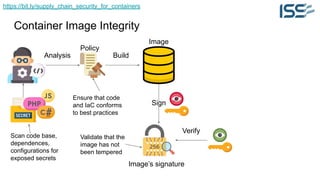
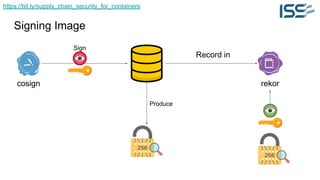
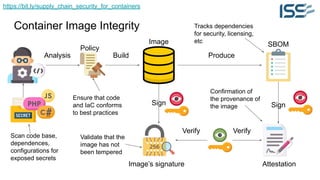
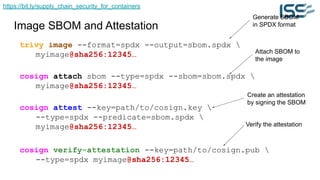
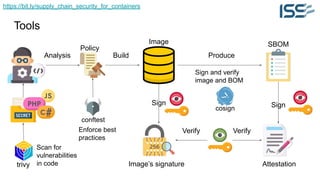
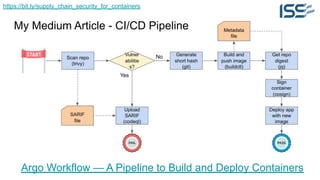
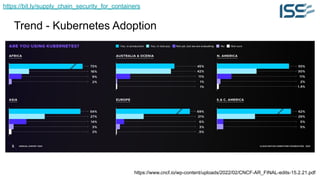
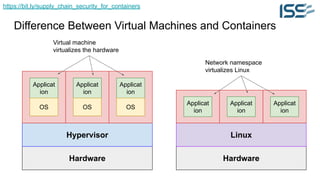
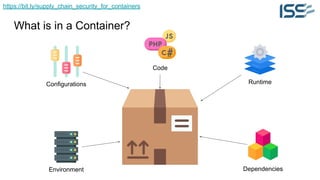
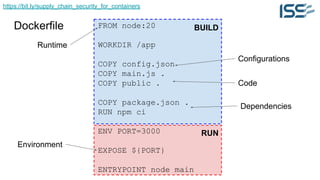
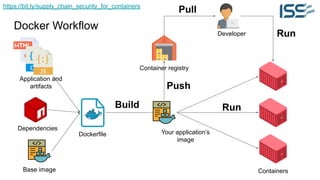
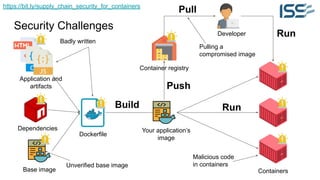
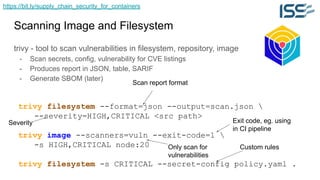
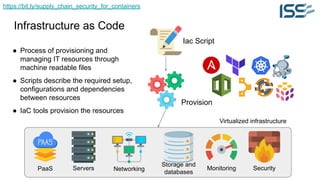
The document discusses supply chain security for containerized workloads, emphasizing the importance of integrating various tools into CI/CD pipelines to enhance security. It covers topics such as the rise of container adoption, differences between containers and virtual machines, and the significance of managing dependencies and images safely within container environments. The document also introduces tools and practices for scanning vulnerabilities, signing images, and ensuring best practices in infrastructure as code.










![https://bit.ly/supply_chain_security_for_containers
Example of Policy File
deny[msg] {
input[i].Cmd = “from”
val = input[i].Value
contains(val[_], “:latest”)
msg = sprintf(“Cannot use :latest tag %s”, val)
}
deny[msg] {
input[i].Cmd = “from”
val = input[i].Value
count(split(val, “:”)) < 2
msg = sprintf(“Please add an image tag to %s”, val)
}
More examples https://www.conftest.dev/examples
Policy
Prevent pulling images
with the ‘latest’ tag](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningfest2023securingcontainerisedworkloads-231122090619-eae3c1fe/85/Supply-Chain-Security-for-Containerised-Workloads-Lee-Chuk-Munn-20-320.jpg)