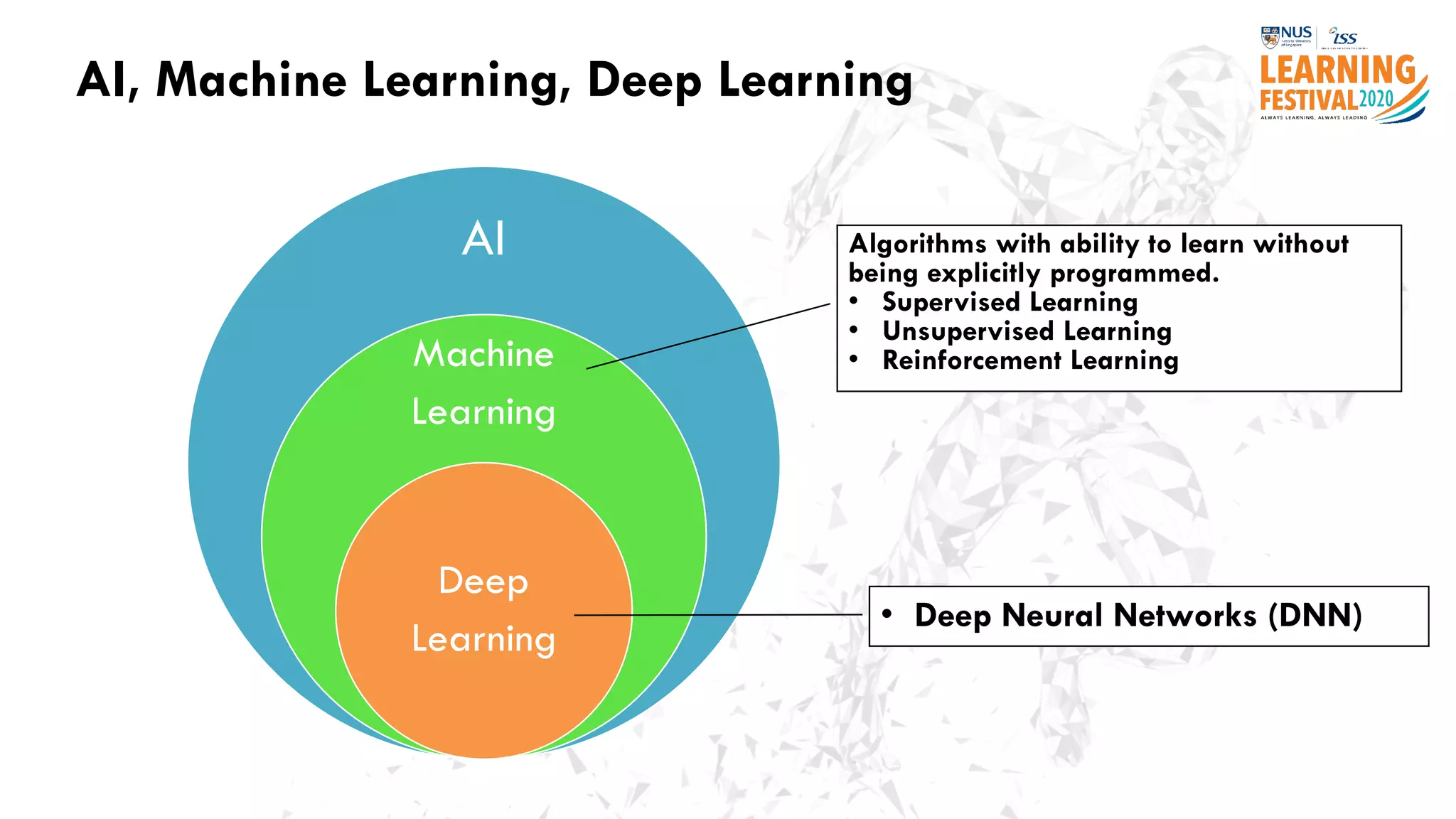
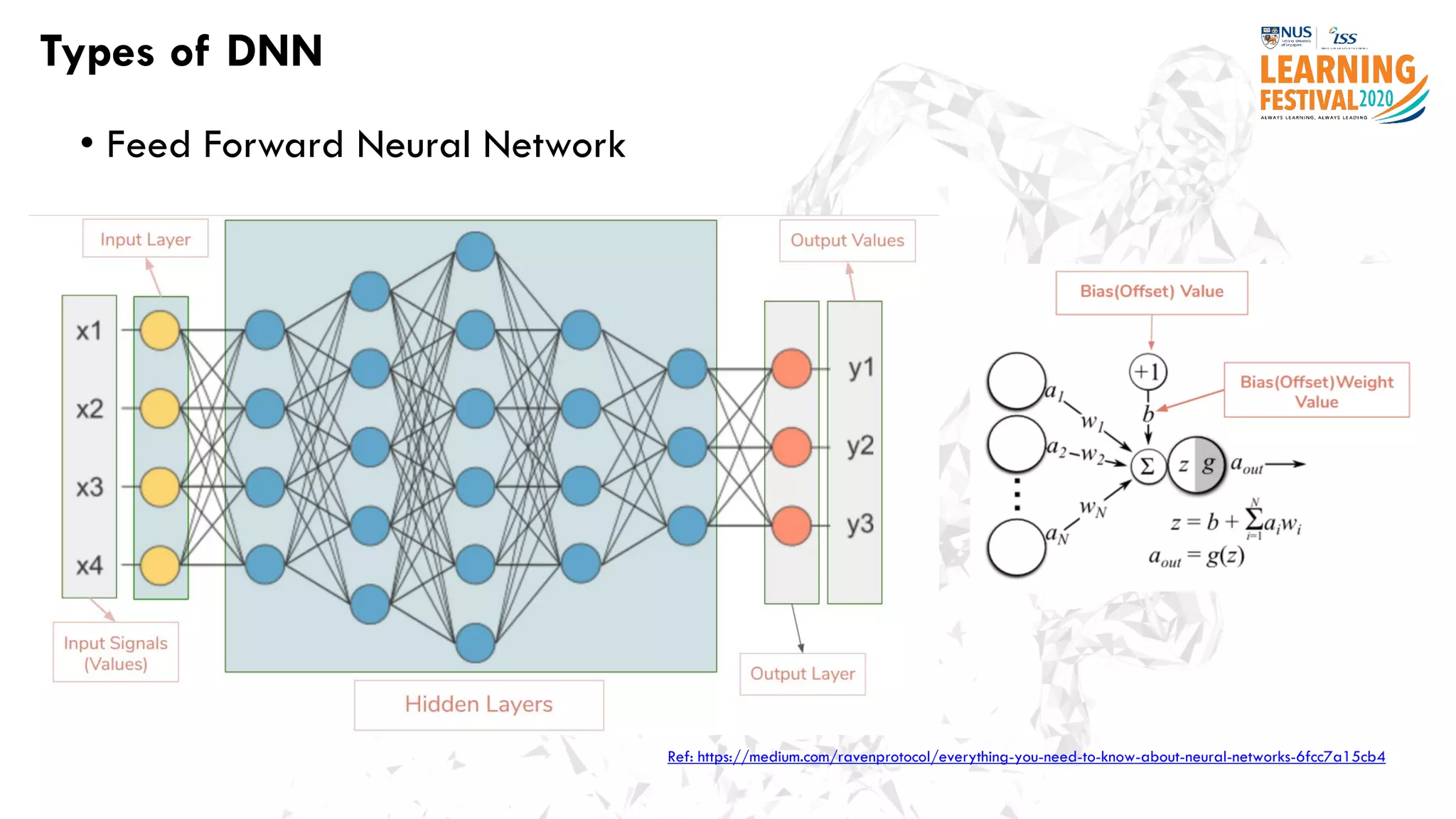
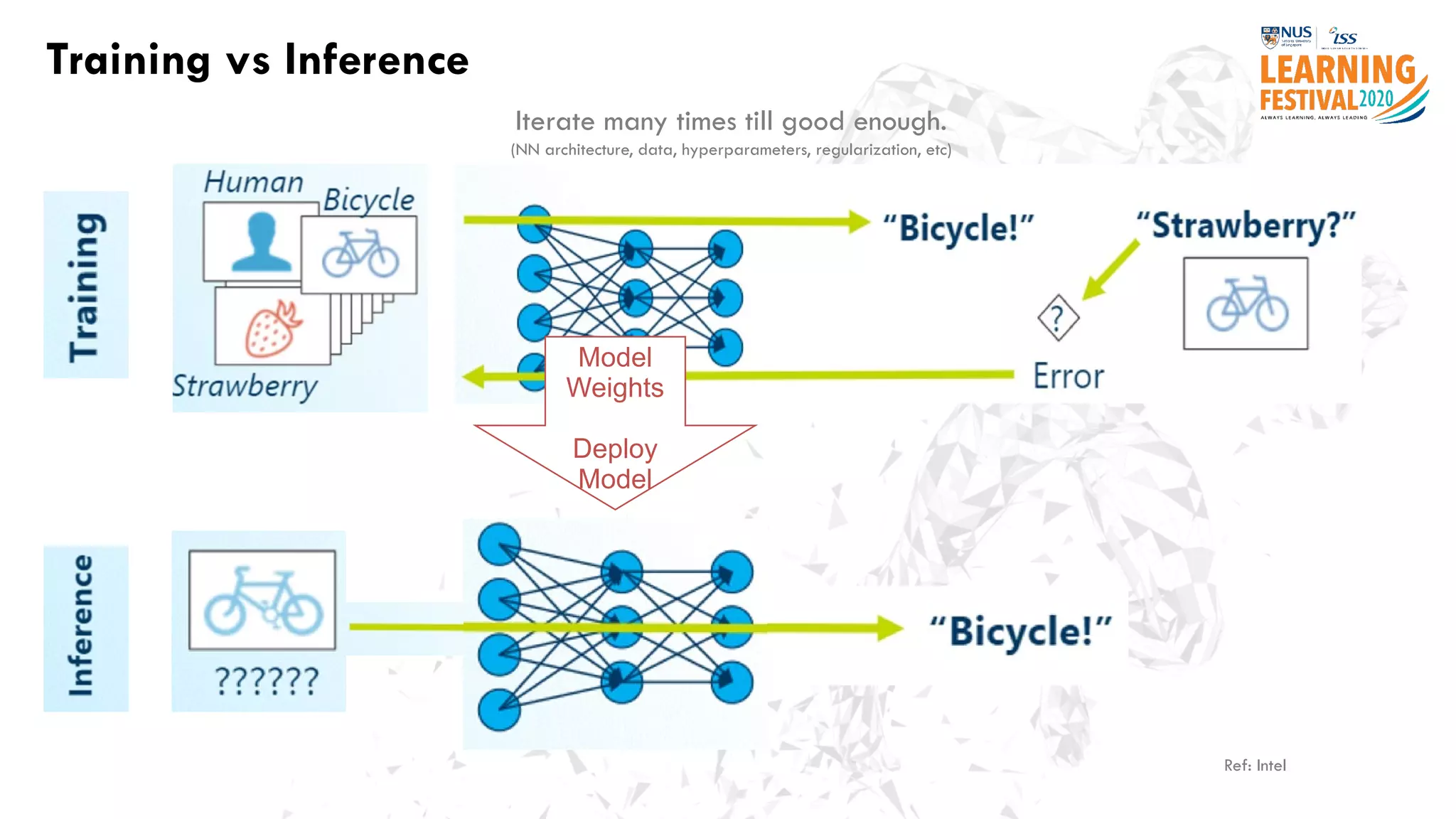
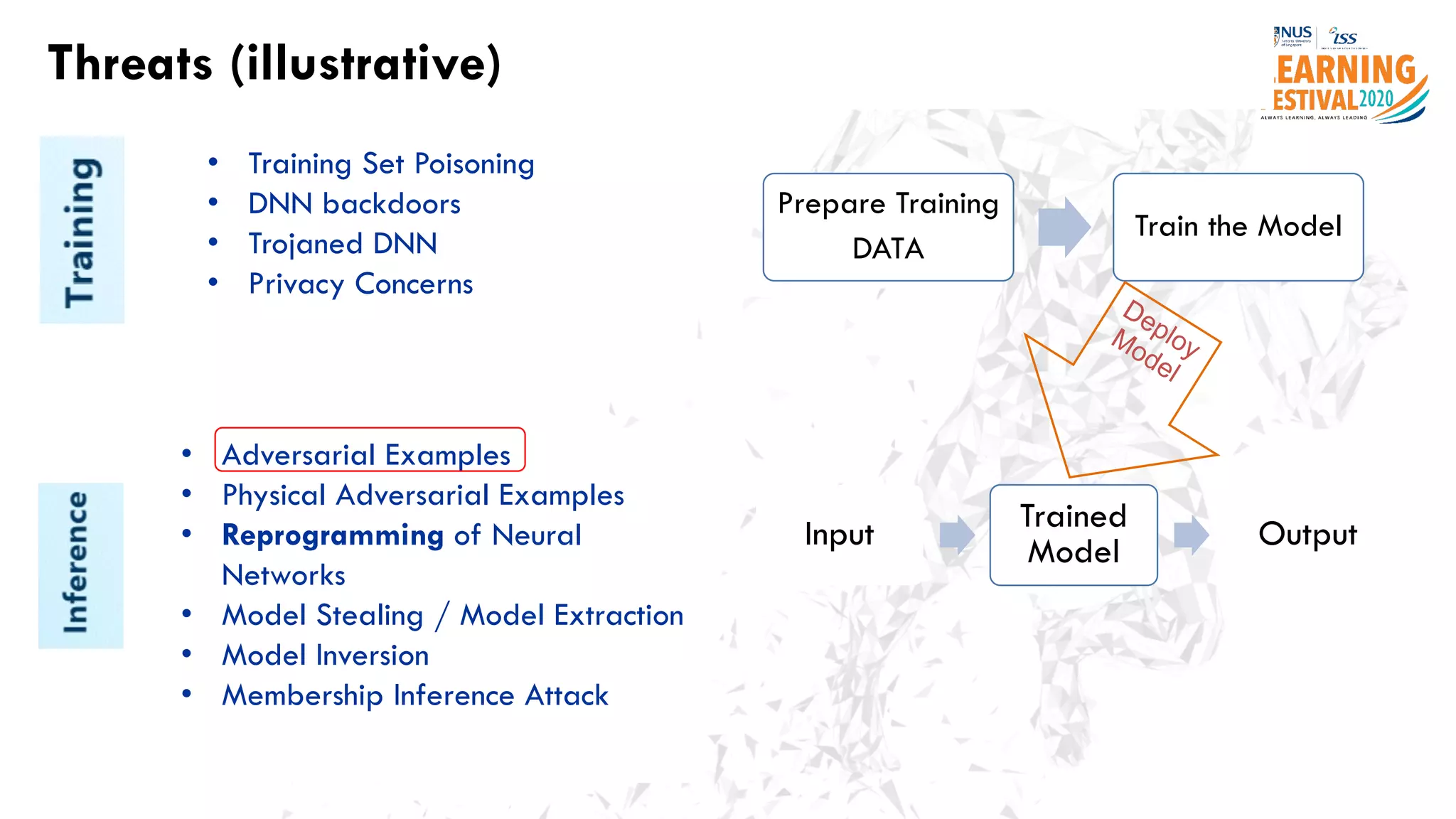
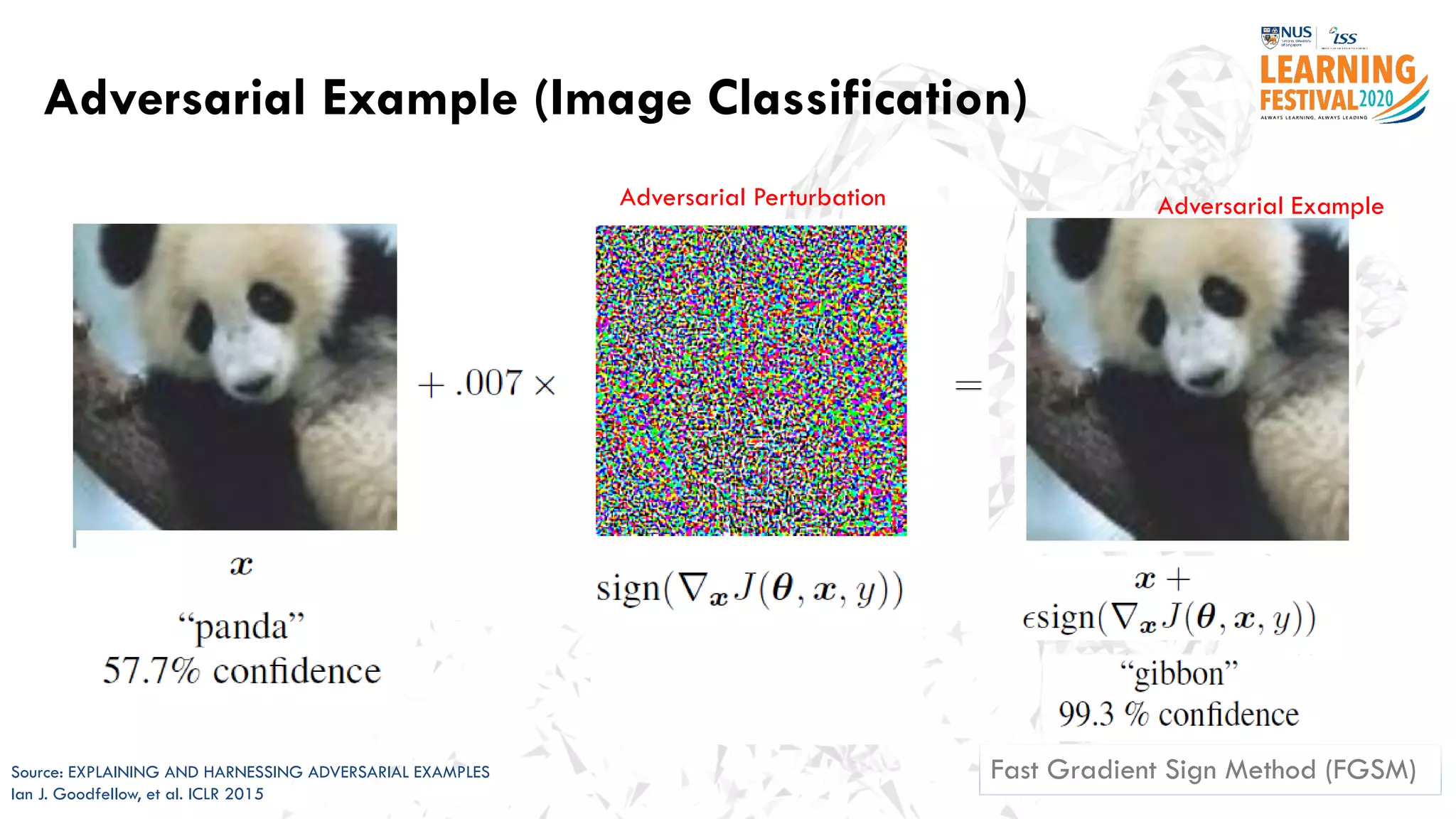
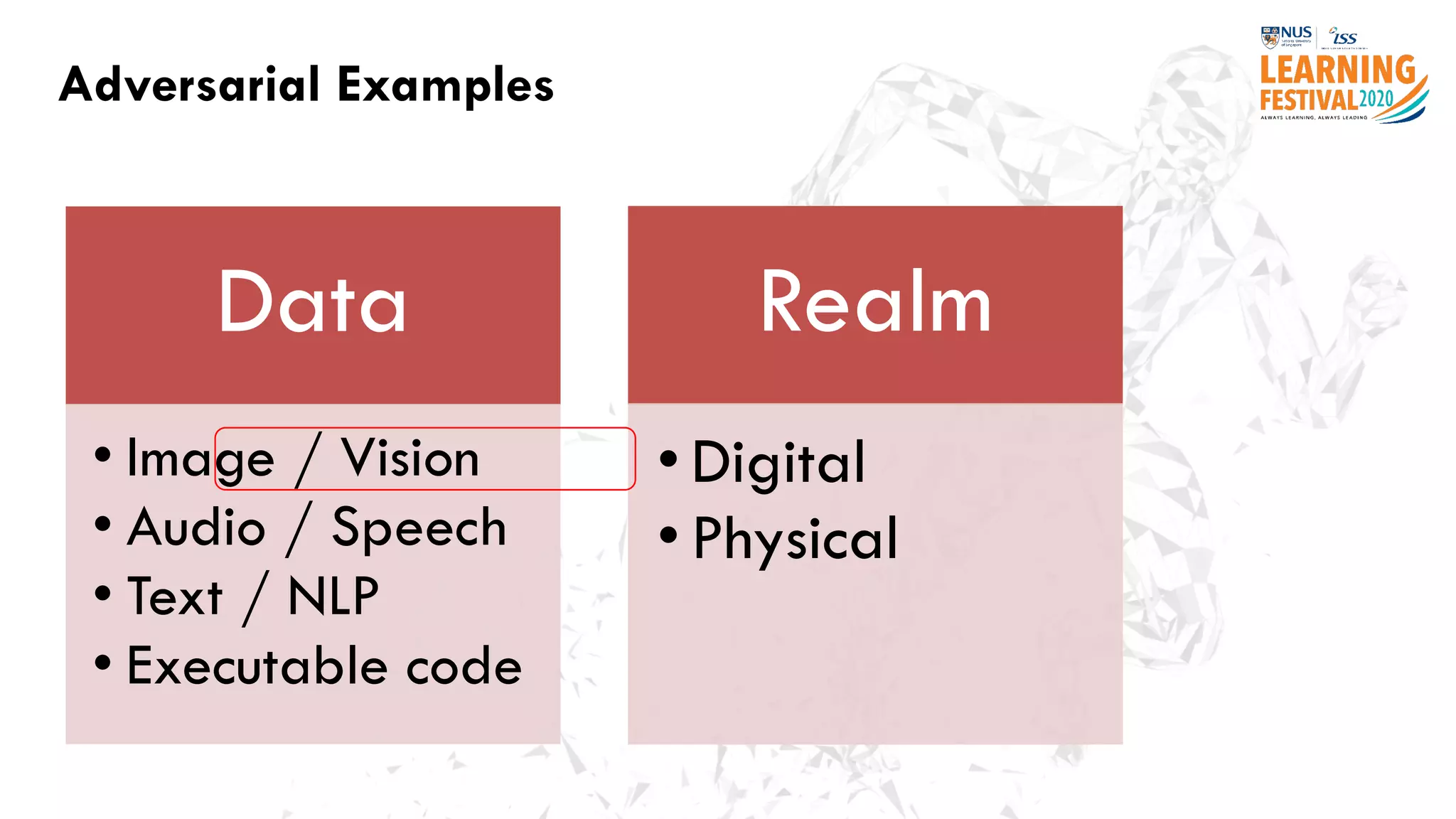
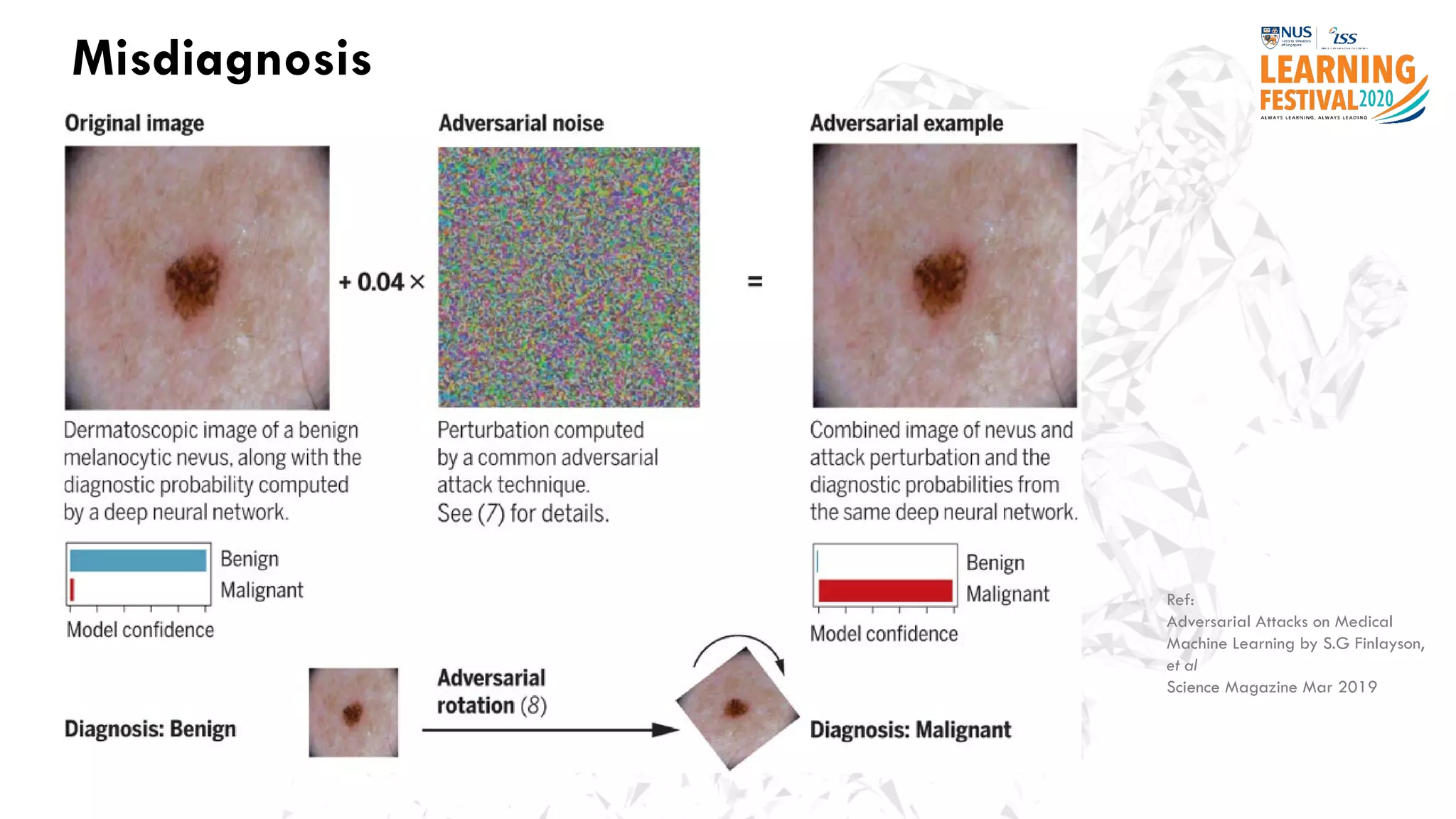
The document discusses the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and cybersecurity, outlining the threats posed by AI systems, including adversarial examples, impersonation, and AI-aided attacks. It emphasizes the need for new security frameworks to address the unique challenges brought by AI in the cybersecurity landscape. Additionally, the importance of protecting AI products and training data is highlighted, alongside the need for organizations to incorporate AI considerations into their cybersecurity risk assessments.