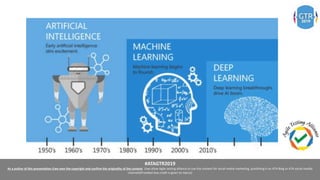
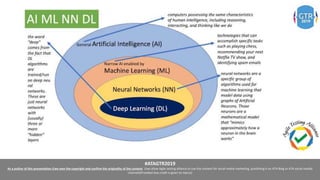
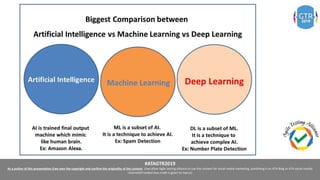
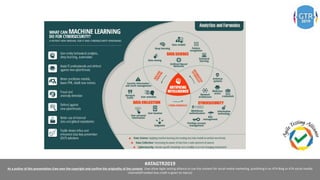
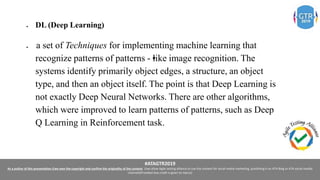
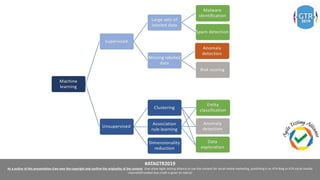
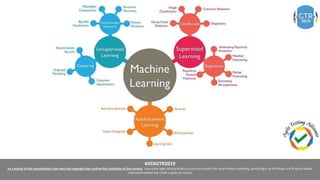
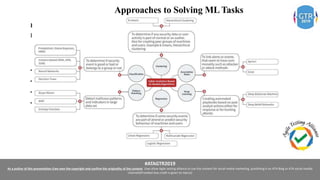
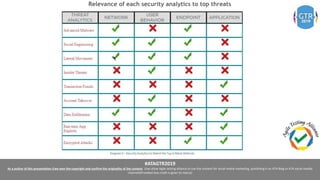
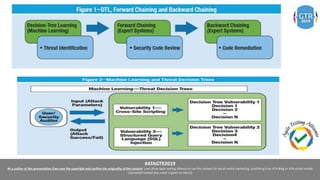
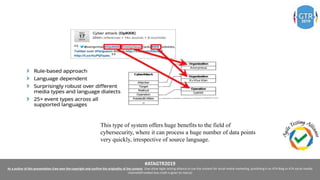
The document discusses the application of machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and deep learning (DL) in enhancing cybersecurity measures to counter increasing cyber threats. It explores the benefits of automating security tasks through ML techniques, which can aid in threat detection, malware prevention, and response efficiency. Furthermore, the paper addresses the dual use of ML in both offensive and defensive cyber operations, underscoring the importance of professionals staying updated on advancements in these technologies to combat sophisticated cyber-attacks.