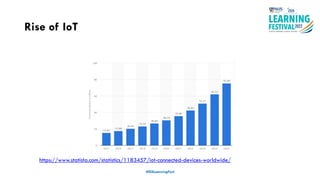
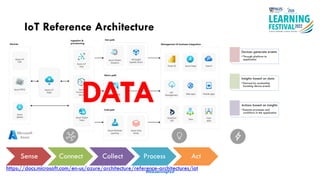
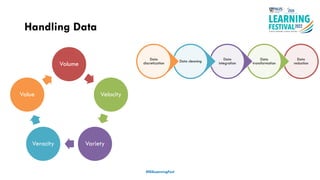
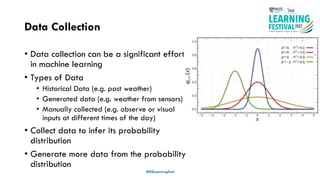
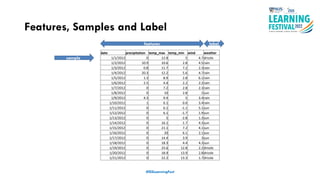
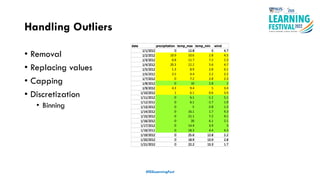
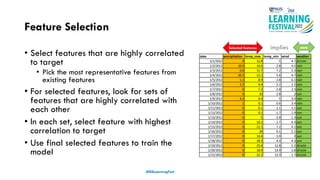
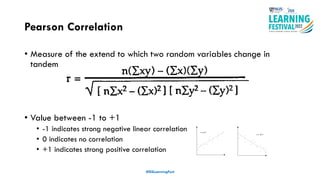
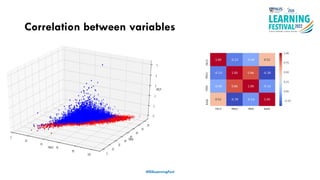
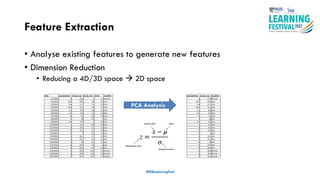
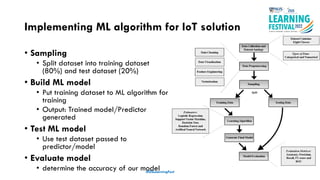
The document discusses feature engineering in the context of IoT and machine learning, focusing on data collection, transformation, and feature selection. It covers important concepts such as handling missing data, outlier management, and correlation analysis to improve the accuracy of machine learning models. Various types of data and techniques for creating valuable features from the data are highlighted.